给定完整的二叉树,任务是按有序方式查找镜像节点的总和,即找到左子树的有序遍历,并且对于遍历的每个节点,将其镜像节点的值添加到当前节点的值中。
例子:
Input: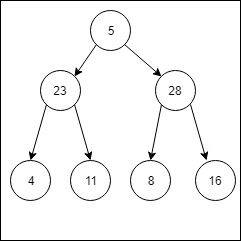
Output:
20
51
19
10
Inorder traversal of the left sub-tree of the given tree is 4 23 11 5.
Adding the mirror nodes,
4 + 16 = 20
23 + 28 = 51
11 + 8 = 19
5 + 5 = 10
方法:我们将使用2个指针来维护2个节点,它们是彼此的镜像。因此,让我们以root1和root2为2个镜像节点。现在,root1的左子级和root2的右子级将成为彼此的镜像。我们将传递这两个节点(root1-> left和root2-> right)进行下一个递归调用。由于我们必须以有序的方式遍历,因此一旦遍历了左子树,那么我们将打印当前的根数据,然后遍历右子树。类似地,对于右子树,root1的右子节点和root2的左子节点将是彼此的镜像。我们将传递这两个节点(root1-> right和root2-> left)以进行下一个递归调用。
下面是上述方法的实现
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
// struct to store data and links to
// its left and right child
int data;
struct node* l;
struct node* r;
node(int d)
{
// Initialize data for the current node
// with the passed value as d
data = d;
// Initialize left child to NULL
l = NULL;
// Initialize right child to NULL
r = NULL;
}
} Node;
// Function to print the required inorder traversal
void printInorder(Node* rootL, Node* rootR)
{
// We are using 2 pointers for the nodes
// which are mirror image of each other
// If both child are NULL return
if (rootL->l == NULL && rootR->r == NULL)
return;
// Since inorder traversal is required
// First left, then root and then right
printInorder(rootL->l, rootR->r);
cout << rootL->l->data + rootR->r->data << endl;
printInorder(rootL->r, rootR->l);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* root = new Node(5);
root->l = new Node(23);
root->r = new Node(28);
root->l->l = new Node(4);
root->l->r = new Node(11);
root->r->l = new Node(8);
root->r->r = new Node(16);
printInorder(root, root);
// Since root is mirror image of itself
if (root)
cout << root->data * 2 << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
// struct to store data and links to
// its left and right child
int data;
Node l;
Node r;
Node(int d)
{
// Initialize data for the current Node
// with the passed value as d
data = d;
// Initialize left child to null
l = null;
// Initialize right child to null
r = null;
}
}
// Function to print the required inorder traversal
static void printInorder(Node rootL, Node rootR)
{
// We are using 2 pointers for the Nodes
// which are mirror image of each other
// If both child are null return
if (rootL.l == null && rootR.r == null)
return;
// Since inorder traversal is required
// First left, then root and then right
printInorder(rootL.l, rootR.r);
System.out.println(rootL.l.data + rootR.r.data );
printInorder(rootL.r, rootR.l);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = new Node(5);
root.l = new Node(23);
root.r = new Node(28);
root.l.l = new Node(4);
root.l.r = new Node(11);
root.r.l = new Node(8);
root.r.r = new Node(16);
printInorder(root, root);
// Since root is mirror image of itself
if (root != null)
System.out.println(root.data * 2 );
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
class Node:
def __init__(self, d):
self.data = d
self.l = None
self.r = None
# Function to print the required inorder traversal
def printInorder(rootL, rootR):
# We are using 2 pointers for the nodes
# which are mirror image of each other
# If both child are None return
if rootL.l == None and rootR.r == None:
return
# Since inorder traversal is required
# First left, then root and then right
printInorder(rootL.l, rootR.r)
print(rootL.l.data + rootR.r.data)
printInorder(rootL.r, rootR.l)
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(5)
root.l = Node(23)
root.r = Node(28)
root.l.l = Node(4)
root.l.r = Node(11)
root.r.l = Node(8)
root.r.r = Node(16)
printInorder(root, root)
# Since root is mirror image of itself
if root:
print(root.data * 2)
# This code is contributed by Rituraj JainC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
public class Node
{
// struct to store data and links to
// its left and right child
public int data;
public Node l;
public Node r;
public Node(int d)
{
// Initialize data for the current Node
// with the passed value as d
data = d;
// Initialize left child to null
l = null;
// Initialize right child to null
r = null;
}
}
// Function to print the required inorder traversal
static void printInorder(Node rootL, Node rootR)
{
// We are using 2 pointers for the Nodes
// which are mirror image of each other
// If both child are null return
if (rootL.l == null && rootR.r == null)
return;
// Since inorder traversal is required
// First left, then root and then right
printInorder(rootL.l, rootR.r);
Console.WriteLine(rootL.l.data + rootR.r.data );
printInorder(rootL.r, rootR.l);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = new Node(5);
root.l = new Node(23);
root.r = new Node(28);
root.l.l = new Node(4);
root.l.r = new Node(11);
root.r.l = new Node(8);
root.r.r = new Node(16);
printInorder(root, root);
// Since root is mirror image of itself
if (root != null)
Console.WriteLine(root.data * 2 );
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu输出:
20
51
19
10