在本文中,我们将讨论“图表到直方图”,也称为“间隔查找” 。在处理统计数据时,图表用单个点(或相应的数字)表示,例如星星,这应该是具有一定宽度的直方图,如下图所示。
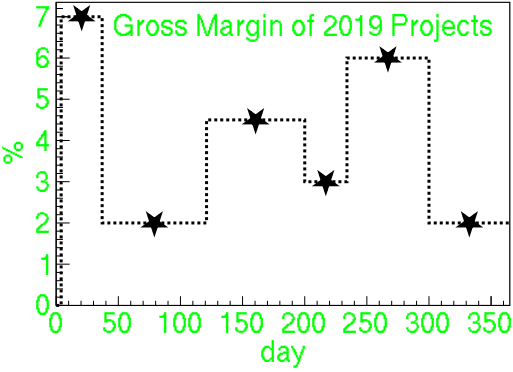
分析问题:
在此问题陈述中,假设所有间隔都无缝地粘在一起,即没有间隙也没有重叠。垃圾箱的右边缘与后续垃圾箱的左边缘相同。给定N个点(即N个仓位) ,任务是找到(N +1)个仓位边缘。每个给定点都位于其X间隔的确切中心。这给出了(N +1)个未知量的N个方程,因此该系统的不确定性。有两个建议:
- 垃圾桶应均匀。从数学上讲,其箱宽的变化应最小化。
- 一个直接为面元边缘提供一个固定值,只有其他固定值是从该值派生的。
计算方式:
以下是一些假设:
- 令x i为该点的坐标(它们的y值对我们而言完全不相关)。
- w i各自的箱宽。
- e i垃圾箱边缘的坐标。
- 假设x i以升序排序。
下图说明了上述概念:
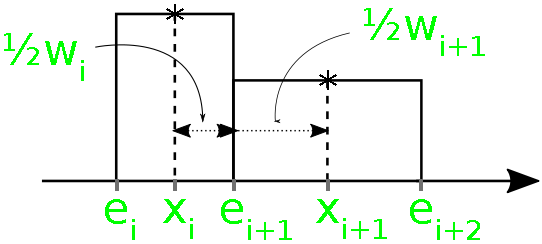
从上面的表示中,可以很容易地验证两个简单的关系:
上面的公式特别简化了偶数N的计算,这就是为什么对N的奇数和偶数获得不同结果的原因。后者直接是递归公式,需要填写数组e [] (直方图X轴上的点)。
如何最小化方差?
这个想法类似于所有最小化问题,即检查导数0 。问题在于将其公式简化为仅一个未知变量,然后我们可以使用它来找到最小值。
- 方差由下式给出:
- 上式中的平均值表示为:
- 关于任意量z推导上式为:
- 通过将w i替换为(z = e 0 )来迭代地应用上面导出的第一个方程。例如:
- 将以上所有获得的值放入以找到e 0的值:
When N is odd, then
![]()
When N is even, then
![]()
- 或者,使用z = e N的值,给出一个更简单的公式:
When N is odd, then
![]()
When N is even, then
![]()
方法:解决给定问题的想法是迭代两个嵌套循环,一个用于根据派生的公式查找e 0或e N的值,另一个用于查找数组e []的元素的循环。因此,所有变量的时间复杂度均为O(N)。两个循环都递归工作,第二个循环根据上面给出的第二个等式从前一个找到数组e []的元素。
笔记:
- 整数除法的舍入效应用于处理N的奇数和偶数情况。
- 如果在以下实现中省略了关键字register,则C函数也将在C++中工作。
- 该程序将分别需要标准C99的C编译器和C++ 14的C++编译器。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
#define N 6
// Function to fill the array elements
// e[] from the end
double* pointsToIntervalsN(
int n, const double* x,
double* e)
{
// Check for array overlap
if (n < 2 || !x || e < x && e + n >= x)
return NULL;
// If e is a NULL pointer, then
// allocate the array
if (e
|| (e
= (double*)malloc(
(n + 1) * sizeof(double)))) {
// Find the value of m on the
// basis of odd or even value of N
const int m = n & 1 ? n : 2;
const int j = m * n;
register double sum = 0.;
// Count i and x downwards
for (int i = m / 2; i < j; i += m) {
sum = i * *x++ - sum;
}
sum /= j / 2;
// Note: m/2 and j/2 above are
// integer divisions!
for (e[n] = sum; n--; e[n] = sum)
sum = 2 * *--x - sum;
}
// Including e==NULL for the case
// of malloc error
return e;
}
// Function to fill the output array
// from the front
double* pointsToIntervals0(const int n,
const double* x,
double* e)
{
// Check for overlaps
if (n < 2 || !x || e >= x && e < x + n)
return NULL;
if (e
|| (e
= (double*)malloc(
(n + 1) * sizeof(double)))) {
const int m = n & 1 ? n : 2;
const int j = m * n;
register double sum = 0.;
// Count i down and x
// from the front
x += n;
for (int i = m / 2; i < j;
i += m) {
sum = i * *--x - sum;
}
// Update the value of sum
sum /= j / 2;
*e = sum;
for (int i = 0; i < n;
e[++i] = sum)
sum = 2 * x[i] - sum;
}
// Return the updated e
return e;
}
// Function to find thefixed single
// e value from which all other e's
// are derived
double* pointsToIntervalsFix(const int n,
const double* x,
double e_base,
double* e)
{
// Base Case
if (n < 1 || !x)
return NULL;
int k = 0;
// Perform Binary Search for e_base
for (int l = n; l > 1; l /= 2)
if (e_base > x[k + l / 2])
k += (l + 1) / 2;
// The e_base is either the left
// or the right edge of the bin
// around x[k]
if (e_base > x[k])
++k;
// Now it's the left.
// Assume e is filled the left side
// first, the right side of e can
// overlap with x
if (e + k >= x && e < x + n)
return NULL;
// If the right side is filled
// first, so that the left side
// of e can overlap with x
if (e || (e = (double*)malloc(
(n + 1) * sizeof(double)))) {
e[k] = e_base;
// Fill in both sides of array
// e[] starting from k
for (int i = k; i--; e[i] = e_base)
e_base = 2 * x[i] - e_base;
for (e_base = e[k]; k < n;
e[++k] = e_base)
e_base = 2 * x[k] - e_base;
}
return e;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
double e_orig[N + 1]
= { 4, 37, 121, 200, 234, 300, 365 };
double x[N], e_recN[N + 1], e_rec0[N + 1];
double e_base = 235.4, e_fix[N + 1];
// Make x the mean values of the
// neighbouring e_orig values:
for (int i = N; i--;
x[i] = (e_orig[i + 1] + e_orig[i]) / 2)
;
// Function Call
pointsToIntervalsN(N, x, e_recN);
pointsToIntervals0(N, x, e_rec0);
pointsToIntervalsFix(N, x, e_base, e_fix);
printf("Example for n = %d:", N);
printf("\nx ");
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
printf("% .3f", x[i]);
printf("\ne_orig ");
for (int i = 0; i <= N; ++i)
printf("% .3f", e_orig[i]);
printf("\ne_recN ");
for (int i = 0; i <= N; ++i)
printf("% .3f", e_recN[i]);
printf("\ne_rec0 ");
for (int i = 0; i <= N; ++i)
printf("% .3f", e_rec0[i]);
printf("\ne_fix ");
for (int i = 0; i <= N; ++i)
printf("% .3f", e_fix[i]);
return 0;
} 输出:
Example for n = 6:
x 20.500 79.000 160.500 217.000 267.000 332.500
e_orig 4.000 37.000 121.000 200.000 234.000 300.000 365.000
e_recN 3.583 37.417 120.583 200.417 233.583 300.417 364.583
e_rec0 3.583 37.417 120.583 200.417 233.583 300.417 364.583
e_fix 5.400 35.600 122.400 198.600 235.400 298.600 366.400
注意事项和前景:
- 这两种方法(即最小方差和固定边沿)有时都会失败,从而无法获得一个或多个宽度为负的直方图块,即有些e i > e (i + 1 )似乎没有正确分类。当将任何随机X值用作输入时,总是会发生这种情况。
- 尝试以所有“最负数”的宽度固定垃圾箱,希望其他所有垃圾箱也看起来合理。
- 这将我们带入了前景,因为上述两种方法到目前为止并不是制定额外条件的唯一可能性。代替“可能相等”的条带宽度,假设趋势像是w i的线性增加或所有w i的绝对最小值。
