给定两个点A(x1,y1)和B(x2,y2)的坐标。查找在像素计算机屏幕上绘制线AB所需的所有中间点的任务。请注意,每个像素都有整数坐标。
例子:
Input : A(0,0), B(4,4)
Output : (0,0), (1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (4,4)
Input : A(0,0), B(4,2)
Output : (0,0), (1,0), (2,1), (3,1), (4,2)以下是使算法保持简单的一些假设。
- 我们从左到右画线。
- x1
- 该线的斜率在0到1之间。我们从左下到右上画一条线。
让我们通过首先考虑幼稚的方式来了解该过程。
// A naive way of drawing line
void naiveDrawLine(x1, x2, y1, y2)
{
m = (y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1)
for (x = x1; x <= x2; x++)
{
// Assuming that the round function finds
// closest integer to a given float.
y = round(mx + c);
print(x, y);
}
}上面的算法有效,但是速度很慢。 Bresenham算法的思想是避免浮点乘法和加法来计算mx + c,然后在每一步中计算(mx + c)的舍入值。在布雷森纳姆(Bresenham)的算法中,我们以单位间隔在x轴上移动。
- 我们总是将x加1,然后选择下一个y,无论我们需要y + 1还是保留在y上。换句话说,从任何位置(X k ,Y k ),我们都需要在(X k + 1,Y k )和(X k + 1,Y k + 1)之间进行选择。
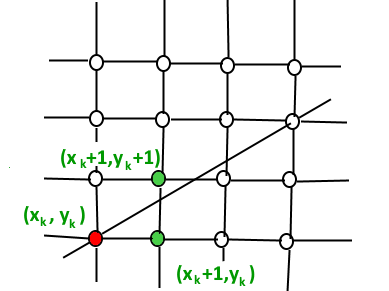
- 我们想选择与更接近原始线的点相对应的y值(在Y k +1和Y k中)。
我们需要一个决策参数来决定是选择Y k +1还是选择Y k作为下一个点。这个想法是要跟踪从先前的增量到y的斜率误差。如果斜率误差变得大于0.5,我们知道线已经向上移动了一个像素,并且我们必须增加y坐标并重新调整误差以表示距新像素顶部的距离-这是通过减去1来完成的。从错误。
// Modifying the naive way to use a parameter
// to decide next y.
void withDecisionParameter(x1, x2, y1, y2)
{
m = (y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1)
slope_error = [Some Initial Value]
for (x = x1, y = y1; x = 0.5)
{
y++;
slope_error -= 1.0;
}
}如何避免浮点运算
上述算法仍然包括浮点算法。为避免浮点运算,请考虑低于值m的值。
m =(y2 – y1)/(x2 – x1)
我们将两边都乘以(x2 – x1)
我们还将“ slope_error”更改为“ slope_error *(x2 – x1)”。为了避免与0.5进行比较,我们将其进一步更改为lope_error *(x2 – x1)* 2。
同样,通常最好将0与1进行比较。
// Modifying the above algorithm to avoid floating
// point arithmetic and use comparison with 0.
void bresenham(x1, x2, y1, y2)
{
m_new = 2 * (y2 - y1)
slope_error_new = [Some Initial Value]
for (x = x1, y = y1; x = 0)
{
y++;
slope_error_new -= 2 * (x2 - x1);
}
} lope_error_new的初始值为2 *(y2 – y1)–(x2 – x1)。请参考此值的证明
下面是上述算法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for Bresenham’s Line Generation
// Assumptions :
// 1) Line is drawn from left to right.
// 2) x1 < x2 and y1 < y2
// 3) Slope of the line is between 0 and 1.
// We draw a line from lower left to upper
// right.
#include
using namespace std;
// function for line generation
void bresenham(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
int m_new = 2 * (y2 - y1);
int slope_error_new = m_new - (x2 - x1);
for (int x = x1, y = y1; x <= x2; x++)
{
cout << "(" << x << "," << y << ")\n";
// Add slope to increment angle formed
slope_error_new += m_new;
// Slope error reached limit, time to
// increment y and update slope error.
if (slope_error_new >= 0)
{
y++;
slope_error_new -= 2 * (x2 - x1);
}
}
}
// driver function
int main()
{
int x1 = 3, y1 = 2, x2 = 15, y2 = 5;
bresenham(x1, y1, x2, y2);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for Bresenhams Line Generation
// Assumptions :
// 1) Line is drawn from left to right.
// 2) x1 < x2 and y1 < y2
// 3) Slope of the line is between 0 and 1.
// We draw a line from lower left to upper
// right.
class GFG
{
// function for line generation
static void bresenham(int x1, int y1, int x2,
int y2)
{
int m_new = 2 * (y2 - y1);
int slope_error_new = m_new - (x2 - x1);
for (int x = x1, y = y1; x <= x2; x++)
{
System.out.print("(" +x + "," + y + ")\n");
// Add slope to increment angle formed
slope_error_new += m_new;
// Slope error reached limit, time to
// increment y and update slope error.
if (slope_error_new >= 0)
{
y++;
slope_error_new -= 2 * (x2 - x1);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int x1 = 3, y1 = 2, x2 = 15, y2 = 5;
bresenham(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.Python3
# Python 3 program for Bresenham’s Line Generation
# Assumptions :
# 1) Line is drawn from left to right.
# 2) x1 < x2 and y1 < y2
# 3) Slope of the line is between 0 and 1.
# We draw a line from lower left to upper
# right.
# function for line generation
def bresenham(x1,y1,x2, y2):
m_new = 2 * (y2 - y1)
slope_error_new = m_new - (x2 - x1)
y=y1
for x in range(x1,x2+1):
print("(",x ,",",y ,")\n")
# Add slope to increment angle formed
slope_error_new =slope_error_new + m_new
# Slope error reached limit, time to
# increment y and update slope error.
if (slope_error_new >= 0):
y=y+1
slope_error_new =slope_error_new - 2 * (x2 - x1)
# driver function
if __name__=='__main__':
x1 = 3
y1 = 2
x2 = 15
y2 = 5
bresenham(x1, y1, x2, y2)
#This code is contributed by ash264C#
// C# program for Bresenhams Line Generation
// Assumptions :
// 1) Line is drawn from left to right.
// 2) x1 < x2 and y1< y2
// 3) Slope of the line is between 0 and 1.
// We draw a line from lower left to upper
// right.
using System;
class GFG {
// function for line generation
static void bresenham(int x1, int y1, int x2,
int y2)
{
int m_new = 2 * (y2 - y1);
int slope_error_new = m_new - (x2 - x1);
for (int x = x1, y = y1; x <= x2; x++)
{
Console.Write("(" + x + "," + y + ")\n");
// Add slope to increment angle formed
slope_error_new += m_new;
// Slope error reached limit, time to
// increment y and update slope error.
if (slope_error_new >= 0)
{
y++;
slope_error_new -= 2 * (x2 - x1);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main ()
{
int x1 = 3, y1 = 2, x2 = 15, y2 = 5;
bresenham(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.PHP
= 0)
{
$y++;
$slope_error_new -= 2 * ($x2 - $x1);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
$x1 = 3; $y1 = 2; $x2 = 15; $y2 = 5;
bresenham($x1, $y1, $x2, $y2);
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
?>Javascript
输出 :
(3,2)
(4,3)
(5,3)
(6,3)
(7,3)
(8,4)
(9,4)
(10,4)
(11,4)
(12,5)
(13,5)
(14,5)
(15,5) 上面的解释是为了在算法后面提供一个粗略的想法。有关详细说明和证明,读者可以参考以下参考资料。
相关文章:
- 中点线生成算法
- DDA线描算法