Python中使用Turtle的Y分形树
分形是一种永无止境的模式。分形是无限复杂的模式,在不同的尺度上是自相似的。它们是通过在持续的反馈循环中一遍又一遍地重复一个简单的过程来创建的。在递归的驱动下,分形是动态系统的图像——混沌的图像。
在本文中,我们将使用Python中的递归技术绘制彩色 Y 分形树。
例子:
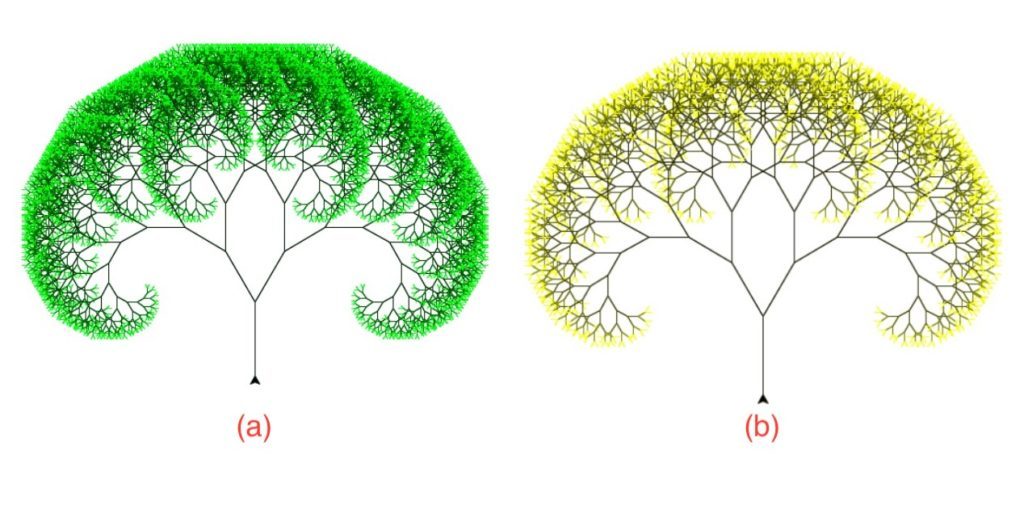
深度级别的输出:(a) 14 (b) 12
所需模块
turtle:海龟库使用户能够使用命令绘制图片或形状,为他们提供虚拟画布。 turtle带有 Python 的标准库。它需要一个支持Tk的Python版本,因为它使用tkinter进行图形处理。
使用的功能:
- fd(x) : 将光标向前绘制x 个像素。
- rt(x), lt(x) :将光标的朝向分别向右和向左旋转x度。
- colormode() :将颜色模式更改为 rgb。
- pencolor(r, g, b) : 设置海龟笔的颜色。
- speed() : 设置海龟的速度。
方法:
- 我们首先为基础(1 级)树绘制一个“Y”形。然后'Y'的两个分支都作为其他两个'Y'(2级)的基础。
- 这个过程递归地重复,并且 Y 的大小随着级别的增加而减小。
- 树的着色是按级别完成的:基础级别最暗,最顶层最亮。
在下面的实现中,我们将绘制一棵大小为80和级别为7的树。
from turtle import *
speed('fastest')
# turning the turtle to face upwards
rt(-90)
# the acute angle between
# the base and branch of the Y
angle = 30
# function to plot a Y
def y(sz, level):
if level > 0:
colormode(255)
# splitting the rgb range for green
# into equal intervals for each level
# setting the colour according
# to the current level
pencolor(0, 255//level, 0)
# drawing the base
fd(sz)
rt(angle)
# recursive call for
# the right subtree
y(0.8 * sz, level-1)
pencolor(0, 255//level, 0)
lt( 2 * angle )
# recursive call for
# the left subtree
y(0.8 * sz, level-1)
pencolor(0, 255//level, 0)
rt(angle)
fd(-sz)
# tree of size 80 and level 7
y(80, 7)
输出 :