使用 TensorBoard 可视化训练
在机器学习中,要改进某些东西,您通常需要能够衡量它。 TensorBoard 是一种工具,用于提供机器学习工作流程中所需的测量和可视化。它可以跟踪实验指标,如损失和准确性、可视化模型图、将 NLP 嵌入投影到低维空间等等。
TensorBoard 提供以下功能:
- 借助不同的图和直方图可视化不同的指标,例如损失、准确性。
- 借助图形可视化模型层和操作。
- 提供训练中涉及的权重和偏差的直方图。
- 显示训练数据(图像、音频和文本数据)。
TensorBoard 具有以下选项卡:
- 标量:此选项卡用于可视化标量指标,例如损失和准确性。
- Graph:可视化模型的计算图,例如以层和操作形式呈现的神经网络模型。
- 分布:可视化训练过程随时间的变化,例如权重/偏差变化。
- 直方图:以 3D 直方图的形式可视化上述分布。
- 投影仪:此选项卡用于可视化自然语言处理的词嵌入。
- 图像:此选项卡用于可视化训练/测试图像数据的内容。
- 音频:此选项卡用于可视化音频数据以用于音频处理等应用程序
- 文本:此选项卡用于可视化音频数据。
执行 :
- 加载 TensorBoard 扩展:
代码:
python3
# Install it using pip
!pip install -q tf-nightly-2.0-preview
# To load tensorflow extension
import tensorflow as tf
import datetime, os
# location of log directory
logs_base_dir = "./logs"
os.makedirs(logs_base_dir, exist_ok=True)
%tensorboard --logdir {logs_base_dir}python3
# Import necessary modules
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import io
# Copy previous logs if any
!rm -rf ./logs/
# Load datasets (Here,we use cifar 10
cifar_10 = tf.keras.datasets.cifar10
(x_train, y_train), (x_test,y_test) = cifar_10.load_data()
# List class Names
class_names =["airplane","automobile","bird","cat","deer",
"dog","frog","horse", "ship","truck"]
# Data Preprocessing
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')
x_train = x_train/255.0
x_test = x_test/255.0
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train)
y_test = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test)
# Creates a directory inside log/train_data folder
# In which we store training images
logdir = "logs/train_data/" + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
# Creates a file writer for the log directory.
file_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(logdir)
# write first 25 training images
with file_writer.as_default():
# Reshape the images because tf.summary expects a 4 dimensional matrices
# having (batch_size,height, width, color_channels)
images = np.reshape(x_train[0:25], (-1, 32, 32, 3))
tf.summary.image("Display training data", images, max_outputs=25, step=0)
# start TensorBoard and display those images (in images tab)
%tensorboard --logdir logs/train_datapython3
# remove old plots data (if any)
!rm -rf logs/plots
logdir = "logs/plots/" + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
file_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(logdir)
def plot_to_image(figure):
"""Converts the matplotlib plot to a PNG image and returns it.
The supplied figure is closed and inaccessible after this call."""
# Save the plot to a PNG in memory.
buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(buf, format='png')
# Closing the figure prevents it from being displayed directly inside
# the notebook.
plt.close(figure)
buf.seek(0)
# Convert PNG buffer to TF image
image = tf.image.decode_png(buf.getvalue(), channels=4)
# Add the batch dimension
print(image.shape)
image = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
return image
def image_grid():
"""Return a 5x5 grid of the training images as a matplotlib figure."""
# Create a figure to contain the plot.
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(25):
# create the next subplot with class name as its title
plt.subplot(5, 5, i + 1, title = class_names[np.int(np.where(y_train[i] ==1)[0])])
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(x_train[i])
return figure
# Prepare the plot
figure = image_grid()
# Convert to image and log
with file_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.image("Training data", plot_to_image(figure), step=0)
# start tensorboard and display plot
%tensorboard --logdir logs/plotspython3
# Define CNN model
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', input_shape=(32, 32, 3)),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
# Compile CNN model
model.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate= 0.01 , momentum=0.1),
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
# Print model summary()
model.summary()python3
# Code to plot confusion matrix
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, class_names):
"""
Returns a matplotlib figure containing the plotted confusion matrix.
Args:
cm (array, shape = [n, n]): a confusion matrix of integer classes
class_names (array, shape = [n]): String names of the integer classes
"""
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.title("Confusion matrix")
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(class_names))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, class_names, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, class_names)
# Normalize the confusion matrix.
cm = np.around(cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis], decimals=2)
# Use white text if squares are dark; otherwise black.
threshold = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
color = "white" if cm[i, j] > threshold else "black"
plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j], horizontalalignment="center", color=color)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
return figurepython3
logdir = "logs/image/" + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
# Define the basic TensorBoard callback.
tensorboard_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=logdir)
# Create file Writer for Confusion Metrics
file_writer_cm = tf.summary.create_file_writer(logdir + '/cm')python3
# sklearn confusion metrics
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import itertools
def log_confusion_matrix(epoch, logs):
# Use the model to predict the values from the validation dataset.
test_pred_raw = model.predict(x_test)
test_pred = np.argmax(test_pred_raw, axis=1)
y_test_cls = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
# Calculate the confusion matrix.
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test_cls, test_pred)
figure = plot_confusion_matrix(cm, class_names=class_names)
cm_image = plot_to_image(figure)
# Log the confusion matrix as an image summary.
with file_writer_cm.as_default():
tf.summary.image("Confusion Matrix", cm_image, step=epoch)
# Define the per-epoch callback to plot confusion metrics after each epoch.
cm_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.LambdaCallback(on_epoch_end=log_confusion_matrix)python3
%tensorboard --logdir logs/image
# Train the classifier.
model.fit(
x_train,
y_train,
epochs=20,
callbacks=[tensorboard_callback, cm_callback],
validation_data=(x_test, y_test)
)- 绘制训练图像:
代码:
蟒蛇3
# Import necessary modules
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import io
# Copy previous logs if any
!rm -rf ./logs/
# Load datasets (Here,we use cifar 10
cifar_10 = tf.keras.datasets.cifar10
(x_train, y_train), (x_test,y_test) = cifar_10.load_data()
# List class Names
class_names =["airplane","automobile","bird","cat","deer",
"dog","frog","horse", "ship","truck"]
# Data Preprocessing
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')
x_train = x_train/255.0
x_test = x_test/255.0
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train)
y_test = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test)
# Creates a directory inside log/train_data folder
# In which we store training images
logdir = "logs/train_data/" + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
# Creates a file writer for the log directory.
file_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(logdir)
# write first 25 training images
with file_writer.as_default():
# Reshape the images because tf.summary expects a 4 dimensional matrices
# having (batch_size,height, width, color_channels)
images = np.reshape(x_train[0:25], (-1, 32, 32, 3))
tf.summary.image("Display training data", images, max_outputs=25, step=0)
# start TensorBoard and display those images (in images tab)
%tensorboard --logdir logs/train_data
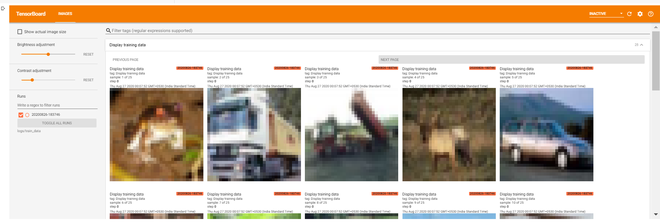
训练图像
- Plot Images Data Using Matplotlib:我们可以看到上面的训练图像不是很清晰。这是因为上述训练图像的大小为 (32, 32, 3),分辨率非常低。让我们在 matplotlib 中绘制一些图像。
代码:
蟒蛇3
# remove old plots data (if any)
!rm -rf logs/plots
logdir = "logs/plots/" + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
file_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(logdir)
def plot_to_image(figure):
"""Converts the matplotlib plot to a PNG image and returns it.
The supplied figure is closed and inaccessible after this call."""
# Save the plot to a PNG in memory.
buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(buf, format='png')
# Closing the figure prevents it from being displayed directly inside
# the notebook.
plt.close(figure)
buf.seek(0)
# Convert PNG buffer to TF image
image = tf.image.decode_png(buf.getvalue(), channels=4)
# Add the batch dimension
print(image.shape)
image = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
return image
def image_grid():
"""Return a 5x5 grid of the training images as a matplotlib figure."""
# Create a figure to contain the plot.
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(25):
# create the next subplot with class name as its title
plt.subplot(5, 5, i + 1, title = class_names[np.int(np.where(y_train[i] ==1)[0])])
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(x_train[i])
return figure
# Prepare the plot
figure = image_grid()
# Convert to image and log
with file_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.image("Training data", plot_to_image(figure), step=0)
# start tensorboard and display plot
%tensorboard --logdir logs/plots
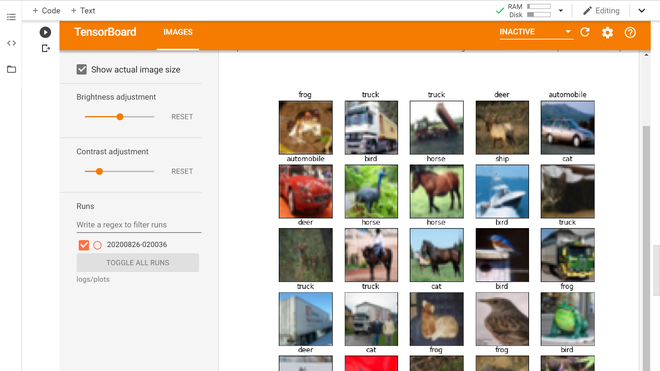
使用 matplotlib 训练图像
- 显示训练结果指标:在本节中,我们将在 TensorBoard 上绘制结果指标。我们将使用标量和图像选项卡来显示我们的结果。为此,我们将定义一个卷积神经网络模型并在 CIFAR 10 数据集上训练 20 个 epoch。
代码:
蟒蛇3
# Define CNN model
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', input_shape=(32, 32, 3)),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
# Compile CNN model
model.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate= 0.01 , momentum=0.1),
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
# Print model summary()
model.summary()
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 32) 896
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 32) 9248
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) (None, 16, 16, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout (Dropout) (None, 16, 16, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 64) 18496
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_3 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 64) 36928
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling2 (None, 8, 8, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 8, 8, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten (Flatten) (None, 4096) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 64) 262208
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 10) 650
=================================================================
Total params: 328,426
Trainable params: 328,426
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________- 现在,我们定义了使用测试数据绘制混淆矩阵的函数
代码:
蟒蛇3
# Code to plot confusion matrix
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, class_names):
"""
Returns a matplotlib figure containing the plotted confusion matrix.
Args:
cm (array, shape = [n, n]): a confusion matrix of integer classes
class_names (array, shape = [n]): String names of the integer classes
"""
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.title("Confusion matrix")
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(class_names))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, class_names, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, class_names)
# Normalize the confusion matrix.
cm = np.around(cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis], decimals=2)
# Use white text if squares are dark; otherwise black.
threshold = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
color = "white" if cm[i, j] > threshold else "black"
plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j], horizontalalignment="center", color=color)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
return figure
- 现在,我们定义 TensorBoard 回调来显示模型预测对测试数据的混淆矩阵。
代码:
蟒蛇3
logdir = "logs/image/" + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
# Define the basic TensorBoard callback.
tensorboard_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=logdir)
# Create file Writer for Confusion Metrics
file_writer_cm = tf.summary.create_file_writer(logdir + '/cm')
- 现在,我们定义了将混淆矩阵记录到 Tensorboard 中的函数。
代码:
蟒蛇3
# sklearn confusion metrics
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import itertools
def log_confusion_matrix(epoch, logs):
# Use the model to predict the values from the validation dataset.
test_pred_raw = model.predict(x_test)
test_pred = np.argmax(test_pred_raw, axis=1)
y_test_cls = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
# Calculate the confusion matrix.
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test_cls, test_pred)
figure = plot_confusion_matrix(cm, class_names=class_names)
cm_image = plot_to_image(figure)
# Log the confusion matrix as an image summary.
with file_writer_cm.as_default():
tf.summary.image("Confusion Matrix", cm_image, step=epoch)
# Define the per-epoch callback to plot confusion metrics after each epoch.
cm_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.LambdaCallback(on_epoch_end=log_confusion_matrix)
代码:
蟒蛇3
%tensorboard --logdir logs/image
# Train the classifier.
model.fit(
x_train,
y_train,
epochs=20,
callbacks=[tensorboard_callback, cm_callback],
validation_data=(x_test, y_test)
)
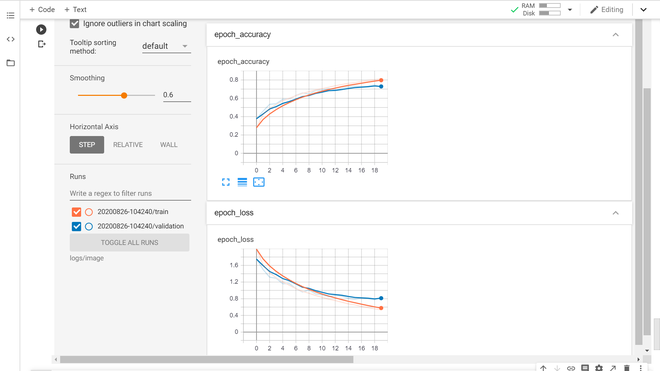
损失和准确度图(标量选项卡)
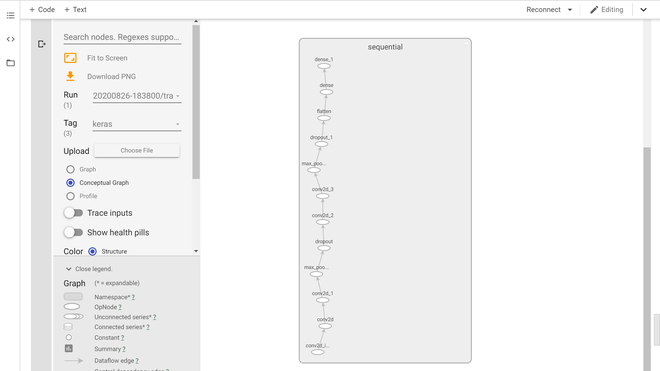
Keras 模型图(图形选项卡)
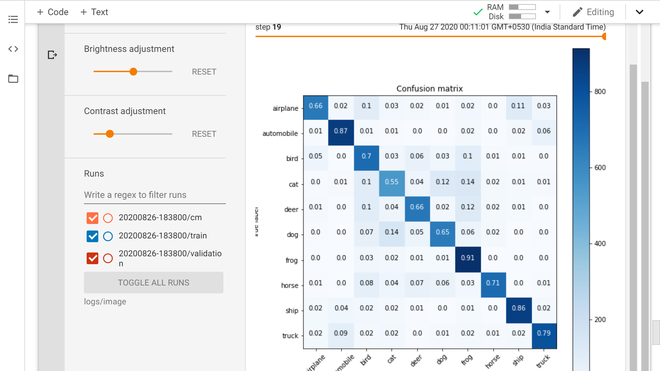
混淆矩阵(图像选项卡)
参考:
- TensorBoard 教程