给定一个由V个顶点和E个边缘组成的加权有向图。任务是打印权重之和为负的循环路径。如果不存在这样的路径,则打印“ -1” 。
Input: V = 5, E = 5, Below is the graph:
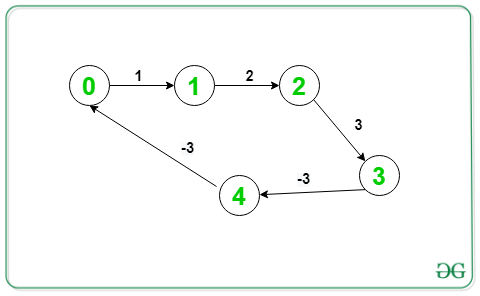
Output: 1 2 3 4 1
Explanation:
Given graph contains a negative cycle, (1->2->3->4->1)
Input: V = 5, E = 5, Below is the graph:
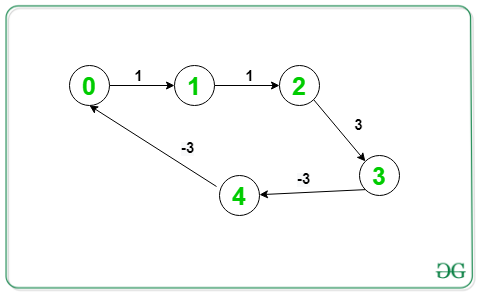
Output: 0 1 2 3 4 0
Explanation:
Given graph contains a negative cycle, (0->1->2->3->4->0)
方法:想法是使用Bellman-Ford算法来检测负周期。要打印负周期,请执行Bellman-Ford的第N次迭代,并从该迭代中松弛的任何边上选取一个顶点。使用此顶点及其祖先,可以打印负周期。步骤如下:
- 执行Bellman-Ford算法的N-1次迭代,并放宽每个边(u,v) 。跟踪每个顶点的父级,并将其存储在数组parent []中。
- 现在,再进行一次迭代,如果在第N次迭代中没有发生边缘松弛,则图中不存在负权重的循环。
- 否则,取变量C并从任意边(u,v)存储顶点v ,在第N次迭代中将其放宽。
- 现在,从C顶点开始向其祖先移动,直到找到一个循环并最终将其打印出来。
- 该周期将是负重量的期望周期。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure to represent a weighted
// edge in graph
struct Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
};
// Structure to represent a directed
// and weighted graph
struct Graph {
// V -> Number of vertices,
// E -> Number of edges
int V, E;
// Graph is represented as an
// array of edges
struct Edge* edge;
};
// Creates a new graph with V vertices
// and E edges
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E)
{
struct Graph* graph = new Graph;
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = new Edge[graph->E];
return graph;
}
// Function runs Bellman-Ford algorithm
// and prints negative cycle(if present)
void NegCycleBellmanFord(struct Graph* graph,
int src)
{
int V = graph->V;
int E = graph->E;
int dist[V];
int parent[V];
// Initialize distances from src
// to all other vertices as INFINITE
// and all parent as -1
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
parent[i] = -1;
}
dist[src] = 0;
// Relax all edges |V| - 1 times.
for (int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < E; j++) {
int u = graph->edge[j].src;
int v = graph->edge[j].dest;
int weight = graph->edge[j].weight;
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX
&& dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
parent[v] = u;
}
}
}
// Check for negative-weight cycles
int C = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = graph->edge[i].src;
int v = graph->edge[i].dest;
int weight = graph->edge[i].weight;
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX
&& dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
// Store one of the vertex of
// the negative weight cycle
C = v;
break;
}
}
if (C != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
C = parent[C];
// To store the cycle vertex
vector cycle;
for (int v = C;; v = parent[v]) {
cycle.push_back(v);
if (v == C
&& cycle.size() > 1)
break;
}
// Reverse cycle[]
reverse(cycle.begin(), cycle.end());
// Printing the negative cycle
for (int v : cycle)
cout << v << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
else
cout << "-1" << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of vertices in graph
int V = 5;
// Number of edges in graph
int E = 5;
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
// Given Graph
graph->edge[0].src = 0;
graph->edge[0].dest = 1;
graph->edge[0].weight = 1;
graph->edge[1].src = 1;
graph->edge[1].dest = 2;
graph->edge[1].weight = 2;
graph->edge[2].src = 2;
graph->edge[2].dest = 3;
graph->edge[2].weight = 3;
graph->edge[3].src = 3;
graph->edge[3].dest = 4;
graph->edge[3].weight = -3;
graph->edge[4].src = 4;
graph->edge[4].dest = 1;
graph->edge[4].weight = -3;
// Function Call
NegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG{
// Structure to represent a weighted
// edge in graph
static class Edge
{
int src, dest, weight;
}
// Structure to represent a directed
// and weighted graph
static class Graph
{
// V. Number of vertices, E.
// Number of edges
int V, E;
// Graph is represented as
// an array of edges.
Edge[] edge;
}
// Creates a new graph with V vertices
// and E edges
static Graph createGraph(int V, int E)
{
Graph graph = new Graph();
graph.V = V;
graph.E = E;
graph.edge = new Edge[graph.E];
for(int i = 0; i < graph.E; i++)
{
graph.edge[i] = new Edge();
}
return graph;
}
// Function runs Bellman-Ford algorithm
// and prints negative cycle(if present)
static void NegCycleBellmanFord(Graph graph, int src)
{
int V = graph.V;
int E = graph.E;
int[] dist = new int[V];
int[] parent = new int[V];
// Initialize distances from src
// to all other vertices as INFINITE
// and all parent as -1
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
dist[i] = 1000000;
parent[i] = -1;
}
dist[src] = 0;
// Relax all edges |V| - 1 times.
for(int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < E; j++)
{
int u = graph.edge[j].src;
int v = graph.edge[j].dest;
int weight = graph.edge[j].weight;
if (dist[u] != 1000000 &&
dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
{
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
parent[v] = u;
}
}
}
// Check for negative-weight cycles
int C = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
int u = graph.edge[i].src;
int v = graph.edge[i].dest;
int weight = graph.edge[i].weight;
if (dist[u] != 1000000 &&
dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
{
// Store one of the vertex of
// the negative weight cycle
C = v;
break;
}
}
if (C != -1)
{
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
C = parent[C];
// To store the cycle vertex
ArrayList cycle = new ArrayList<>();
for(int v = C;; v = parent[v])
{
cycle.add(v);
if (v == C && cycle.size() > 1)
break;
}
// Reverse cycle[]
Collections.reverse(cycle);
// Printing the negative cycle
for(int v : cycle)
System.out.print(v + " ");
System.out.println();
}
else
System.out.println(-1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of vertices in graph
int V = 5;
// Number of edges in graph
int E = 5;
Graph graph = createGraph(V, E);
// Given Graph
graph.edge[0].src = 0;
graph.edge[0].dest = 1;
graph.edge[0].weight = 1;
graph.edge[1].src = 1;
graph.edge[1].dest = 2;
graph.edge[1].weight = 2;
graph.edge[2].src = 2;
graph.edge[2].dest = 3;
graph.edge[2].weight = 3;
graph.edge[3].src = 3;
graph.edge[3].dest = 4;
graph.edge[3].weight = -3;
graph.edge[4].src = 4;
graph.edge[4].dest = 1;
graph.edge[4].weight = -3;
// Function Call
NegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Structure to represent a weighted
# edge in graph
class Edge:
def __init__(self):
self.src = 0
self.dest = 0
self.weight = 0
# Structure to represent a directed
# and weighted graph
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
# V. Number of vertices, E.
# Number of edges
self.V = 0
self.E = 0
# Graph is represented as
# an array of edges.
self.edge = []
# Creates a new graph with V vertices
# and E edges
def createGraph(V, E):
graph = Graph();
graph.V = V;
graph.E = E;
graph.edge = [Edge() for i in range(graph.E)]
return graph;
# Function runs Bellman-Ford algorithm
# and prints negative cycle(if present)
def NegCycleBellmanFord(graph, src):
V = graph.V;
E = graph.E;
dist =[1000000 for i in range(V)]
parent =[-1 for i in range(V)]
dist[src] = 0;
# Relax all edges |V| - 1 times.
for i in range(1, V):
for j in range(E):
u = graph.edge[j].src;
v = graph.edge[j].dest;
weight = graph.edge[j].weight;
if (dist[u] != 1000000 and
dist[u] + weight < dist[v]):
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
parent[v] = u;
# Check for negative-weight cycles
C = -1;
for i in range(E):
u = graph.edge[i].src;
v = graph.edge[i].dest;
weight = graph.edge[i].weight;
if (dist[u] != 1000000 and
dist[u] + weight < dist[v]):
# Store one of the vertex of
# the negative weight cycle
C = v;
break;
if (C != -1):
for i in range(V):
C = parent[C];
# To store the cycle vertex
cycle = []
v = C
while (True):
cycle.append(v)
if (v == C and len(cycle) > 1):
break;
v = parent[v]
# Reverse cycle[]
cycle.reverse()
# Printing the negative cycle
for v in cycle:
print(v, end = " ");
print()
else:
print(-1);
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Number of vertices in graph
V = 5;
# Number of edges in graph
E = 5;
graph = createGraph(V, E);
# Given Graph
graph.edge[0].src = 0;
graph.edge[0].dest = 1;
graph.edge[0].weight = 1;
graph.edge[1].src = 1;
graph.edge[1].dest = 2;
graph.edge[1].weight = 2;
graph.edge[2].src = 2;
graph.edge[2].dest = 3;
graph.edge[2].weight = 3;
graph.edge[3].src = 3;
graph.edge[3].dest = 4;
graph.edge[3].weight = -3;
graph.edge[4].src = 4;
graph.edge[4].dest = 1;
graph.edge[4].weight = -3;
# Function Call
NegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0);
# This code is contributed by Pratham76C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Structure to represent a weighted
// edge in graph
class Edge {
public int src, dest, weight;
}
// Structure to represent a directed
// and weighted graph
class Graph {
// V. Number of vertices, E. Number of edges
public int V, E;
// graph is represented as an array of edges.
public Edge[] edge;
}
// Creates a new graph with V vertices
// and E edges
static Graph createGraph(int V, int E)
{
Graph graph = new Graph();
graph.V = V;
graph.E = E;
graph.edge = new Edge[graph.E];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.E; i++) {
graph.edge[i] = new Edge();
}
return graph;
}
// Function runs Bellman-Ford algorithm
// and prints negative cycle(if present)
static void NegCycleBellmanFord(Graph graph, int src)
{
int V = graph.V;
int E = graph.E;
int[] dist = new int[V];
int[] parent = new int[V];
// Initialize distances from src
// to all other vertices as INFINITE
// and all parent as -1
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
dist[i] = 1000000;
parent[i] = -1;
}
dist[src] = 0;
// Relax all edges |V| - 1 times.
for (int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < E; j++) {
int u = graph.edge[j].src;
int v = graph.edge[j].dest;
int weight = graph.edge[j].weight;
if (dist[u] != 1000000
&& dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
parent[v] = u;
}
}
}
// Check for negative-weight cycles
int C = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = graph.edge[i].src;
int v = graph.edge[i].dest;
int weight = graph.edge[i].weight;
if (dist[u] != 1000000
&& dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
// Store one of the vertex of
// the negative weight cycle
C = v;
break;
}
}
if (C != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
C = parent[C];
// To store the cycle vertex
ArrayList cycle = new ArrayList();
for (int v = C;; v = parent[v]) {
cycle.Add(v);
if (v == C && cycle.Count > 1)
break;
}
// Reverse cycle[]
cycle.Reverse();
// Printing the negative cycle
foreach(int v in cycle) Console.Write(v + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
Console.WriteLine(-1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Number of vertices in graph
int V = 5;
// Number of edges in graph
int E = 5;
Graph graph = createGraph(V, E);
// Given Graph
graph.edge[0].src = 0;
graph.edge[0].dest = 1;
graph.edge[0].weight = 1;
graph.edge[1].src = 1;
graph.edge[1].dest = 2;
graph.edge[1].weight = 2;
graph.edge[2].src = 2;
graph.edge[2].dest = 3;
graph.edge[2].weight = 3;
graph.edge[3].src = 3;
graph.edge[3].dest = 4;
graph.edge[3].weight = -3;
graph.edge[4].src = 4;
graph.edge[4].dest = 1;
graph.edge[4].weight = -3;
// Function Call
NegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56输出:
1 2 3 4 1时间复杂度: O(V * E)
辅助空间: O(V)