蒸馏分离
蒸馏是一种分离技术,用于提取液体中的混合物固体。它基本上是将液体加热形成蒸汽,然后将蒸汽冷凝以取回液体的过程。通过对蒸气进行冷凝而获得的液体称为馏出物。可混溶的液体混合在一起形成溶液,例如乙醇和水的混合物。不混溶的液体不能很好地混合在一起。例如,油和水。以所有比例相互混溶的两种液体可以称为液体的二元混合物。该技术用于分离两种具有足够沸点 (BP) 差异的混溶液体混合物的成分,这种液体可以在不分解的情况下煮沸。挥发性液体在加热时蒸发,可通过冷凝过程冷却其蒸气来回收。
在必须从溶液中提取固体和液体的情况下,蒸馏是优选的。也称为简单蒸馏,它基于在混合物成分中观察到的挥发性和相应蒸气压的差异。
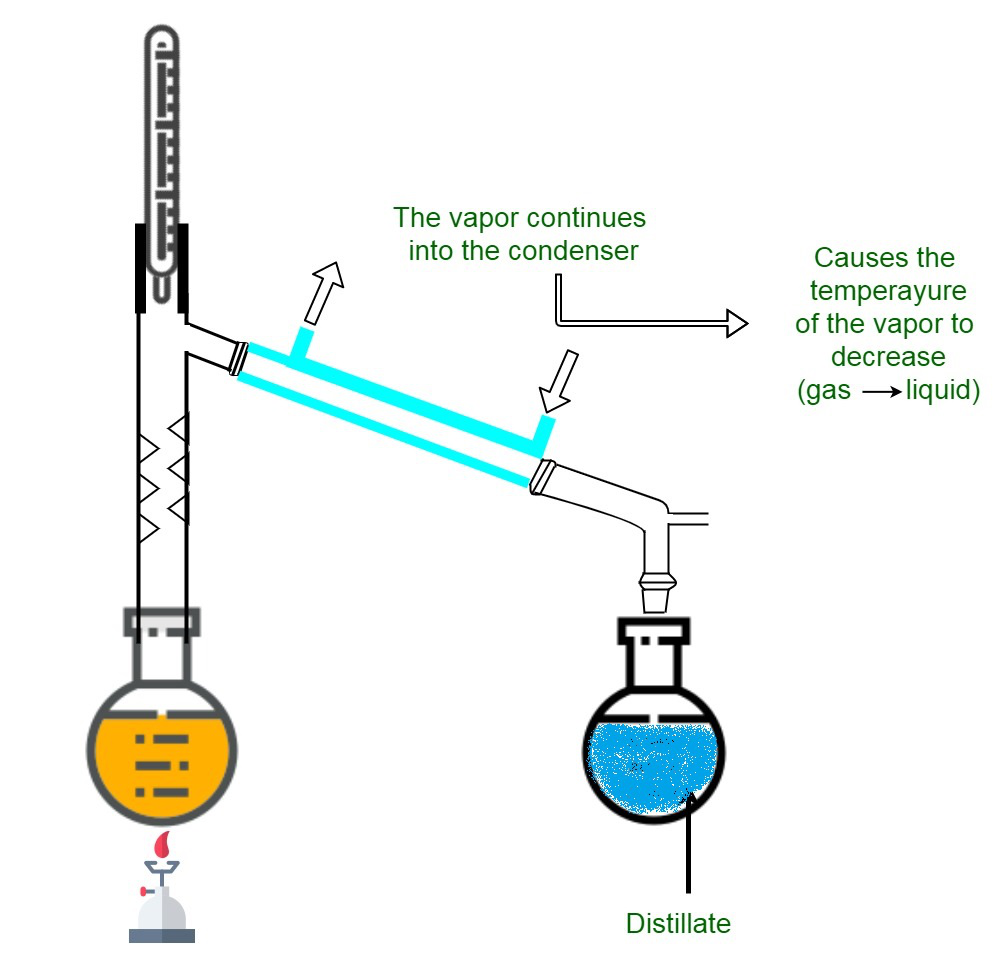
蒸馏过程
- 含有固体和液体的均匀混合物在密闭的蒸馏烧瓶中一起加热。
- 液体逸出形成蒸气,因为它们是挥发性的。
- 这些蒸气通过使它们通过冷凝器而被冷却。
- 在所取容器中冷凝得到纯液体。
- 非挥发性固体作为残余物留下。
蒸馏所需设备
蒸馏过程主要使用以下设备:
- Still:汽化室用于放置要蒸馏的材料。它被加热以提供挥发性成分的蒸发。它还连接到冷凝器上,中间固定有一个疏水阀。
- 冷凝器:用于冷凝蒸汽。通过使水/空气循环通过夹套来保持低温。冷凝器可用作单表面冷凝器、多表面冷凝器。
- 接收器:用于收集馏出物。
蒸馏原理
- 在溶剂的沸点下进行蒸馏。当蒸气压与大气压相等时发生沸腾。
- 在液体的相对挥发性较高的情况下,混合物组分的分离会更好。
- 在向液体供热时,蒸汽沸腾,然后发生冷凝。
分馏
分馏用于分离本质上易挥发的混溶液体。这些液体的沸点足够接近。分馏柱装置用于模拟分离。也称为精馏,因为蒸气被部分冷凝并以液体形式返回。它基本上是一个过程,其中液体混合物的蒸发产生成分的混合物,然后以纯净形式提取所需的成分。
然而,这种技术只能用于分离形成纯共沸混合物的混溶液体。
原则:
- 在液体混合物蒸馏时,蒸气的部分冷凝发生在分馏塔中。
- 在塔中,来自蒸馏器的前进蒸汽与返回蒸馏器的冷凝蒸汽接触。这会导致蒸汽富含挥发性更强的成分。
- 通过蒸汽的不断冷凝和加热,液体和蒸汽之间达到平衡。这导致从混合物中提取出更易挥发的成分。
分馏的应用:
分馏可用于分离混合物,例如:
- 丙酮和水
- 氯仿和苯
- 空气气体的分离
分液漏斗
用于分离两种不混溶液体的技术是使用称为分液漏斗的设备完成的。它是一种特殊类型的漏斗,其阀杆上有一个旋塞阀,可以允许或阻止液体从中流出。通过分液漏斗分离两种不混溶的液体取决于组成液体的密度差异。较重的液体沉淀在底部,较轻的液体保留为上层。
分液漏斗的应用:
- 水和煤油
- 石油和水
蒸馏的应用:
- 有机溶剂的提纯——无水酒精(100%)。
- 非挥发性物质与挥发性物质的分离。
- 使用化学工艺制造的药物的纯化。
- 石油产品的精炼-石油醚 60,80。
- 溶剂回收——合成。
- 去除水中的盐分以制备饮用水。
- 甲醇或乙醇
- 食品工业中油和饮料的浓度。
示例问题
问题1、简单蒸馏和分馏的区别?
回答: Simple Distillation Fractional DistillationVapour is directly passed through the condenser. Vapour must pass through a fractionating column in which partial condensation of vapour occurs. Condensate is collected directly onto the receiver. Condensation occurs in the fractionating column, which results in a part of the condensing vapour returning to the still.
问题 2. 是否可以在蒸馏的基础上完全纯化混合物?
回答:
Any component in the mixture cannot have zero partial pressure. As a result of this, a completely pure sample of a component from a mixture cannot be obtained. However, samples of high purity can be obtained if any of the components of the mixture has a partial pressure whose value is close to zero.
问题 3. 实验证明海水含有盐分。
解决方案:
It can be proved with the help of distillation that seawater contains salt. When the seawater is boiled, the water molecules contained within it evaporate from the surface in the form of steam. They are then condensed at the cooler part of the beaker. As a result of this, all the water evaporation takes place, leaving only salt behind as residue.
问题 4. 分馏塔中的阻塞物如何帮助分馏?
回答:
In fractional distillation, separation of the components occur based on their boiling point. These obstructions help in arrangement of the substances in the order such that the substances having a lower boiling point will be on the top whereas the substances with higher boiling point will be at the bottom.
问题 5. 增加蒸馏塔中的压力会发生什么?
回答:
- Distillation efficiency will decrease.
- Relative volatility will decrease.
- Reflux ratio will be higher.
- The equilibrium curve shrinks to a larger extent towards diagonal line.
问题 6. 执行简单蒸馏过程的约束条件是什么?
回答:
Simple distillation can be carried out for:
- A pure or “almost pure” substance. Any substances with lesser than 10% impurities is considered to be pure.
- A mixture where the boiling points of the impurities are very high,
- A Mixture with a large difference between the boiling points of the constituents.
问题 7. 解释烧瓶底部残留物的性质。
回答:
The process of distillation is performed for the mixture of liquids that have a sufficient difference in their corresponding boiling points. Therefore, the residue at the bottom of the flash should be non-volatile in nature.