质量和重量
重量是力的量度,而质量是惯性的量度。许多人交替使用这两个词。然而,事实并非如此。我们可以帮助您研究质量和重量之间的众多区别。
要改变物体的速度或方向,需要一个力。如果你从高处掉下任何东西,它会落向地球表面。行星围绕太阳转,月亮围绕地球转。一定有某种力作用于物体、行星和其他天体。艾萨克·牛顿指出,所有这些都是同一个力量造成的。这种力称为万有引力。
大量的
Mass is defined as the measure of the amount of matter present in a body. The mass of the body remains the same everywhere, irrespective of location. Thus, mass refers to both, the property of a physical body and the measure of the resistance of the object to acceleration when we apply a net force.
物体的惯性是通过其质量来衡量的,即物体的质量是其惯性的量度。当物体的质量增加时,惯性也会增加。
身体的质量不随地点而变化。无论一个物体是在地球上、月球上,还是在太空中,它的质量都保持不变。因此,物体的质量是恒定的,不会随其位置而变化。
The formula to calculate the mass of an object is:
Mass (m) = Volume (V) × Density (ρ)
or
m = V × ρ
It is a scalar quantity and its SI unit is kilogram (kg).
使用普通天平、横梁天平或数字天平测量的物体质量。
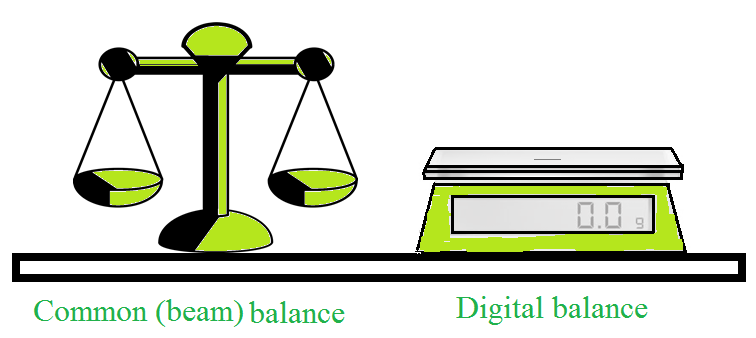
测量物体质量的仪器。
重量
The weight of an object is defined as the measure of the amount of force that acts on mass because of the pull of gravity. Weigh is the measure of force. Therefore, Weight will vary depending on the location.
地球以与物体质量 (m) 和重力加速度 (g) 成正比的力吸引每一件物品。将物体拉向地球的力称为其重量。
它是一个向量。它具有大小并指向地球中心或其他重力。
重量的 SI 单位是牛顿,与力的 SI 单位 (N) 相同。
使用弹簧秤测量物体的重量。
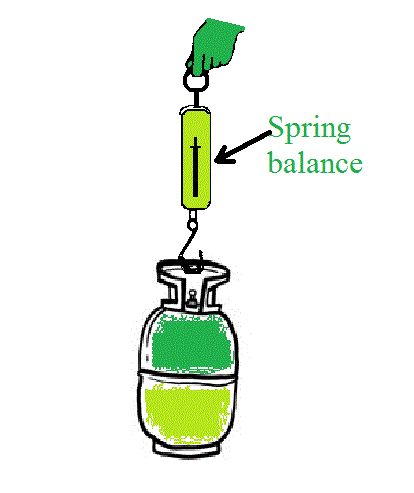
重力加速度(g):当物体落向地球时,它会经历加速度。地球的引力是造成这种加速度的原因。这种加速度称为重力加速度。它用g表示。 g 的单位是ms –2 ,与加速度的单位相同。
重量公式
一切都以一定的力被地球吸引,这个力取决于物体的质量(m)和重力加速度(g)。
力可以表示为,
F = m × a
其中,m是物体的质量,a是物体的加速度。
IE
F = 米 × 克
物体的重量定义为地球对它的吸引力,用 W 表示。
所以表达式可以写成,
W = 米 × 克
重量是一个向下作用的力,它既有大小又有方向,所以它是一个矢量。
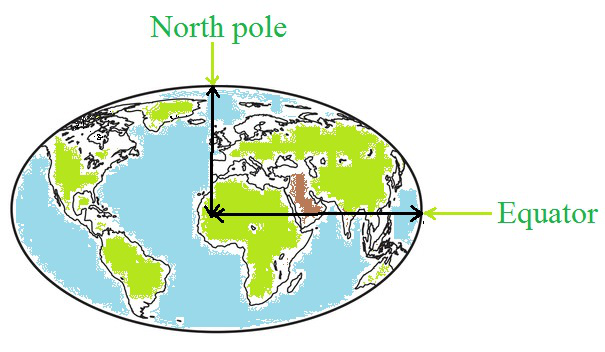
赤道上一点到地球中心的距离和北极点到地球中心的距离。
地球的形状看起来是球形的,但它是一个形状不均匀的椭圆体。赤道一点到地球中心的距离大于北极点到地球中心的距离。从上面的表达式可以看出,重力加速度(g)与物体与地球之间距离的平方成反比,放置在北极的物体会比赤道的重量更大。因此,由于质量保持不变,但重力加速度因地而异,因此物体在地球表面上的重量也可能因地而异。
月球上物体的重量:地球上物体的重量是地球吸引物体的力。同样,月球上物体的重量是将该物体吸引到月球的力。月球的质量小于地球的质量。因此,月球对物体的吸引力较小。
示例问题
问题 1:一个物体的质量是 10 公斤。它在地球上的重量是多少?
解决方案:
Given that,
The mass (m) = 10 kg
The acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m s–2
The expression of the weight is
W = m × g
Substitute the values in the above equation.
W = 10 kg × 9.8 m s-2 = 98 N
Thus, the weight of the object is 98 N.
问题 2:一个物体在地球表面测量时重 10 N。在月球表面测量时它的重量是多少
解决方案:
Given,
The weight of an object on the earth is 10 N.
Relation between the weight of an object on the earth (We) and the weight of an object on the moon (Wm)
Wm = (1⁄6)×We
Substitute the value in the above expression.
Wm = (1⁄6)×10 N
Wm=1.67 N
Thus, the weight of the object on the surface of the moon would be 1.67 N.
问题3:物体的质量与其重量有什么区别?
解决方案:
The difference between the mass and the weight are as follows,Mass Weight The mass of an object can never be zero. When there is no gravity acting on an item, such as in space, weight can be zero. The mass is a property of matter. An object’s mass is constant everywhere. The effect of gravity has an impact on weight. With higher or lower gravity, weight increases or decreases. Mass is a scalar quantity. It has only magnitude, not direction. Weight is a vector quantity. It has both magnitudes as well as direction. Mass is commonly measured in kilograms (kg) and grams (g). Weight is measured in Newtons (N). The mass of an object does not change with its position. The weight of an object change with its position. The mass of an object measured by using an ordinary balance. Weight of an object measured by using a spring balance.
问题4:地球上物体的重量和月球上物体的重量之间的关系是什么。
解决方案:
The mass of the earth is 5.98 ×1024 kg.
The mass of the moon is 7.36×1022 kg.
The radius of the earth is 6.37×106 m.
The radius of the moon is 1.74×106 m.
Let the mass of an object be m, the weight on the moon be Wm, the mass of the moon be Mm and its radius be Rm.
From the universal law of gravitation, the expression for the weight of the object on the moon is
Wm = (G Mm m)/(R)2
Substitute the values in the above expression.
Wm = (G 7.36×1022 kg m)/(1.74×106 m)2 …….(1)
Let the weight of the same object on the earth be We, the mass of the earth is M and its radius is R then the expression for the weight of the object on the earth is
We = (G M m)/(R)2
Substitute the values in the above expression
We = (5.98 ×1024 kg m)/(6.37×106 m)2 ……..(2)
Divide equation (1) and (2),
Wm/We = 2.431 1010/1.474 1011
= 0.165
≈ 1/6
or
Wm = (1⁄6)×We
问题5:地球与物体之间的引力叫什么?
解决方案:
The gravitation force between the earth and the object is called weight. It is also equal to the product of acceleration due to the gravity and mass of the object.
W = m × g,
where,
m is the mass of the object,
g is the acceleration due to gravity and its value on earth is 9.8m/s2.