Waves 简介 – 定义、类型、属性
波是物理、数学和相关学科中一个或多个量的传播动态扰动(从平衡变化),通常用波动方程来描述。波介质中至少有两个场量涉及物理波。当变量以特定频率围绕平衡(静止)值周期性振荡时,就会出现周期性波。当整个波形向一个方向移动时,就会出现行波;当两个叠加的周期性波沿相反方向移动时,就会出现驻波。当波幅似乎减小甚至为零时,驻波中的振动幅度在某些点处为零。
海浪
波是介质中的一种扰动,它在不引起净粒子运动的情况下传输能量。弹性变形、压力变化、电或磁强度、电势或温度变化都是示例。
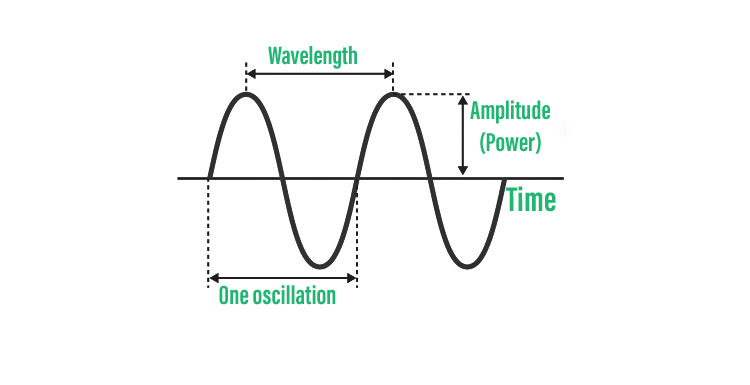
波浪的图形表示。
波浪的特征
波浪包括以下特征:
- 被波穿过的介质粒子仅在它们的平均位置附近轻微振动,但它们不会在波的传播方向上永久移位。
- 沿着或垂直于波的行进线,介质的每个后续粒子都执行与其前身完全相同的运动。
- 在波动过程中,只有能量被传递,而不是介质的一部分。
波浪的类型
这里列出了几种形式的波浪:
1.横波:
介质与波的方向成一定角度移动的波。
Examples of transverse waves:
- Water waves (ripples of gravity waves, not sound through water)
- Light waves
- S-wave earthquake waves
- Stringed instruments
- Torsion wave
波峰是横波的最高点。这是底部的一个低谷。
2.纵波:
纵波中粒子在介质中的运动与波的运动方向在同一维度上。
Examples of longitudinal waves:
- Sound waves
- P-type earthquake waves
- Compression wave
部分纵波:
- 压缩——在这种情况下,粒子是靠得很近的。
- 稀薄——颗粒分散的地方
3. 电磁波:
这些是在不使用物质介质的情况下产生和传播的波,即它们可以穿过真空和任何其他物质介质。
Examples of electromagnetic waves:
- visible light
- ultra-violet light
- radio waves
- microwaves
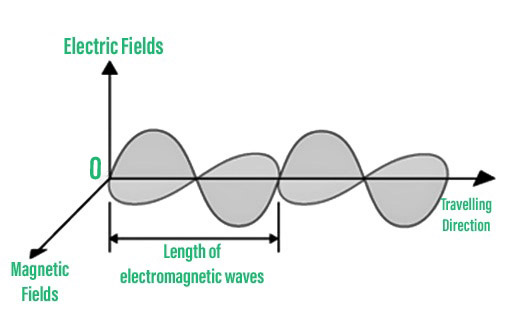
电磁波。
4.机械波:
只有物质介质才能产生或传播机械波。牛顿运动方程适用于这些波。
Examples of mechanical waves:
- waves on water surface
- waves on strings
- sound waves
机械波有两种类型:
- 横波运动——介质的粒子在横波中与波的传播方向成直角振动。横波包括字符串、地表水波和电磁波。在电磁波(包括光波)中传播的干扰是由与波的传播方向成直角的电场和磁场的振荡引起的。
- 纵向波动——介质中的粒子在这些波中沿着能量传播方向围绕它们的平均位置来回振动。它们也被称为压力波。纵向机械波就是声波。
5.物质波:
这些波与物质粒子的运动有关。
Examples of matter waves:
- electrons
- protons
- neutrons
波速公式
It’s the entire distance a wave travels in a particular amount of time. The formula for calculating wave speed is as follows:
Wave Speed = Distance Covered/Time taken
波浪的性质
以下是波浪的主要特征:
- 振幅——波是能量传输的一种形式。波的振幅是它的高度,通常以米为单位。它与波传输的能量成正比。
- 波长——波长是波峰相邻周期中相同位置之间的距离。此外,它以米为单位。
- 周期——波的周期是介质上的一个粒子完成一个完整的振动周期所花费的时间。因为周期是时间单位,所以以秒或分钟为单位。
- 频率 -在一定时间内通过一个点的波数称为波的频率。赫兹 (Hz) 频率单位每秒测量一个波。
The frequency’s reciprocal is the period, and vice versa.
Period=1 / Frequency
OR
Frequency = 1 / Period
- 速度 -物体的速度是指它移动的速度,通常表示为行进的距离除以行进所需的时间。在给定的时间内,波上特定点(波峰)行进的距离称为波速。因此,波的速度以米每秒或 m/s 为单位测量。
示例问题
问题 1:在特定介质中,波以每秒 900 米的速度传播。如果 3000 波在 2 分钟内通过,计算介质中特定点的波长。
解决方案:
The speed of a wave in medium v = 900 ms-1
Freq. of wave = no. of waves passing per sec (n) = 3000 waves/2 min = 3000 / 2 × 60 = 25 s
Wave length (λ) = ?
v = n × (λ)
λ = v/n
= 900/25
= 36 m
问题2:我们国家动物的吼声和蚊子的吼声有什么区别?
解决方案:
The buzzing of a mosquito creates a sound of high pitch and low intensity or loudness, but the roaring of a national animal (tiger) produces a sound of low pitch and high intensity or loudness.
问题 3:是否可以判断维护在水龙头下的容器何时会溢出?
解决方案:
The length of an air column is inversely related to the frequency of the note it produces. The length of the air column above the vessel reduces as the level of water in the vessel rises. It generates a sound with a decreasing frequency, i.e. the sound gets shorter. It is possible to determine whether the vessel is filled with water based on the shrillness of the sound.
问题 4:海中的船底将 SONAR 波直接射入海水中。 3.5 秒后,信号从深底基岩反射并返回到船上。当船到达 100 km 时,它会发射另一个信号,该信号在 2 s 后被接收。计算每个示例中的海深,以及两者之间的高度差。
解决方案:
Velocity of SONAR waves in water C = 1500 ms-1
Time taken by be wave after reflection from the bottom of sea
2t = 3.5s
t =1.75s
Distance covered (d) = ?
C = d/t => d = c.t = 1500 × 1.75 – 2625 m
After moving 100km
The time taken by the wave = 2t = 2s
T = 2/2 = 1s
d =?
d = 1500 × l
= 1500
The different between these two heights = 2625 – 1500
= 1125m
问题 5:为什么在空房间里的声音比在有家具和其他物品的房间里响亮?
解决方案:
Sound is an energy form. The majority of the energy is absorbed by the furniture that acts as an obstruction. As a result, the strength of sound decreases, yet in an empty room, the intensity of sound remains relatively constant due to the absence of impediments, and we perceive it as louder.