条形磁铁作为等效螺线管
永磁体是条形磁体,但电磁体是螺线管,仅当通过它提供电流时才作为磁体工作。当条形磁铁被分成两半时,两个部分的行为就像具有相同磁特性的磁铁,然而,当螺线管被切成两半时,磁场较弱。
条形磁铁的磁极是固定的,但螺线管的磁极可以改变。条形磁铁的磁场强度保持不变,但螺线管的磁场强度取决于通过它的电流。
什么是磁性?
Magnetism is the property of a matter to get attracted or repelled from other matter. This property depends on the movement of electric charges.
实际上,电和磁是相互关联的。这就是为什么同时研究电场和磁场的物理学分支被称为电磁学。每种物质内部都有许多原子和许多电子。但最初,它是电中性的。当它被充电时,它会产生一个电场和相应的磁场。
存在的磁性类型有:
- 铁磁性
- 铁磁性
- 反铁磁性
- 顺磁性
- 抗磁性
- 超顺磁性
磁铁
Magnet is a material present in this world that gets attracted or repelled by other objects and it produces a magnetic field around it. There are two poles in magnet: North pole and South pole
- N – N = repels
- N – S = attracts
- S – N = attracts
- S – S = repels
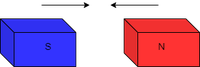
Attraction of magnets
磁铁总是以双极形式存在,这些极不能被隔离。如果我们试图通过将磁铁分成几块来隔离这些磁极,那么它就不会被隔离。事实上,现在每一块磁铁都有自己的北极和南极。
基本上有两种类型的磁铁:
- 永磁体:这些磁体具有内部结构,因此它们可以永久地获得磁性,这意味着磁场始终存在。例如条形磁铁
- 临时磁铁:这些磁铁只有在与某些永磁体或电流接触时才会暂时获得磁性。例如电磁铁
由于物质可以以任何状态存在,因此磁铁也可以处于不同的状态。例如
- 固态:钕磁铁,
- 液态:铁磁流体,和
- 气态:实际上在气态中看不到强磁性。在气态顺磁性材料中可以发现不是铁磁性材料。顺磁性气体的一个例子是氧气。
条形磁铁
A bar magnet is a cuboidal-shaped object which is made up of certain ferromagnetic materials. It has two poles in it one is the north pole and another is the south pole.
大多数时候,磁铁的北极的一半被涂成红色,而磁铁的其他部分被涂成蓝色,表现为南极。
用于制造条形磁铁的材料是铁、镍、钴或任何其他铁磁材料。条形磁铁有两个极:北极和南极。
- N – N = 排斥
- N – S = 吸引
- S – N = 吸引
- S – S = 排斥

简单的条形磁铁
Formula used for Bar Magnet-
Pole strength of the magnet is given by,
P = W / I
where
- W is work done by the magnet to move around the wire, and
- I is the current flowing through the wire.
The S.I. unit is N.Tesla-1.
例1:若磁铁绕导线做的功为30J,流经导线的电流为15A,求磁极强度。
解决方案:
We know that formula of pole strength is,
P = W/I
= 30 / 15
= 2 N.Tesla-1
条形磁铁的特性
- 条形磁铁产生磁场,磁力线从同一磁铁的一极到另一极。
- 当自由悬挂时,磁体的北方指向存在地球磁南的地球北极,而磁体的南指向存在磁北极的地球南极。
- 磁力线的密度在两极处最大,因此磁力在两极处更强。
- 条形磁铁产生的磁场线不相交。
条形磁铁的用途
- 大型条形磁铁可用于垃圾场对垃圾进行磁选。
- 条形磁铁在医疗领域具有治疗疾病的作用。
- 条形磁铁在实验室中用于各种目的。
- 条形磁铁可用于制作指南针以找到正确的方向。
电磁铁
The solenoid is a device that is made using a wire which is twisted around to make a coil of a certain number of rounds.
当电流流过螺线管时,它充当磁铁并在其周围产生磁场并获得磁性,但一旦电流停止,它就会失去磁性。所以,这是一个临时磁铁的例子。
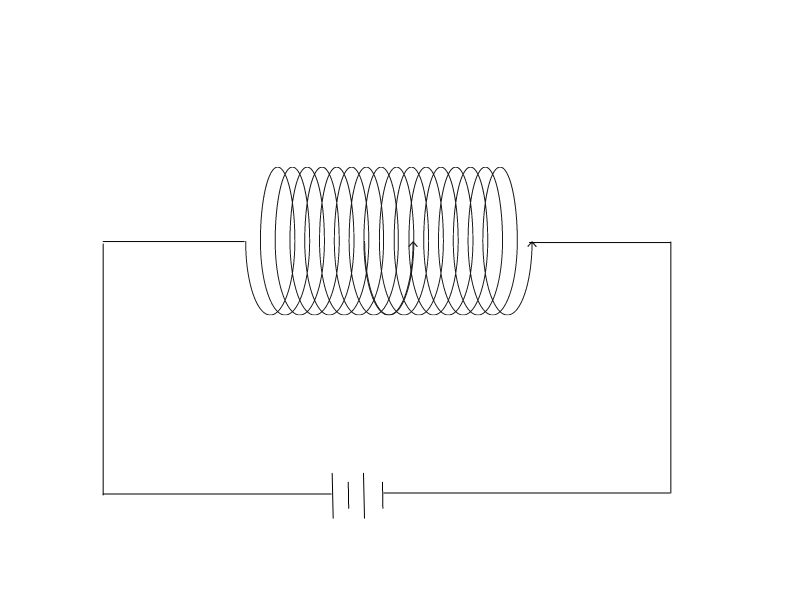
电磁铁
Formula for Magnetic field of a Solenoid-
The magnetic field of a solenoid is given by,
B = μo NI / l
where
- μo is magnetic constant equal to 4π × 10-7
- N is the number of rings in coil
- I is the current and
- l is the length of the solenoid
The S.I. unit of magnetic fields is Tesla.
示例 2:如果线圈的匝数为 200,电流为 1000 A,螺线管的长度为 3.14 m,则求螺线管的磁场。
解决方案:
We know that formula for finding magnetic field is B = μo NI / l
= 4π × 10-7 × 200 × 1000 / 3.14
= 4 × 10-7 × 2 × 105
= 8 × 10-2 T
电磁铁的特性:
- 当电流从“+”端流向“-”端时。螺线管开始表现为磁铁并开始吸引附近的磁性设备。
- 螺线管末端的磁力线密度最大,因此末端附近的磁性更强。
- 螺线管产生的磁场线不会相互切割。
电磁铁的用途:
- 它用于计算机硬盘驱动器中以存储内存
- 它用于制作电铃。
- 用于制造空调系统中使用的阀门
- 它用于制造MRI机器。
示例问题
问题1:定义磁铁和磁力。
回答:
Magnet is a material present in this world which gets attracted or repelled by other objects and it produces a magnetic field around it. There are two poles in magnet : North pole and South pole.
Magnetism is property of a matter to get attracted or repelled from other matter. This property depends on movement of electric charges.
问题 2:如果在电流为 20 A 的载流导体附近买了一个磁极强度为 5 的磁铁,请找出这样做的功。
回答:
We know that, P = W/I
W = P.I
= 20 × 5
= 100
So, the work done in moving magnet is 100 J.
问题 3:两个条形磁铁在四个不同位置的状态行为。
回答:
Two bar magnets can be placed in four different positions:
- North facing North
- North facing South
- South facing North
- South facing South
Their behaviour are as follows:
- N – N = repels
- N – S = attracts
- S – N = attracts
- S – S = repels
问题 4:求面积为 20 m 2的圆盘的磁通量,磁场为 5。给定圆盘面积矢量与磁场方向的夹角为 60度。
回答:
The formulae for magnetic field is , φ = B A cosθ
= 5 × 20 × cos60°
= 5 × 20 × 1/2
= 50 Maxwell
So, the magnetic flux of given disk is 50 Maxwell.
问题5:写出条形磁铁的用途。
回答:
Uses of bar magnet are as follows:
- Large Bar magnets can be used in garbage sites for doing magnetic separation of garbage.
- Bar magnets have scope in medical field in curing diseases.
- Bar magnets are used in laboratories for various purpose.
- Bar magnets can be used in making compass for finding correct directions.