在本文中,讨论了一种称为“闭合”的形态运算。
- 它有助于减少图像内部存在的内部噪声。
- 在本文中,详细介绍了另一种运算符,称为“关闭”,它与“打开”相反,并且先进行膨胀再进行腐蚀。
- 就像Opening运算符一样,它也使用结构化元素,但是它用于去除小孔而不是打扰。
句法:
morphologyEx (src, dst, op, kernel, anchor, iterations, borderType, borderValue)
参数:
- src:它是输入图像。
- dst:它是输出图像。
- op:形态学操作的类型。
- 内核:用于结束的结构元素。
- 锚:在结构元素内的锚位置。默认值为[-1,-1},表示位置为结构元素的中心。
- 迭代:应用关闭的次数。
- borderType:边框类型(BORDER_CONSTANT,BORDER_REPLICATE等)
- borderValue:边框值
- 返回值:输出图像(垫子对象)
关闭操作由以下表达式给出:

- 该表达式表示A是A的子图像的事实。 B.
- 该运算符用于去除图像上的小孔。
- 它还有助于平滑轮廓,并融合窄缝和长而细的海湾。
下面是演示闭合形态运算符的程序:
C++
// C++ program for demonstrating the
// closing morphological operator
// For drawing shapes
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
// Function to demonstrate the
// closing morphological operator
void closingMorphological()
{
// Reading the Image
Mat image = imread(
"C:/Users/harsh/Downloads/geeks.png",
IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
// Check if the image is
// created successfully
if (!image.data) {
cout << "Could not open or "
<< "find the image\n";
return 0;
}
int morph_size = 2;
// Create structuring element
Mat element = getStructuringElement(
MORPH_RECT,
Size(2 * morph_size + 1,
2 * morph_size + 1),
Point(morph_size, morph_size));
Mat output;
// Closing
morphologyEx(image, output,
MORPH_CLOSE, element,
Point(-1, -1), 2);
// Displays the source and
// the closing image formed
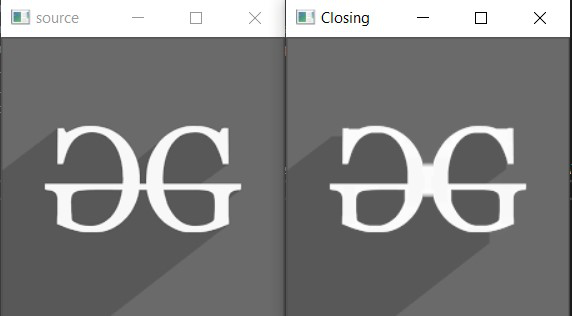
imshow("source", image);
imshow("Closing", output);
waitKey();
}
// Driver Code
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// Function Call
closingMorphological();
return 0;
} 输出:
要从最佳影片策划和实践问题去学习,检查了C++基础课程为基础,以先进的C++和C++ STL课程基础加上STL。要完成从学习语言到DS Algo等的更多准备工作,请参阅“完整面试准备课程” 。