给定一棵二叉树和一个整数目标,表示一个节点的值,任务是找到所有节点到给定节点的距离之和。
例子:
Input: target = 3
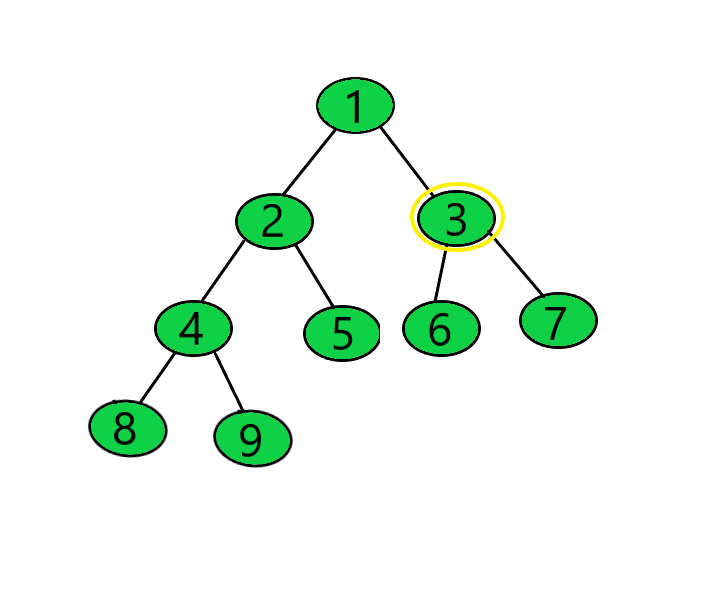
Output: 19
Explanation:
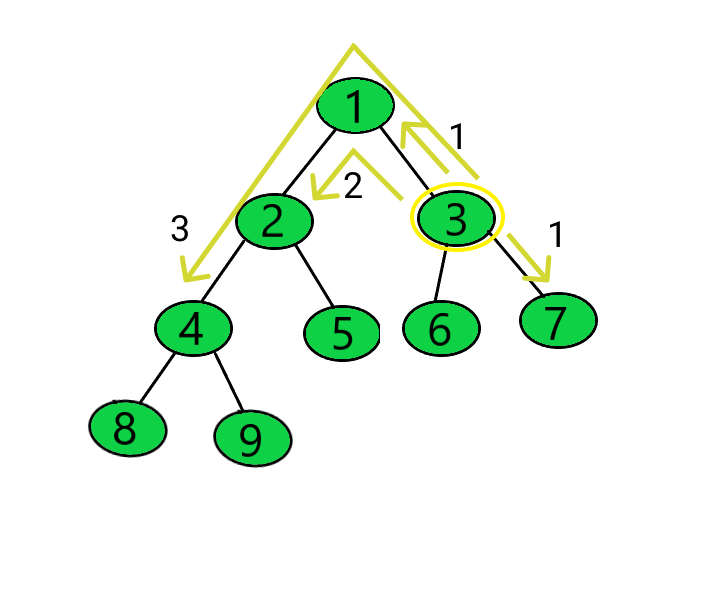
Distance of Nodes 1, 6, 7 from the Node 3 = 1
Distance of the Node 2 from the Node 3 = 2
Distance of the Nodes 4, 5 from the Node 3 = 3
Distance of the Nodes 8, 9 from the Node 3 = 4
Sum of the distances = (1 + 1 + 1) + (2) + (3 + 3) + (4 + 4) = 19.
Input: target = 4
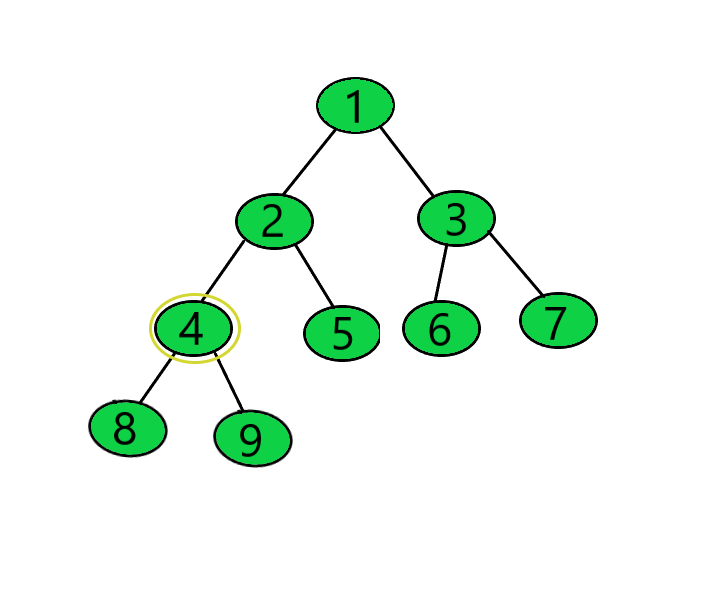
Output: 18
天真的方法:解决此问题的最简单方法是,每当在一个节点的左侧或右侧遍历一个节点时,则其子树的节点距离将减少1,其余节点与该节点的距离将减少增加1。
因此,以下关系给出了所有节点到一个节点的距离之和,即u :
sumDists(u)= sumDists(parent(u)) – (Nodes in the left and right substree of u) + (N – Nodes in the left and right substree of u)
where,
sumDists(u): Sum of distances of all nodes from the node u
sumDists(parent(u)): Sum of distances of all nodes from the parent node of u
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 创建一个函数以查找给定节点(包括给定节点)的左右子树中的节点数。
- 创建一个函数以查找节点的深度之和,变量sum表示所有节点距目标的距离之和。
- 使用DFS(深度优先搜索)遍历树,并对每个节点执行以下操作:
- 如果目标与当前节点匹配,则将sum更新为distance 。
- 别的:
- 如果root-> left不为null ,请找到左子树中的节点数,并将所有节点到root-> left节点的距离之和作为tempSum传递。
- 如果root-> right不为null ,则找到右子树中的节点数,并将所有节点到root-> rightnode的距离之和作为tempSum传递。
- 到达目标节点后,打印节点到目标节点的距离之和。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a
// Binary Tree Node
class TreeNode {
public:
int data;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to its
// left and right pointers
TreeNode* newNode(int data)
{
// Allocate the node
TreeNode* Node = new TreeNode();
// Allocate Memory
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
// Function which calculates sum
// of depths of all nodes
int sumofdepth(TreeNode* root, int l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Return recurssively
return l + sumofdepth(root->left,
l + 1)
+ sumofdepth(root->right,
l + 1);
}
// Function to count of nodes
// in the left and right subtree
int Noofnodes(TreeNode* root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Return recurssively
return Noofnodes(root->left)
+ Noofnodes(root->right)
+ 1;
}
// Stores the sum of distances
// of all nodes from given node
int sum = 0;
// Function to find sum of distances
// of all nodes from a given node
void distance(TreeNode* root,
int target,
int distancesum,
int n)
{
// If target node matches
// with the current node
if (root->data == target) {
sum = distancesum;
return;
}
// If left of current node exists
if (root->left) {
// Count number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(
root->left);
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- nodes
+ (n - nodes);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root->left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If right is not null
if (root->right) {
// Find number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(
root->right);
// Applying the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- nodes + (n - nodes);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root->right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input tree
TreeNode* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->left->left->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left->right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
// Sum of depth of all
// nodes from root node
int distanceroot
= sumofdepth(root, 0);
// Number of nodes in the
// left and right subtree
int totalnodes = Noofnodes(root);
distance(root, target, distanceroot,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
cout << sum;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of a
// Binary Tree Node
static class TreeNode
{
int data;
TreeNode left, right;
}
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to its
// left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = Node.right = null;
return (Node);
}
// Function which calculates sum
// of depths of all nodes
static int sumofdepth(TreeNode root, int l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recurssively
return l + sumofdepth(root.left, l + 1) +
sumofdepth(root.right, l + 1);
}
// Function to count of nodes
// in the left and right subtree
static int Noofnodes(TreeNode root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recurssively
return Noofnodes(root.left) +
Noofnodes(root.right) + 1;
}
// Stores the sum of distances
// of all nodes from given node
public static int sum = 0;
// Function to find sum of distances
// of all nodes from a given node
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches
// with the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
return;
}
// If left of current node exists
if (root.left != null)
{
// Count number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(root.left);
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum - nodes +
(n - nodes);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n);
}
// If right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Find number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(root.right);
// Applying the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum - nodes +
(n - nodes);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
// Sum of depth of all
// nodes from root node
int distanceroot = sumofdepth(root, 0);
// Number of nodes in the
// left and right subtree
int totalnodes = Noofnodes(root);
distance(root, target, distanceroot,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L VPython3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Structure of a
# Binary Tree Node
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function which calculates sum
# of depths of all nodes
def sumofdepth(root, l):
# Base Case
if (root == None):
return 0
# Return recurssively
return l + sumofdepth(root.left, l + 1)+ sumofdepth(root.right, l + 1)
# Function to count of nodes
# in the left and right subtree
def Noofnodes(root):
# Base Case
if (root == None):
return 0
# Return recurssively
return Noofnodes(root.left) + Noofnodes(root.right) + 1
# Stores the sum of distances
# of all nodes from given node
sum = 0
# Function to find sum of distances
# of all nodes from a given node
def distance(root, target, distancesum, n):
global sum
# If target node matches
# with the current node
if (root.data == target):
sum = distancesum
return
# If left of current node exists
if (root.left):
# Count number of nodes
# in the left subtree
nodes = Noofnodes(root.left)
# Update sum
tempsum = distancesum - nodes + (n - nodes)
# Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n)
# If right is not null
if (root.right):
# Find number of nodes
# in the left subtree
nodes = Noofnodes(root.right)
# Applying the formula given
# in the approach
tempsum = distancesum - nodes + (n - nodes)
# Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Input tree
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
root.left.right = TreeNode(5)
root.right.left = TreeNode(6)
root.right.right = TreeNode(7)
root.left.left.left = TreeNode(8)
root.left.left.right = TreeNode(9)
target = 3
# Sum of depth of all
# nodes from root node
distanceroot = sumofdepth(root, 0)
# Number of nodes in the
# left and right subtree
totalnodes = Noofnodes(root)
distance(root, target, distanceroot, totalnodes)
# Prthe sum of distances
print (sum)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG{
// Structure of a
// Binary Tree Node
class TreeNode
{
public int data;
public TreeNode left, right;
}
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to its
// left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = Node.right = null;
return (Node);
}
// Function which calculates sum
// of depths of all nodes
static int sumofdepth(TreeNode root, int l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recurssively
return l + sumofdepth(root.left, l + 1) +
sumofdepth(root.right, l + 1);
}
// Function to count of nodes
// in the left and right subtree
static int Noofnodes(TreeNode root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recurssively
return Noofnodes(root.left) +
Noofnodes(root.right) + 1;
}
// Stores the sum of distances
// of all nodes from given node
public static int sum = 0;
// Function to find sum of distances
// of all nodes from a given node
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches
// with the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
return;
}
// If left of current node exists
if (root.left != null)
{
// Count number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(root.left);
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum - nodes +
(n - nodes);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n);
}
// If right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Find number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(root.right);
// Applying the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum - nodes +
(n - nodes);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
// Sum of depth of all
// nodes from root node
int distanceroot = sumofdepth(root, 0);
// Number of nodes in the
// left and right subtree
int totalnodes = Noofnodes(root);
distance(root, target, distanceroot,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajputC++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
class TreeNode {
public:
int data, size;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to
// its left and right pointers
TreeNode* newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode* Node = new TreeNode();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
pair sumofsubtree(TreeNode* root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair p = make_pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root->left) {
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root->left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root->right) {
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root->right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root->size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
void distance(TreeNode* root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root->data == target) {
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root->left is not null
if (root->left) {
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root->left->size
+ (n - root->left->size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root->left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root->right is not null
if (root->right) {
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root->right->size
+ (n - root->right->size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root->right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input tree
TreeNode* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->left->left->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left->right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
static class TreeNode
{
int data, size;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and null to
// its left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = null;
Node.right = null;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
static pair sumofsubtree(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair p = new pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root.left != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root.right != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root.size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
static int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root.left is not null
if (root.left != null)
{
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.left.size
+ (n - root.left.size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root.right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.right.size
+ (n - root.right.size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
System.out.print(sum +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajputPython3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Stores the sum of distances of all
# nodes from the given node
sum = 0
# Structure of a
# binary tree node
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.size = 0
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to count the number of
# nodes in the left and right subtrees
def sumofsubtree(root):
# Initialize a pair that stores
# the pair {number of nodes, depth}
p = [1, 0]
# Finding the number of nodes
# in the left subtree
if (root.left):
ptemp = sumofsubtree(root.left)
p[1] += ptemp[0] + ptemp[1]
p[0] += ptemp[0]
# Find the number of nodes
# in the right subtree
if (root.right):
ptemp = sumofsubtree(root.right)
p[1] += ptemp[0] + ptemp[1]
p[0] += ptemp[0]
# Filling up size field
root.size = p[0]
return p
# Function to find the total distance
def distance(root, target, distancesum, n):
global sum
# If target node matches with
# the current node
if (root.data == target):
sum = distancesum
# If root.left is not null
if (root.left):
# Update sum
tempsum = (distancesum - root.left.size +
(n - root.left.size))
# Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n)
# If root.right is not null
if (root.right):
# Apply the formula given
# in the approach
tempsum = (distancesum - root.right.size +
(n - root.right.size))
# Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Input tree
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
root.left.right = TreeNode(5)
root.right.left = TreeNode(6)
root.right.right = TreeNode(7)
root.left.left.left = TreeNode(8)
root.left.left.right = TreeNode(9)
target = 3
p = sumofsubtree(root)
# Total number of nodes
totalnodes = p[0]
distance(root, target, p[1], totalnodes)
# Print the sum of distances
print(sum)
# This code is contributed by ipg2016107C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG
{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
class TreeNode
{
public int data, size;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and null to
// its left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = null;
Node.right = null;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
static pair sumofsubtree(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair p = new pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root.left != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root.right != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root.size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
static int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root.left is not null
if (root.left != null)
{
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.left.size
+ (n - root.left.size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root.right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.right.size
+ (n - root.right.size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
Console.Write(sum +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput19时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(1)
高效的方法:可以通过添加一个额外的变量(例如size)来优化上述方法,以表示节点结构中其左侧和右侧子树中的节点数。这样可以将计算子树大小的任务减少到恒定的计算时间
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
class TreeNode {
public:
int data, size;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to
// its left and right pointers
TreeNode* newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode* Node = new TreeNode();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
pair sumofsubtree(TreeNode* root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair p = make_pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root->left) {
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root->left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root->right) {
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root->right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root->size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
void distance(TreeNode* root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root->data == target) {
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root->left is not null
if (root->left) {
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root->left->size
+ (n - root->left->size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root->left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root->right is not null
if (root->right) {
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root->right->size
+ (n - root->right->size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root->right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input tree
TreeNode* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->left->left->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left->right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
static class TreeNode
{
int data, size;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and null to
// its left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = null;
Node.right = null;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
static pair sumofsubtree(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair p = new pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root.left != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root.right != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root.size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
static int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root.left is not null
if (root.left != null)
{
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.left.size
+ (n - root.left.size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root.right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.right.size
+ (n - root.right.size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
System.out.print(sum +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Stores the sum of distances of all
# nodes from the given node
sum = 0
# Structure of a
# binary tree node
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.size = 0
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to count the number of
# nodes in the left and right subtrees
def sumofsubtree(root):
# Initialize a pair that stores
# the pair {number of nodes, depth}
p = [1, 0]
# Finding the number of nodes
# in the left subtree
if (root.left):
ptemp = sumofsubtree(root.left)
p[1] += ptemp[0] + ptemp[1]
p[0] += ptemp[0]
# Find the number of nodes
# in the right subtree
if (root.right):
ptemp = sumofsubtree(root.right)
p[1] += ptemp[0] + ptemp[1]
p[0] += ptemp[0]
# Filling up size field
root.size = p[0]
return p
# Function to find the total distance
def distance(root, target, distancesum, n):
global sum
# If target node matches with
# the current node
if (root.data == target):
sum = distancesum
# If root.left is not null
if (root.left):
# Update sum
tempsum = (distancesum - root.left.size +
(n - root.left.size))
# Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n)
# If root.right is not null
if (root.right):
# Apply the formula given
# in the approach
tempsum = (distancesum - root.right.size +
(n - root.right.size))
# Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Input tree
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
root.left.right = TreeNode(5)
root.right.left = TreeNode(6)
root.right.right = TreeNode(7)
root.left.left.left = TreeNode(8)
root.left.left.right = TreeNode(9)
target = 3
p = sumofsubtree(root)
# Total number of nodes
totalnodes = p[0]
distance(root, target, p[1], totalnodes)
# Print the sum of distances
print(sum)
# This code is contributed by ipg2016107
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG
{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
class TreeNode
{
public int data, size;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and null to
// its left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = null;
Node.right = null;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
static pair sumofsubtree(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair p = new pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root.left != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root.right != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root.size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
static int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root.left is not null
if (root.left != null)
{
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.left.size
+ (n - root.left.size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root.right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.right.size
+ (n - root.right.size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
Console.Write(sum +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
19时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)