我们强烈建议您参考以下帖子作为此操作的先决条件。
分界线|套装1(带0/1背包的简介)
我们讨论了解决上述问题的不同方法,并发现当项目权重不是整数时,Branch and Bound解决方案是最合适的方法。
在这篇文章中,讨论了针对0/1背包问题的Branch and Bound方法的实现。
如何找到0/1背包的每个节点的界限?
想法是利用贪婪方法为分数阶背包问题提供最佳解决方案的事实。
为了检查特定节点是否可以为我们提供更好的解决方案,我们使用贪婪方法(通过该节点)计算最佳解决方案。如果由Greedy方法计算的解决方案本身不仅仅是迄今为止最好的解决方案,那么我们将无法通过该节点获得更好的解决方案。
完整算法:
- 以单位重量的价值比率的降序对所有项目进行排序,以便可以使用贪婪方法计算上限。
- 初始化最大利润,maxProfit = 0
- 创建一个空队列,Q。
- 创建决策树的虚拟节点并将其排队到Q。虚拟节点的利润和权重为0。
- 在Q不为空时执行以下操作。
- 从Q中提取项目。让提取的项目为u。
- 计算下一级节点的利润。如果利润大于maxProfit,则更新maxProfit。
- 计算下一级节点的边界。如果bound大于maxProfit,则将下一级节点添加到Q。
- 考虑以下情况:不将下一个级别的节点视为解决方案的一部分,并添加一个要与下一个级别作为队列的节点,但是要增加权重和利润而不考虑下一个级别的节点。
插图:
输入://每对中的第一件事是商品的重量//第二件事是商品的价值arr [] = {{2,40},{3.14,50},{1.98,100},{5,95 },{3,30}};背包容量W = 10输出:最大可能的利润= 235下图显示了插图。物品被视为按价值/重量排序。 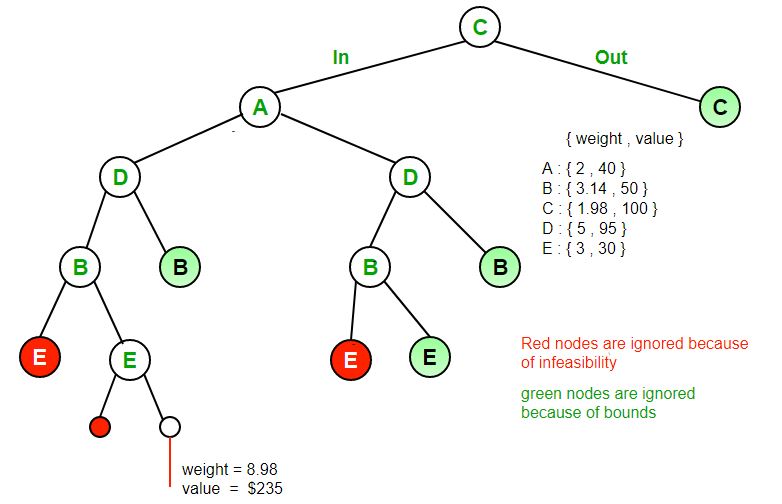 注意:由于图像中没有虚拟节点,因此图像不严格遵循算法/代码。
注意:由于图像中没有虚拟节点,因此图像不严格遵循算法/代码。
以下是上述想法的C++实现。
// C++ program to solve knapsack problem using
// branch and bound
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure for Item which store weight and corresponding
// value of Item
struct Item
{
float weight;
int value;
};
// Node structure to store information of decision
// tree
struct Node
{
// level --> Level of node in decision tree (or index
// in arr[]
// profit --> Profit of nodes on path from root to this
// node (including this node)
// bound ---> Upper bound of maximum profit in subtree
// of this node/
int level, profit, bound;
float weight;
};
// Comparison function to sort Item according to
// val/weight ratio
bool cmp(Item a, Item b)
{
double r1 = (double)a.value / a.weight;
double r2 = (double)b.value / b.weight;
return r1 > r2;
}
// Returns bound of profit in subtree rooted with u.
// This function mainly uses Greedy solution to find
// an upper bound on maximum profit.
int bound(Node u, int n, int W, Item arr[])
{
// if weight overcomes the knapsack capacity, return
// 0 as expected bound
if (u.weight >= W)
return 0;
// initialize bound on profit by current profit
int profit_bound = u.profit;
// start including items from index 1 more to current
// item index
int j = u.level + 1;
int totweight = u.weight;
// checking index condition and knapsack capacity
// condition
while ((j < n) && (totweight + arr[j].weight <= W))
{
totweight += arr[j].weight;
profit_bound += arr[j].value;
j++;
}
// If k is not n, include last item partially for
// upper bound on profit
if (j < n)
profit_bound += (W - totweight) * arr[j].value /
arr[j].weight;
return profit_bound;
}
// Returns maximum profit we can get with capacity W
int knapsack(int W, Item arr[], int n)
{
// sorting Item on basis of value per unit
// weight.
sort(arr, arr + n, cmp);
// make a queue for traversing the node
queue Q;
Node u, v;
// dummy node at starting
u.level = -1;
u.profit = u.weight = 0;
Q.push(u);
// One by one extract an item from decision tree
// compute profit of all children of extracted item
// and keep saving maxProfit
int maxProfit = 0;
while (!Q.empty())
{
// Dequeue a node
u = Q.front();
Q.pop();
// If it is starting node, assign level 0
if (u.level == -1)
v.level = 0;
// If there is nothing on next level
if (u.level == n-1)
continue;
// Else if not last node, then increment level,
// and compute profit of children nodes.
v.level = u.level + 1;
// Taking current level's item add current
// level's weight and value to node u's
// weight and value
v.weight = u.weight + arr[v.level].weight;
v.profit = u.profit + arr[v.level].value;
// If cumulated weight is less than W and
// profit is greater than previous profit,
// update maxprofit
if (v.weight <= W && v.profit > maxProfit)
maxProfit = v.profit;
// Get the upper bound on profit to decide
// whether to add v to Q or not.
v.bound = bound(v, n, W, arr);
// If bound value is greater than profit,
// then only push into queue for further
// consideration
if (v.bound > maxProfit)
Q.push(v);
// Do the same thing, but Without taking
// the item in knapsack
v.weight = u.weight;
v.profit = u.profit;
v.bound = bound(v, n, W, arr);
if (v.bound > maxProfit)
Q.push(v);
}
return maxProfit;
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int W = 10; // Weight of knapsack
Item arr[] = {{2, 40}, {3.14, 50}, {1.98, 100},
{5, 95}, {3, 30}};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Maximum possible profit = "
<< knapsack(W, arr, n);
return 0;
}
输出 :
Maximum possible profit = 235