打印距给定节点距离为 k 的所有节点
给定一棵二叉树、二叉树中的一个目标节点和一个整数值 k,打印与给定目标节点距离为 k 的所有节点。没有可用的父指针。
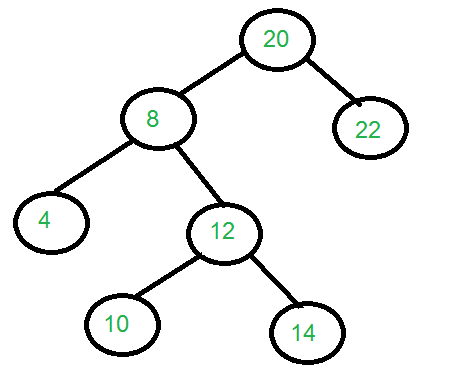
Consider the tree shown in diagram
Input: target = pointer to node with data 8.
root = pointer to node with data 20.
k = 2.
Output : 10 14 22
If target is 14 and k is 3, then output
should be “4 20”
有两种类型的节点需要考虑。
1)以目标节点为根的子树中的节点。例如,如果目标节点是 8,k 是 2,那么这些节点是 10 和 14。
2)其他节点,可能是目标的祖先,或者是某个其他子树中的节点。对于目标节点 8 且 k 为 2,节点 22 属于此类。
找到第一种类型的节点很容易实现。只需遍历以目标节点为根的子树并在递归调用中递减 k。当 k 变为 0 时,打印当前正在遍历的节点(有关详细信息,请参阅此)。这里我们将该函数称为printkdistanceNodeDown() 。
如何找到第二种类型的节点?对于不在以目标节点为根的子树中的输出节点,我们必须遍历所有的祖先。对于每个祖先,我们找到它与目标节点的距离,让距离为d,现在我们去祖先的其他子树(如果在左子树中找到目标,则我们去右子树,反之亦然)并找到所有节点与祖先的距离为kd。
以下是上述方法的实现。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary Tree node
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
/* Recursive function to print all the nodes at distance k in the
tree (or subtree) rooted with given root. See */
void printkdistanceNodeDown(node *root, int k)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL || k < 0) return;
// If we reach a k distant node, print it
if (k==0)
{
cout << root->data << endl;
return;
}
// Recur for left and right subtrees
printkdistanceNodeDown(root->left, k-1);
printkdistanceNodeDown(root->right, k-1);
}
// Prints all nodes at distance k from a given target node.
// The k distant nodes may be upward or downward. This function
// Returns distance of root from target node, it returns -1 if target
// node is not present in tree rooted with root.
int printkdistanceNode(node* root, node* target , int k)
{
// Base Case 1: If tree is empty, return -1
if (root == NULL) return -1;
// If target is same as root. Use the downward function
// to print all nodes at distance k in subtree rooted with
// target or root
if (root == target)
{
printkdistanceNodeDown(root, k);
return 0;
}
// Recur for left subtree
int dl = printkdistanceNode(root->left, target, k);
// Check if target node was found in left subtree
if (dl != -1)
{
// If root is at distance k from target, print root
// Note that dl is Distance of root's left child from target
if (dl + 1 == k)
cout << root->data << endl;
// Else go to right subtree and print all k-dl-2 distant nodes
// Note that the right child is 2 edges away from left child
else
printkdistanceNodeDown(root->right, k-dl-2);
// Add 1 to the distance and return value for parent calls
return 1 + dl;
}
// MIRROR OF ABOVE CODE FOR RIGHT SUBTREE
// Note that we reach here only when node was not found in left subtree
int dr = printkdistanceNode(root->right, target, k);
if (dr != -1)
{
if (dr + 1 == k)
cout << root->data << endl;
else
printkdistanceNodeDown(root->left, k-dr-2);
return 1 + dr;
}
// If target was neither present in left nor in right subtree
return -1;
}
// A utility function to create a new binary tree node
node *newnode(int data)
{
node *temp = new node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
/* Let us construct the tree shown in above diagram */
node * root = newnode(20);
root->left = newnode(8);
root->right = newnode(22);
root->left->left = newnode(4);
root->left->right = newnode(12);
root->left->right->left = newnode(10);
root->left->right->right = newnode(14);
node * target = root->left->right;
printkdistanceNode(root, target, 2);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print all nodes at a distance k from given node
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Recursive function to print all the nodes at distance k in
tree (or subtree) rooted with given root. */
void printkdistanceNodeDown(Node node, int k)
{
// Base Case
if (node == null || k < 0)
return;
// If we reach a k distant node, print it
if (k == 0)
{
System.out.print(node.data);
System.out.println("");
return;
}
// Recur for left and right subtrees
printkdistanceNodeDown(node.left, k - 1);
printkdistanceNodeDown(node.right, k - 1);
}
// Prints all nodes at distance k from a given target node.
// The k distant nodes may be upward or downward.This function
// Returns distance of root from target node, it returns -1
// if target node is not present in tree rooted with root.
int printkdistanceNode(Node node, Node target, int k)
{
// Base Case 1: If tree is empty, return -1
if (node == null)
return -1;
// If target is same as root. Use the downward function
// to print all nodes at distance k in subtree rooted with
// target or root
if (node == target)
{
printkdistanceNodeDown(node, k);
return 0;
}
// Recur for left subtree
int dl = printkdistanceNode(node.left, target, k);
// Check if target node was found in left subtree
if (dl != -1)
{
// If root is at distance k from target, print root
// Note that dl is Distance of root's left child from
// target
if (dl + 1 == k)
{
System.out.print(node.data);
System.out.println("");
}
// Else go to right subtree and print all k-dl-2 distant nodes
// Note that the right child is 2 edges away from left child
else
printkdistanceNodeDown(node.right, k - dl - 2);
// Add 1 to the distance and return value for parent calls
return 1 + dl;
}
// MIRROR OF ABOVE CODE FOR RIGHT SUBTREE
// Note that we reach here only when node was not found in left
// subtree
int dr = printkdistanceNode(node.right, target, k);
if (dr != -1)
{
if (dr + 1 == k)
{
System.out.print(node.data);
System.out.println("");
}
else
printkdistanceNodeDown(node.left, k - dr - 2);
return 1 + dr;
}
// If target was neither present in left nor in right subtree
return -1;
}
// Driver program to test the above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* Let us construct the tree shown in above diagram */
tree.root = new Node(20);
tree.root.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.right = new Node(22);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(12);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(14);
Node target = tree.root.left.right;
tree.printkdistanceNode(tree.root, target, 2);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython3
# Python program to print nodes at distance k from a given node
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# A constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Recursive function to print all the nodes at distance k
# int the tree(or subtree) rooted with given root. See
def printkDistanceNodeDown(root, k):
# Base Case
if root is None or k< 0 :
return
# If we reach a k distant node, print it
if k == 0 :
print (root.data)
return
# Recur for left and right subtree
printkDistanceNodeDown(root.left, k-1)
printkDistanceNodeDown(root.right, k-1)
# Prints all nodes at distance k from a given target node
# The k distant nodes may be upward or downward. This function
# returns distance of root from target node, it returns -1
# if target node is not present in tree rooted with root
def printkDistanceNode(root, target, k):
# Base Case 1 : IF tree is empty return -1
if root is None:
return -1
# If target is same as root. Use the downward function
# to print all nodes at distance k in subtree rooted with
# target or root
if root == target:
printkDistanceNodeDown(root, k)
return 0
# Recur for left subtree
dl = printkDistanceNode(root.left, target, k)
# Check if target node was found in left subtree
if dl != -1:
# If root is at distance k from target, print root
# Note: dl is distance of root's left child
# from target
if dl +1 == k :
print (root.data)
# Else go to right subtreee and print all k-dl-2
# distant nodes
# Note: that the right child is 2 edges away from
# left child
else:
printkDistanceNodeDown(root.right, k-dl-2)
# Add 1 to the distance and return value for
# for parent calls
return 1 + dl
# MIRROR OF ABOVE CODE FOR RIGHT SUBTREE
# Note that we reach here only when node was not found
# in left subtree
dr = printkDistanceNode(root.right, target, k)
if dr != -1:
if (dr+1 == k):
print (root.data)
else:
printkDistanceNodeDown(root.left, k-dr-2)
return 1 + dr
# If target was neither present in left nor in right subtree
return -1
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(20)
root.left = Node(8)
root.right = Node(22)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(12)
root.left.right.left = Node(10)
root.left.right.right = Node(14)
target = root.left.right
printkDistanceNode(root, target, 2)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
using System;
// C# program to print all nodes at a distance k from given node
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
/* Recursive function to print all the nodes at distance k in
tree (or subtree) rooted with given root. */
public virtual void printkdistanceNodeDown(Node node, int k)
{
// Base Case
if (node == null || k < 0)
{
return;
}
// If we reach a k distant node, print it
if (k == 0)
{
Console.Write(node.data);
Console.WriteLine("");
return;
}
// Recur for left and right subtrees
printkdistanceNodeDown(node.left, k - 1);
printkdistanceNodeDown(node.right, k - 1);
}
// Prints all nodes at distance k from a given target node.
// The k distant nodes may be upward or downward.This function
// Returns distance of root from target node, it returns -1
// if target node is not present in tree rooted with root.
public virtual int printkdistanceNode(Node node, Node target, int k)
{
// Base Case 1: If tree is empty, return -1
if (node == null)
{
return -1;
}
// If target is same as root. Use the downward function
// to print all nodes at distance k in subtree rooted with
// target or root
if (node == target)
{
printkdistanceNodeDown(node, k);
return 0;
}
// Recur for left subtree
int dl = printkdistanceNode(node.left, target, k);
// Check if target node was found in left subtree
if (dl != -1)
{
// If root is at distance k from target, print root
// Note that dl is Distance of root's left child from
// target
if (dl + 1 == k)
{
Console.Write(node.data);
Console.WriteLine("");
}
// Else go to right subtree and print all k-dl-2 distant nodes
// Note that the right child is 2 edges away from left child
else
{
printkdistanceNodeDown(node.right, k - dl - 2);
}
// Add 1 to the distance and return value for parent calls
return 1 + dl;
}
// MIRROR OF ABOVE CODE FOR RIGHT SUBTREE
// Note that we reach here only when node was not found in left
// subtree
int dr = printkdistanceNode(node.right, target, k);
if (dr != -1)
{
if (dr + 1 == k)
{
Console.Write(node.data);
Console.WriteLine("");
}
else
{
printkdistanceNodeDown(node.left, k - dr - 2);
}
return 1 + dr;
}
// If target was neither present in left nor in right subtree
return -1;
}
// Driver program to test the above functions
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* Let us construct the tree shown in above diagram */
tree.root = new Node(20);
tree.root.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.right = new Node(22);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(12);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(14);
Node target = tree.root.left.right;
tree.printkdistanceNode(tree.root, target, 2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13Javascript
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode() {}
public TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
}
class GFG {
List path = null;
//Finding all the nodes at a distance K from target
//node.
public List distanceK(TreeNode root,
TreeNode target, int K)
{
path = new ArrayList<>();
findPath(root, target);
List result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
findKDistanceFromNode(
path.get(i), K - i, result,
i == 0 ? null : path.get(i - 1));
}
//Returning list of all nodes at a distance K
return result;
}
// Blocker is used for ancestors node if target at
//left then we have to go in right or if target at
// right then we have to go in left.
public void findKDistanceFromNode(TreeNode node,
int dist,
List result,
TreeNode blocker)
{
if (dist < 0 || node == null
|| (blocker != null && node == blocker)) {
return;
}
if (dist == 0) {
result.add(node.val);
}
findKDistanceFromNode(node.left, dist - 1, result,
blocker);
findKDistanceFromNode(node.right, dist - 1, result,
blocker);
}
//Finding the path of target node from root node
public boolean findPath(TreeNode node, TreeNode target)
{
if (node == null)
return false;
if (node == target || findPath(node.left, target)
|| findPath(node.right, target)) {
path.add(node);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver program to test the above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GFG gfg = new GFG();
/* Let us construct the tree shown in above diagram */
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(20);
root.left = new TreeNode(8);
root.right = new TreeNode(22);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(12);
root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(10);
root.left.right.right = new TreeNode(14);
TreeNode target = root.left.right;
System.out.println(gfg.distanceK(root, target, 2));
}
} 输出:
4
20替代解决方案:
- 从根节点获取路径并添加到列表中
- 对于 Path 中的每个第 i 个元素,只需迭代并打印第 (Ki) 个距离节点。
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode() {}
public TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
}
class GFG {
List path = null;
//Finding all the nodes at a distance K from target
//node.
public List distanceK(TreeNode root,
TreeNode target, int K)
{
path = new ArrayList<>();
findPath(root, target);
List result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
findKDistanceFromNode(
path.get(i), K - i, result,
i == 0 ? null : path.get(i - 1));
}
//Returning list of all nodes at a distance K
return result;
}
// Blocker is used for ancestors node if target at
//left then we have to go in right or if target at
// right then we have to go in left.
public void findKDistanceFromNode(TreeNode node,
int dist,
List result,
TreeNode blocker)
{
if (dist < 0 || node == null
|| (blocker != null && node == blocker)) {
return;
}
if (dist == 0) {
result.add(node.val);
}
findKDistanceFromNode(node.left, dist - 1, result,
blocker);
findKDistanceFromNode(node.right, dist - 1, result,
blocker);
}
//Finding the path of target node from root node
public boolean findPath(TreeNode node, TreeNode target)
{
if (node == null)
return false;
if (node == target || findPath(node.left, target)
|| findPath(node.right, target)) {
path.add(node);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver program to test the above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GFG gfg = new GFG();
/* Let us construct the tree shown in above diagram */
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(20);
root.left = new TreeNode(8);
root.right = new TreeNode(22);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(12);
root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(10);
root.left.right.right = new TreeNode(14);
TreeNode target = root.left.right;
System.out.println(gfg.distanceK(root, target, 2));
}
}
输出
[4, 20]时间复杂度: O(n)