给定自然数n ,打印集合的所有子集![]() 不使用任何数组或循环(仅允许使用递归)。
不使用任何数组或循环(仅允许使用递归)。
例子:
Input : n = 4
Output : { 1 2 3 4 }
{ 1 2 3 }
{ 1 2 4 }
{ 1 2 }
{ 1 3 4 }
{ 1 3 }
{ 1 4 }
{ 1 }
{ 2 3 4 }
{ 2 3 }
{ 2 4 }
{ 2 }
{ 3 4 }
{ 3 }
{ 4 }
{ }
Input : n = 2
Output : { 1 2 }
{ 1 }
{ 2 }
{ }
方法:
- 从…开始
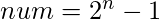 最高为0。
最高为0。 - 考虑具有n位的num的二进制表示形式。
- 从代表1的最左边的位开始,第二位代表2,依此类推,直到代表n的第n位。
- 打印与该位对应的数字(如果已设置)。
- 对num的所有值执行上述步骤,直到它等于0。
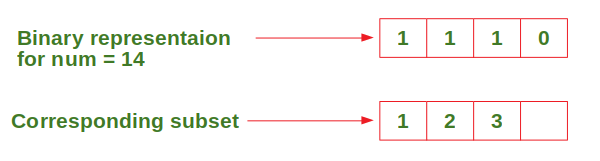
让我们通过一个例子来理解上述方法:
考虑输入n = 4,从![]() 。
。

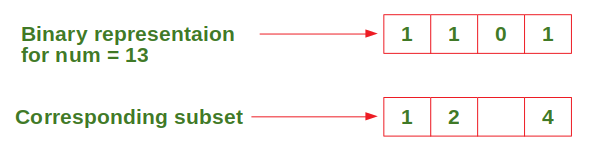
依此类推…直到num = 0。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ code to print all subsets
// of {1, 2, 3, n} without using
// array or loop, just recursion.
#include
using namespace std;
void subset(int, int, int);
// This recursive function calls subset
// function to print the subsets one by one.
// numBits --> number of bits needed to
// represent the number (simply input value n).
// num --> Initially equal to 2 ^ n - 1 and
// decreases by 1 every recursion until 0.
void printSubsets(int numOfBits, int num)
{
if (num >= 0)
{
cout << "{ ";
// Print the subset corresponding to
// binary representation of num.
subset(numOfBits - 1, num, numOfBits);
cout << "}" << endl;
// Call the function recursively to
// print the next subset.
printSubsets(numOfBits, num - 1);
}
else
return;
}
// This function recursively prints the
// subset corresponding to the binary
// representation of num.
// nthBit --> nth bit from right side
// starting from n and decreases until 0
void subset(int nthBit, int num, int numOfBits)
{
if (nthBit >= 0)
{
// Print number in given subset only
// if the bit corresponding to it
// is set in num.
if (num & (1 << nthBit))
{
cout << numOfBits - nthBit << " ";
}
// Check for the next bit
subset(nthBit - 1, num, numOfBits);
}
else
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 4;
printSubsets(n, pow(2, n) - 1);
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Java
// Java code to print all subsets
// of {1, 2, 3, n} without using
// array or loop, just recursion.
class GfG
{
// This recursive function calls subset
// function to print the subsets one by one.
// numBits --> number of bits needed to
// represent the number (simply input value n).
// num --> Initially equal to 2 ^ n - 1 and
// decreases by 1 every recursion until 0.
static void printSubSets(int numOfBits, int num)
{
if (num >= 0)
{
System.out.print("{ ");
// Print the subset corresponding to
// binary representation of num.
subset(numOfBits - 1, num, numOfBits);
System.out.println("}");
// Call the function recursively to
// print the next subset.
printSubSets(numOfBits, num - 1);
} else
return;
}
// This function recursively prints the
// subset corresponding to the binary
// representation of num.
// nthBit --> nth bit from right side
// starting from n and decreases until 0.
static void subset(int nthBit, int num, int numOfBits)
{
if (nthBit >= 0)
{
// Print number in given subset only
// if the bit corresponding to it
// is set in num.
if ((num & (1 << nthBit)) != 0)
{
System.out.print(numOfBits - nthBit + " ");
}
// Check for the next bit
subset(nthBit - 1, num, numOfBits);
} else
return;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
printSubSets(n, (int) (Math.pow(2, n)) -1);
}
}
// This code is contributed by laststringxPython3
# Python3 code to print all subsets
# of {1, 2, 3, …n} without using
# array or loop, just recursion.
# This recursive function calls subset
# function to print the subsets one by one.
# numBits --> number of bits needed to
# represent the number (simply input value n).
# num --> Initially equal to 2 ^ n - 1 and
# decreases by 1 every recursion until 0.
def printSubsets(numOfBits, num):
if num >= 0:
print("{", end = " ")
# Print the subset corresponding to
# binary representation of num.
subset(numOfBits-1, num, numOfBits)
print("}")
# Call the function recursively to
# print the next subset.
printSubsets(numOfBits, num-1)
else:
return
# This function recursively prints the
# subset corresponding to the binary
# representation of num.
# nthBit --> nth bit from right side
# starting from n and decreases until 0.
def subset(nthBit, num, numOfBits):
if nthBit >= 0:
# Print number in given subset only
# if the bit corresponding to it
# is set in num.
if num & (1 << nthBit) != 0:
print(numOfBits - nthBit, end = " ")
# Check for the next bit
subset(nthBit-1, num, numOfBits)
else:
return
# Driver Code
n = 4
printSubsets(n, 2**n - 1)C#
// C# code to print all subsets
// of {1, 2, 3, n} without using
// array or loop, just recursion.
using System;
class GfG
{
// This recursive function calls subset
// function to print the subsets one by one.
// numBits --> number of bits needed to
// represent the number (simply input value n).
// num --> Initially equal to 2 ^ n - 1 and
// decreases by 1 every recursion until 0.
static void printSubSets(int numOfBits, int num)
{
if (num >= 0)
{
Console.Write("{ ");
// Print the subset corresponding to
// binary representation of num.
subset(numOfBits - 1, num, numOfBits);
Console.WriteLine("}");
// Call the function recursively to
// print the next subset.
printSubSets(numOfBits, num - 1);
} else
return;
}
// This function recursively prints the
// subset corresponding to the binary
// representation of num.
// nthBit --> nth bit from right side
// starting from n and decreases until 0.
static void subset(int nthBit, int num, int numOfBits)
{
if (nthBit >= 0)
{
// Print number in given subset only
// if the bit corresponding to it
// is set in num.
if ((num & (1 << nthBit)) != 0)
{
Console.Write(numOfBits - nthBit + " ");
}
// Check for the next bit
subset(nthBit - 1, num, numOfBits);
} else
return;
}
// Driver codeM
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
printSubSets(n, (int) (Math.Pow(2, n)) -1);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Srathore输出:
{ 1 2 3 4 }
{ 1 2 3 }
{ 1 2 4 }
{ 1 2 }
{ 1 3 4 }
{ 1 3 }
{ 1 4 }
{ 1 }
{ 2 3 4 }
{ 2 3 }
{ 2 4 }
{ 2 }
{ 3 4 }
{ 3 }
{ 4 }
{ }
时间复杂度: ![]()