最大流量问题的 Ford-Fulkerson 算法
给定一个表示流网络的图,其中每条边都有容量。同样给定图中的两个顶点source 's' 和sink 't',找到从 s 到 t 的最大可能流,具有以下约束:
a)边上的流量不超过边的给定容量。
b)对于除 s 和 t 之外的每个顶点,流入流等于流出流。
例如,考虑 CLRS 书中的下图。
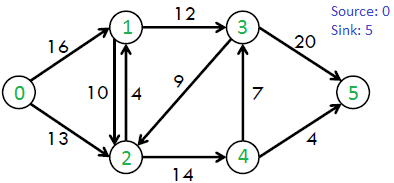
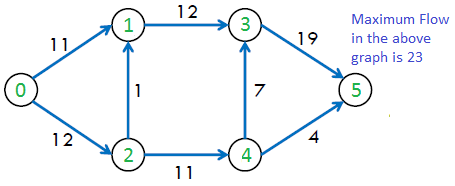
上图中的最大可能流量为 23。
先决条件:最大流量问题介绍
Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm
The following is simple idea of Ford-Fulkerson algorithm:
1) Start with initial flow as 0.
2) While there is a augmenting path from source to sink.
Add this path-flow to flow.
3) Return flow.时间复杂度:上述算法的时间复杂度为 O(max_flow * E)。当有一条增广路径时,我们运行一个循环。在最坏的情况下,我们可能会在每次迭代中添加 1 个单位流。因此时间复杂度变为 O(max_flow * E)。
如何实现上述简单算法?
让我们首先定义理解实现所需的残差图的概念。
流网络的残差图是指示附加可能流的图。如果残差图中存在从源到汇的路径,则可以添加流。残差图的每条边都有一个称为剩余容量的值,该值等于边的原始容量减去当前流量。剩余容量基本上是边缘的当前容量。
现在让我们谈谈实现细节。如果残差图的两个顶点之间没有边,则残差容量为0。我们可以将残差图初始化为原始图,因为没有初始流并且初始剩余容量等于原始容量。要找到增广路径,我们可以对残差图进行 BFS 或 DFS。我们在下面的实现中使用了 BFS。使用 BFS,我们可以查明是否存在从源到接收器的路径。 BFS 还构建 parent[] 数组。使用 parent[] 数组,我们遍历找到的路径,并通过找到沿路径的最小剩余容量来找到通过该路径的可能流。我们稍后将找到的路径流添加到整体流中。
重要的是,我们需要更新残差图中的残差容量。我们从沿路径的所有边中减去路径流,然后沿反向边缘添加路径流 我们需要沿反向边缘添加路径流,因为以后可能需要反向发送流(例如,请参见以下链接)。
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/max-flow-problem-introduction/
下面是 Ford-Fulkerson 算法的实现。为简单起见,图表示为 2D 矩阵。
C++
// C++ program for implementation of Ford Fulkerson
// algorithm
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Number of vertices in given graph
#define V 6
/* Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink
't' in residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the
path */
bool bfs(int rGraph[V][V], int s, int t, int parent[])
{
// Create a visited array and mark all vertices as not
// visited
bool visited[V];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark source
// vertex as visited
queue q;
q.push(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
if (visited[v] == false && rGraph[u][v] > 0) {
// If we find a connection to the sink node,
// then there is no point in BFS anymore We
// just have to set its parent and can return
// true
if (v == t) {
parent[v] = u;
return true;
}
q.push(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// We didn't reach sink in BFS starting from source, so
// return false
return false;
}
// Returns the maximum flow from s to t in the given graph
int fordFulkerson(int graph[V][V], int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// Create a residual graph and fill the residual graph
// with given capacities in the original graph as
// residual capacities in residual graph
int rGraph[V]
[V]; // Residual graph where rGraph[i][j]
// indicates residual capacity of edge
// from i to j (if there is an edge. If
// rGraph[i][j] is 0, then there is not)
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
int parent[V]; // This array is filled by BFS and to
// store path
int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
// Augment the flow while there is path from source to
// sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent)) {
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edges along
// the path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the
// maximum flow through the path found.
int path_flow = INT_MAX;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
path_flow = min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and
// reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
}
// Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow;
}
// Return the overall flow
return max_flow;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create a graph shown in the above example
int graph[V][V]
= { { 0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0 }, { 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
cout << "The maximum possible flow is "
<< fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for implementation of Ford Fulkerson
// algorithm
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
class MaxFlow {
static final int V = 6; // Number of vertices in graph
/* Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to
sink 't' in residual graph. Also fills parent[] to
store the path */
boolean bfs(int rGraph[][], int s, int t, int parent[])
{
// Create a visited array and mark all vertices as
// not visited
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
visited[i] = false;
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark
// source vertex as visited
LinkedList queue
= new LinkedList();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (queue.size() != 0) {
int u = queue.poll();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
if (visited[v] == false
&& rGraph[u][v] > 0) {
// If we find a connection to the sink
// node, then there is no point in BFS
// anymore We just have to set its parent
// and can return true
if (v == t) {
parent[v] = u;
return true;
}
queue.add(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// We didn't reach sink in BFS starting from source,
// so return false
return false;
}
// Returns the maximum flow from s to t in the given
// graph
int fordFulkerson(int graph[][], int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// Create a residual graph and fill the residual
// graph with given capacities in the original graph
// as residual capacities in residual graph
// Residual graph where rGraph[i][j] indicates
// residual capacity of edge from i to j (if there
// is an edge. If rGraph[i][j] is 0, then there is
// not)
int rGraph[][] = new int[V][V];
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
// This array is filled by BFS and to store path
int parent[] = new int[V];
int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
// Augment the flow while there is path from source
// to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent)) {
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edhes
// along the path filled by BFS. Or we can say
// find the maximum flow through the path found.
int path_flow = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
path_flow
= Math.min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and
// reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
}
// Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow;
}
// Return the overall flow
return max_flow;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
throws java.lang.Exception
{
// Let us create a graph shown in the above example
int graph[][] = new int[][] {
{ 0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0 }, { 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }
};
MaxFlow m = new MaxFlow();
System.out.println("The maximum possible flow is "
+ m.fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5));
}
} Python
# Python program for implementation
# of Ford Fulkerson algorithm
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency matrix representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, graph):
self.graph = graph # residual graph
self. ROW = len(graph)
# self.COL = len(gr[0])
'''Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink 't' in
residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path '''
def BFS(self, s, t, parent):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False]*(self.ROW)
# Create a queue for BFS
queue = []
# Mark the source node as visited and enqueue it
queue.append(s)
visited[s] = True
# Standard BFS Loop
while queue:
# Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
u = queue.pop(0)
# Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex u
# If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark it
# visited and enqueue it
for ind, val in enumerate(self.graph[u]):
if visited[ind] == False and val > 0:
# If we find a connection to the sink node,
# then there is no point in BFS anymore
# We just have to set its parent and can return true
queue.append(ind)
visited[ind] = True
parent[ind] = u
if ind == t:
return True
# We didn't reach sink in BFS starting
# from source, so return false
return False
# Returns the maximum flow from s to t in the given graph
def FordFulkerson(self, source, sink):
# This array is filled by BFS and to store path
parent = [-1]*(self.ROW)
max_flow = 0 # There is no flow initially
# Augment the flow while there is path from source to sink
while self.BFS(source, sink, parent) :
# Find minimum residual capacity of the edges along the
# path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the maximum flow
# through the path found.
path_flow = float("Inf")
s = sink
while(s != source):
path_flow = min (path_flow, self.graph[parent[s]][s])
s = parent[s]
# Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow
# update residual capacities of the edges and reverse edges
# along the path
v = sink
while(v != source):
u = parent[v]
self.graph[u][v] -= path_flow
self.graph[v][u] += path_flow
v = parent[v]
return max_flow
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
graph = [[0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0],
[0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0],
[0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20],
[0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
g = Graph(graph)
source = 0; sink = 5
print ("The maximum possible flow is %d " % g.FordFulkerson(source, sink))
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# program for implementation
// of Ford Fulkerson algorithm
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class MaxFlow {
static readonly int V = 6; // Number of vertices in
// graph
/* Returns true if there is a path
from source 's' to sink 't' in residual
graph. Also fills parent[] to store the
path */
bool bfs(int[, ] rGraph, int s, int t, int[] parent)
{
// Create a visited array and mark
// all vertices as not visited
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
visited[i] = false;
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark
// source vertex as visited
List queue = new List();
queue.Add(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (queue.Count != 0) {
int u = queue[0];
queue.RemoveAt(0);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
if (visited[v] == false
&& rGraph[u, v] > 0) {
// If we find a connection to the sink
// node, then there is no point in BFS
// anymore We just have to set its parent
// and can return true
if (v == t) {
parent[v] = u;
return true;
}
queue.Add(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// We didn't reach sink in BFS starting from source,
// so return false
return false;
}
// Returns the maximum flow
// from s to t in the given graph
int fordFulkerson(int[, ] graph, int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// Create a residual graph and fill
// the residual graph with given
// capacities in the original graph as
// residual capacities in residual graph
// Residual graph where rGraph[i,j]
// indicates residual capacity of
// edge from i to j (if there is an
// edge. If rGraph[i,j] is 0, then
// there is not)
int[, ] rGraph = new int[V, V];
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u, v] = graph[u, v];
// This array is filled by BFS and to store path
int[] parent = new int[V];
int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
// Augment the flow while there is path from source
// to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent)) {
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edhes
// along the path filled by BFS. Or we can say
// find the maximum flow through the path found.
int path_flow = int.MaxValue;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
path_flow
= Math.Min(path_flow, rGraph[u, v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and
// reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u, v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v, u] += path_flow;
}
// Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow;
}
// Return the overall flow
return max_flow;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// Let us create a graph shown in the above example
int[, ] graph = new int[, ] {
{ 0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0 }, { 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }
};
MaxFlow m = new MaxFlow();
Console.WriteLine("The maximum possible flow is "
+ m.fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5));
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */ Javascript
输出:
The maximum possible flow is 23 Ford Fulkerson 算法的上述实现称为Edmonds-Karp 算法。 Edmonds-Karp 的想法是在 Ford Fulkerson 实现中使用 BFS,因为 BFS 总是选择一条边数最少的路径。当使用 BFS 时,最坏情况的时间复杂度可以降低到 O(VE 2 )。上述实现使用邻接矩阵表示,尽管 BFS 需要 O(V 2 ) 时间,但上述实现的时间复杂度为 O(EV 3 )(有关时间复杂度的证明,请参阅 CLRS 书籍)
这是一个重要的问题,因为它出现在许多实际情况中。示例包括在给定的流量限制下最大化传输,最大化计算机网络中的数据包流。
Dinc 的 Max-Flow 算法。
锻炼:
修改上述实现,使其在 O(VE 2 ) 时间内运行。