层序二叉树遍历
树的层序遍历是树的广度优先遍历。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。
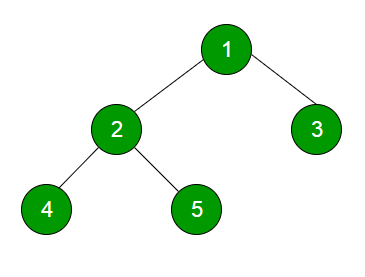
上述树的层序遍历为 1 2 3 4 5
方法一(使用函数打印当前级别)
算法:
这个方法基本上有两个功能。一种是打印给定级别的所有节点(printCurrentLevel),另一种是打印树的级别顺序遍历(printLevelorder)。 printLevelorder 使用printCurrentLevel 从根开始逐一打印所有级别的节点。
/*Function to print level order traversal of tree*/
printLevelorder(tree)
for d = 1 to height(tree)
printCurrentLevel(tree, d);
/*Function to print all nodes at a current level*/
printCurrentLevel(tree, level)
if tree is NULL then return;
if level is 1, then
print(tree->data);
else if level greater than 1, then
printCurrentLevel(tree->left, level-1);
printCurrentLevel(tree->right, level-1);执行:
C++
// Recursive CPP program for level
// order traversal of Binary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node {
public:
int data;
node *left, *right;
};
/* Function prototypes */
void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level);
int height(node* node);
node* newNode(int data);
/* Function to print level
order traversal a tree*/
void printLevelOrder(node* root)
{
int h = height(root);
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++)
printCurrentLevel(root, i);
}
/* Print nodes at a current level */
void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (level == 1)
cout << root->data << " ";
else if (level > 1) {
printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1);
printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1);
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int height(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else {
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node->left);
int rheight = height(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight) {
return (lheight + 1);
}
else {
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates
a new node with the given data and
NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n";
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
// Recursive C program for level
// order traversal of Binary Tree
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
/* Function prototypes */
void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level);
int height(struct node* node);
struct node* newNode(int data);
/* Function to print level order traversal a tree*/
void printLevelOrder(struct node* root)
{
int h = height(root);
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++)
printCurrentLevel(root, i);
}
/* Print nodes at a current level */
void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (level == 1)
printf("%d ", root->data);
else if (level > 1) {
printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1);
printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1);
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int height(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else {
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node->left);
int rheight = height(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n");
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Recursive Java program for level
// order traversal of Binary Tree
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
public BinaryTree() { root = null; }
/* function to print level order traversal of tree*/
void printLevelOrder()
{
int h = height(root);
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++)
printCurrentLevel(root, i);
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int height(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
else {
/* compute height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(root.left);
int rheight = height(root.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
/* Print nodes at the current level */
void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level)
{
if (root == null)
return;
if (level == 1)
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
else if (level > 1) {
printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1);
printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1);
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Level order traversal of
binary tree is ");
tree.printLevelOrder();
}
}Python3
# Recursive Python program for level
# order traversal of Binary Tree
# A node structure
class Node:
# A utility function to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print level order traversal of tree
def printLevelOrder(root):
h = height(root)
for i in range(1, h+1):
printCurrentLevel(root, i)
# Print nodes at a current level
def printCurrentLevel(root, level):
if root is None:
return
if level == 1:
print(root.data, end=" ")
elif level > 1:
printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1)
printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1)
""" Compute the height of a tree--the number of nodes
along the longest path from the root node down to
the farthest leaf node
"""
def height(node):
if node is None:
return 0
else:
# Compute the height of each subtree
lheight = height(node.left)
rheight = height(node.right)
# Use the larger one
if lheight > rheight:
return lheight+1
else:
return rheight+1
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print("Level order traversal of binary tree is -")
printLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// Recursive c# program for level
// order traversal of Binary Tree
using System;
/* Class containing left and right
child of current node and key value*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// Root of the Binary Tree
public Node root;
public void BinaryTree() { root = null; }
/* function to print level order
traversal of tree*/
public virtual void printLevelOrder()
{
int h = height(root);
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) {
printCurrentLevel(root, i);
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree --
the number of nodes along the longest
path from the root node down to the
farthest leaf node.*/
public virtual int height(Node root)
{
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
else {
/* compute height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(root.left);
int rheight = height(root.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight) {
return (lheight + 1);
}
else {
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
}
/* Print nodes at the current level */
public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Node root,
int level)
{
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (level == 1) {
Console.Write(root.data + " ");
}
else if (level > 1) {
printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1);
printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
GFG tree = new GFG();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Level order traversal "
+ "of binary tree is ");
tree.printLevelOrder();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13C++
/* C++ program to print level
order traversal using STL */
#include
using namespace std;
// A Binary Tree Node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree
void printLevelOrder(Node* root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Create an empty queue for level order traversal
queue q;
// Enqueue Root and initialize height
q.push(root);
while (q.empty() == false) {
// Print front of queue and remove it from queue
Node* node = q.front();
cout << node->data << " ";
q.pop();
/* Enqueue left child */
if (node->left != NULL)
q.push(node->left);
/*Enqueue right child */
if (node->right != NULL)
q.push(node->right);
}
}
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create binary tree shown in above diagram
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n";
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
} C
// Iterative Queue based C program
// to do level order traversal
// of Binary Tree
#include
#include
#define MAX_Q_SIZE 500
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* frunction prototypes */
struct node** createQueue(int*, int*);
void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*);
struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*);
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order
using array for implementing queue */
void printLevelOrder(struct node* root)
{
int rear, front;
struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear);
struct node* temp_node = root;
while (temp_node) {
printf("%d ", temp_node->data);
/*Enqueue left child */
if (temp_node->left)
enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left);
/*Enqueue right child */
if (temp_node->right)
enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right);
/*Dequeue node and make it temp_node*/
temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front);
}
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
struct node** createQueue(int* front, int* rear)
{
struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc(
sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE);
*front = *rear = 0;
return queue;
}
void enQueue(struct node** queue, int* rear,
struct node* new_node)
{
queue[*rear] = new_node;
(*rear)++;
}
struct node* deQueue(struct node** queue, int* front)
{
(*front)++;
return queue[*front - 1];
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n");
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Iterative Queue based Java program
// to do level order traversal
// of Binary Tree
/* importing the inbuilt java classes
required for the program */
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/* Class to represent Tree node */
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
/* Class to print Level Order Traversal */
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree. Print
its nodes in level order
using array for implementing queue */
void printLevelOrder()
{
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
/* poll() removes the present head.
For more information on poll() visit
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/
util/linkedlist_poll.htm */
Node tempNode = queue.poll();
System.out.print(tempNode.data + " ");
/*Enqueue left child */
if (tempNode.left != null) {
queue.add(tempNode.left);
}
/*Enqueue right child */
if (tempNode.right != null) {
queue.add(tempNode.right);
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
/* creating a binary tree and entering
the nodes */
BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree();
tree_level.root = new Node(1);
tree_level.root.left = new Node(2);
tree_level.root.right = new Node(3);
tree_level.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree_level.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Level order traversal
of binary tree is - ");
tree_level.printLevelOrder();
}
} Python3
# Python program to print level
# order traversal using Queue
# A node structure
class Node:
# A utility function to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Iterative Method to print the
# height of a binary tree
def printLevelOrder(root):
# Base Case
if root is None:
return
# Create an empty queue
# for level order traversal
queue = []
# Enqueue Root and initialize height
queue.append(root)
while(len(queue) > 0):
# Print front of queue and
# remove it from queue
print(queue[0].data)
node = queue.pop(0)
# Enqueue left child
if node.left is not None:
queue.append(node.left)
# Enqueue right child
if node.right is not None:
queue.append(node.right)
# Driver Program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print("Level Order Traversal of binary tree is -")
printLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// Iterative Queue based C# program
// to do level order traversal
// of Binary Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
/* Class to represent Tree node */
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
/* Class to print Level Order Traversal */
public class BinaryTree {
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree. Print
its nodes in level order using
array for implementing queue */
void printLevelOrder()
{
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.Enqueue(root);
while (queue.Count != 0) {
/* poll() removes the present head.
For more information on poll() visit
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/
java/util/linkedlist_poll.htm */
Node tempNode = queue.Dequeue();
Console.Write(tempNode.data + " ");
/*Enqueue left child */
if (tempNode.left != null) {
queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left);
}
/*Enqueue right child */
if (tempNode.right != null) {
queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
/* creating a binary tree and entering
the nodes */
BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree();
tree_level.root = new Node(1);
tree_level.root.left = new Node(2);
tree_level.root.right = new Node(3);
tree_level.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree_level.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Level order traversal "
+ "of binary tree is - ");
tree_level.printLevelOrder();
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */ 输出
Level Order traversal of binary tree is
1 2 3 4 5 时间复杂度:最坏情况下为 O(n^2)。对于倾斜树,printGivenLevel() 花费 O(n) 时间,其中 n 是倾斜树中的节点数。所以 printLevelOrder() 的时间复杂度是 O(n) + O(n-1) + O(n-2) + .. + O(1) 即 O(n^2)。
空间复杂度:最坏情况下为 O(n)。对于倾斜的树,printGivenLevel() 使用 O(n) 空间作为调用堆栈。对于平衡树,调用堆栈使用 O(log n) 空间,(即平衡树的高度)。
方法二(使用队列)
算法:
对于每个节点,首先访问该节点,然后将其子节点放入 FIFO 队列。
printLevelorder(tree)
1) Create an empty queue q
2) temp_node = root /*start from root*/
3) Loop while temp_node is not NULL
a) print temp_node->data.
b) Enqueue temp_node’s children
(first left then right children) to q
c) Dequeue a node from q.执行:
下面是上述算法的简单实现。队列使用最大大小为 500 的数组实现。我们也可以将队列实现为链表。
C++
/* C++ program to print level
order traversal using STL */
#include
using namespace std;
// A Binary Tree Node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree
void printLevelOrder(Node* root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Create an empty queue for level order traversal
queue q;
// Enqueue Root and initialize height
q.push(root);
while (q.empty() == false) {
// Print front of queue and remove it from queue
Node* node = q.front();
cout << node->data << " ";
q.pop();
/* Enqueue left child */
if (node->left != NULL)
q.push(node->left);
/*Enqueue right child */
if (node->right != NULL)
q.push(node->right);
}
}
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create binary tree shown in above diagram
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n";
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
C
// Iterative Queue based C program
// to do level order traversal
// of Binary Tree
#include
#include
#define MAX_Q_SIZE 500
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* frunction prototypes */
struct node** createQueue(int*, int*);
void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*);
struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*);
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order
using array for implementing queue */
void printLevelOrder(struct node* root)
{
int rear, front;
struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear);
struct node* temp_node = root;
while (temp_node) {
printf("%d ", temp_node->data);
/*Enqueue left child */
if (temp_node->left)
enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left);
/*Enqueue right child */
if (temp_node->right)
enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right);
/*Dequeue node and make it temp_node*/
temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front);
}
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
struct node** createQueue(int* front, int* rear)
{
struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc(
sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE);
*front = *rear = 0;
return queue;
}
void enQueue(struct node** queue, int* rear,
struct node* new_node)
{
queue[*rear] = new_node;
(*rear)++;
}
struct node* deQueue(struct node** queue, int* front)
{
(*front)++;
return queue[*front - 1];
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n");
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// Iterative Queue based Java program
// to do level order traversal
// of Binary Tree
/* importing the inbuilt java classes
required for the program */
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/* Class to represent Tree node */
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
/* Class to print Level Order Traversal */
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree. Print
its nodes in level order
using array for implementing queue */
void printLevelOrder()
{
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
/* poll() removes the present head.
For more information on poll() visit
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/
util/linkedlist_poll.htm */
Node tempNode = queue.poll();
System.out.print(tempNode.data + " ");
/*Enqueue left child */
if (tempNode.left != null) {
queue.add(tempNode.left);
}
/*Enqueue right child */
if (tempNode.right != null) {
queue.add(tempNode.right);
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
/* creating a binary tree and entering
the nodes */
BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree();
tree_level.root = new Node(1);
tree_level.root.left = new Node(2);
tree_level.root.right = new Node(3);
tree_level.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree_level.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Level order traversal
of binary tree is - ");
tree_level.printLevelOrder();
}
}
蟒蛇3
# Python program to print level
# order traversal using Queue
# A node structure
class Node:
# A utility function to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Iterative Method to print the
# height of a binary tree
def printLevelOrder(root):
# Base Case
if root is None:
return
# Create an empty queue
# for level order traversal
queue = []
# Enqueue Root and initialize height
queue.append(root)
while(len(queue) > 0):
# Print front of queue and
# remove it from queue
print(queue[0].data)
node = queue.pop(0)
# Enqueue left child
if node.left is not None:
queue.append(node.left)
# Enqueue right child
if node.right is not None:
queue.append(node.right)
# Driver Program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print("Level Order Traversal of binary tree is -")
printLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// Iterative Queue based C# program
// to do level order traversal
// of Binary Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
/* Class to represent Tree node */
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
/* Class to print Level Order Traversal */
public class BinaryTree {
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree. Print
its nodes in level order using
array for implementing queue */
void printLevelOrder()
{
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.Enqueue(root);
while (queue.Count != 0) {
/* poll() removes the present head.
For more information on poll() visit
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/
java/util/linkedlist_poll.htm */
Node tempNode = queue.Dequeue();
Console.Write(tempNode.data + " ");
/*Enqueue left child */
if (tempNode.left != null) {
queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left);
}
/*Enqueue right child */
if (tempNode.right != null) {
queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
/* creating a binary tree and entering
the nodes */
BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree();
tree_level.root = new Node(1);
tree_level.root.left = new Node(2);
tree_level.root.right = new Node(3);
tree_level.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree_level.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Level order traversal "
+ "of binary tree is - ");
tree_level.printLevelOrder();
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
输出
Level Order traversal of binary tree is
1 2 3 4 5 时间复杂度: O(n) 其中 n 是二叉树中的节点数
空间复杂度: O(n) 其中 n 是二叉树中的节点数