给定一个函数f(x) ,在点列表
![]()
等距
![]()
这样
![]() [Tex] f_2 = f(x_2)[/ Tex]
[Tex] f_2 = f(x_2)[/ Tex]
- …..等等
上限和下限a,b对应于需要找到积分的位置,任务是找到给定方程f(x)的积分值。
例子:
Input: a = 0, b = 4,
![]()
Output: 1.6178
Explanation:
Integral of (1 / (1 + x)) is 4ln(|1 + x|)0 + c.
On substituting the limits, ln(|5|) + ln(|1|) = 1.6178.
Input: a = 0.2, b = 0.6,
![]()
Output: 0.3430
方法:在本文中,讨论了布尔规则,以计算给定函数f(x)的近似积分值。
布尔定律是一种找到积分近似值的数值积分技术。它是由一位自学成才的数学家,哲学家和逻辑学家乔治·布尔(George Boole)命名的。布尔技术的思想是在某些等距值(给定图像中的h)处使用’f k ‘的值来近似积分。下图显示了如何考虑各种f k :
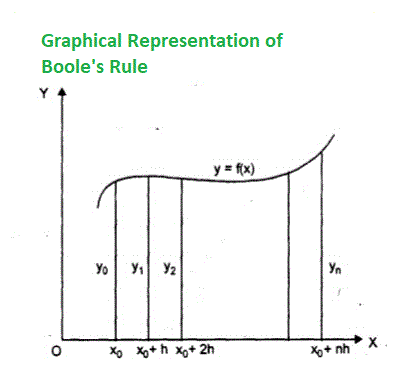
布尔定律的积分值由以下公式给出:
- 在上面的公式中,当积分为6阶时出现的误差项。误差项为
![]() [Tex] f_1,f_2,f_3,f_4,f_5,[/ Tex]
[Tex] f_1,f_2,f_3,f_4,f_5,[/ Tex]
- 是f(x)的值在它们各自的x间隔。
- 因此,可以按照以下步骤计算间隔(a,b)中某些函数f(x)的积分:
- n = 6的值,即间隔被划分成的部分的数量。
- 计算宽度,h =(b – a)/ 4。
- 将x 1到x 5的值计算为
![]()
- 考虑y = f(x)。现在找到值
![]()
- 对于相应的
![]()
- 价值观。
- 将所有值替换为Boole规则以计算积分值。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement Boole's Rule
// on the given function
#include
using namespace std;
// In order to represent the implementation,
// a function f(x) = 1/(1 + x) is considered
// in this program
// Function to return the value of f(x)
// for the given value of x
float y(float x)
{
return (1 / (1 + x));
}
// Function to computes the integrand of y
// at the given intervals of x with
// step size h and the initial limit a
// and final limit b
float BooleRule(float a, float b)
{
// Number of intervals
int n = 4;
int h;
// Computing the step size
h = ((b - a) / n);
float sum = 0;
// Substituing a = 0, b = 4 and h = 1
float bl = ((7 * y(a) +
32 * y(a + h) +
12 * y(a + 2 * h) +
32 * y(a + 3 * h) +
7 * y(a + 4 * h)) *
2 * h / 45);
sum = sum + bl;
return sum;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
float lowlimit = 0;
float upplimit = 4;
cout << fixed << setprecision(4) <<
"f(x) = " << BooleRule(0, 4);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 C
// C program to implement Boole's Rule
// on the given function
#include
#include
// In order to represent the implementation,
// a function f(x) = 1/(1 + x) is considered
// in this program
// Function to return the value of f(x)
// for the given value of x
float y(float x)
{
return (1 / (1 + x));
}
// Function to computes the integrand of y
// at the given intervals of x with
// step size h and the initial limit a
// and final limit b
float BooleRule(float a, float b)
{
// Number of intervals
int n = 4;
int h;
// Computing the step size
h = ((b - a) / n);
float sum = 0;
// Substituing a = 0, b = 4 and h = 1
float bl = (7 * y(a) + 32 * y(a + h)
+ 12 * y(a + 2 * h)
+ 32 * y(a + 3 * h)
+ 7 * y(a + 4 * h))
* 2 * h / 45;
sum = sum + bl;
return sum;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
float lowlimit = 0;
float upplimit = 4;
printf("f(x) = %.4f",
BooleRule(0, 4));
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement Boole's Rule
// on the given function
class GFG{
// In order to represent the implementation,
// a function f(x) = 1/(1 + x) is considered
// in this program
// Function to return the value of f(x)
// for the given value of x
static float y(float x)
{
return (1 / (1 + x));
}
// Function to computes the integrand of y
// at the given intervals of x with
// step size h and the initial limit a
// and final limit b
static float BooleRule(float a, float b)
{
// Number of intervals
int n = 4;
int h;
// Computing the step size
h = (int) ((b - a) / n);
float sum = 0;
// Substituing a = 0, b = 4 and h = 1
float bl = (7 * y(a) + 32 * y(a + h)
+ 12 * y(a + 2 * h)
+ 32 * y(a + 3 * h)
+ 7 * y(a + 4 * h))
* 2 * h / 45;
sum = sum + bl;
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.printf(("f(x) = %.4f"),
BooleRule(0, 4));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python3 program to implement Boole's Rule
# on the given function
# In order to represent the implementation,
# a function f(x) = 1/(1 + x) is considered
# in this program
# Function to return the value of f(x)
# for the given value of x
def y(x):
return (1 / (1 + x))
# Function to computes the integrand of y
# at the given intervals of x with
# step size h and the initial limit a
# and final limit b
def BooleRule(a, b):
# Number of intervals
n = 4
# Computing the step size
h = ((b - a) / n)
sum = 0
# Substituing a = 0, b = 4 and h = 1
bl = (7 * y(a) + 32 * y(a + h) + 12 *
y(a + 2 * h)+32 * y(a + 3 * h)+7 *
y(a + 4 * h))* 2 * h / 45
sum = sum + bl
return sum
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
lowlimit = 0
upplimit = 4
print("f(x) =",round(BooleRule(0, 4),4))
# This code is contributed by Surendra_GangwarC#
// C# program to implement Boole's
// Rule on the given function
using System;
class GFG{
// In order to represent the
// implementation, a function
// f(x) = 1/(1 + x) is considered
// in this program
// Function to return the value of
// f(x) for the given value of x
static float y(float x)
{
return (1 / (1 + x));
}
// Function to computes the integrand
// of y at the given intervals of x
// with step size h and the initial
// limit a and final limit b
static float BooleRule(float a,
float b)
{
// Number of intervals
int n = 4;
int h;
// Computing the step size
h = (int)((b - a) / n);
float sum = 0;
// Substituing a = 0, b = 4
// and h = 1
float bl = (7 * y(a) + 32 *
y(a + h) + 12 *
y(a + 2 * h) +
32 * y(a + 3 *
h) + 7 * y(a +
4 * h)) * 2 *
h / 45;
sum = sum + bl;
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write(("f(x) = " +
System.Math.Round(
BooleRule(0, 4), 4)));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Chitranayal输出:
f(x) = 1.6178