给定一棵树,以及所有节点的权重(以字符串的形式),任务是对那些节点的权重字符串与子树节点的字符串连接在一起时的节点进行统计。
Pangram: Pangram是包含英文字母的每个字母的句子。
例子:
Input:
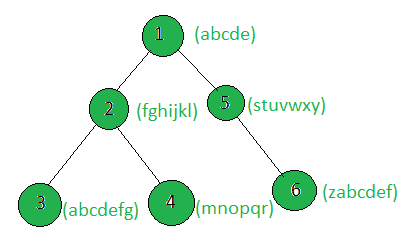
Output: 1
Only the weighted string of sub-tree of node 1 makes the pangram.
方法:在树上执行dfs并更新每个节点的权重,以便它存储其权重与子树节点的权重关联。然后,计算其更新后的加权字符串构成一个聚合图的节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
vector graph[100];
vector weight(100);
// Function that returns if the
// string x is a pangram
bool Pangram(string x)
{
map mp;
int n = x.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
mp[x[i]]++;
if (mp.size() == 26)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Function to return the count of nodes
// which make pangram with the
// sub-tree nodes
int countTotalPangram(int n)
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (Pangram(weight[i]))
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
// Function to perform dfs and update the nodes
// such that weight[i] will store the weight[i]
// concatenated with the weights of
// all the nodes in the sub-tree
void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
weight[node] += weight[to];
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 6;
// Weights of the nodes
weight[1] = "abcde";
weight[2] = "fghijkl";
weight[3] = "abcdefg";
weight[4] = "mnopqr";
weight[5] = "stuvwxy";
weight[6] = "zabcdef";
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(4);
graph[1].push_back(5);
graph[5].push_back(6);
dfs(1, 1);
cout << countTotalPangram(n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector []graph = new Vector[100];
static String []weight = new String[100];
// Function that returns if the
// String x is a pangram
static boolean Pangram(String x)
{
HashMap mp = new HashMap<>();
int n = x.length();
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++)
{
if (mp.containsKey(x.charAt(i)))
{
mp.put(x.charAt(i),
mp.get(x.charAt(i)) + 1);
}
else
{
mp.put(x.charAt(i), 1);
}
}
if (mp.size() == 26)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Function to return the count of nodes
// which make pangram with the
// sub-tree nodes
static int countTotalPangram(int n)
{
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (Pangram(weight[i]))
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
// Function to perform dfs and update the nodes
// such that weight[i] will store the weight[i]
// concatenated with the weights of
// all the nodes in the sub-tree
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
for(int to : graph[node])
{
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
weight[node] += weight[to];
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 6;
// Weights of the nodes
weight[1] = "abcde";
weight[2] = "fghijkl";
weight[3] = "abcdefg";
weight[4] = "mnopqr";
weight[5] = "stuvwxy";
weight[6] = "zabcdef";
for(int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector();
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].add(2);
graph[2].add(3);
graph[2].add(4);
graph[1].add(5);
graph[5].add(6);
dfs(1, 1);
System.out.print(countTotalPangram(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
graph = [[] for i in range(100)]
weight = [0] * 100
# Function that returns if the
# string x is a pangram
def Pangram(x):
mp = {}
n = len(x)
for i in range(n):
if x[i] not in mp:
mp[x[i]] = 0
mp[x[i]] += 1
if (len(mp)== 26):
return True
else:
return False
# Function to return the count of nodes
# which make pangram with the
# sub-tree nodes
def countTotalPangram(n):
cnt = 0
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if (Pangram(weight[i])):
cnt += 1
return cnt
# Function to perform dfs and update the nodes
# such that weight[i] will store the weight[i]
# concatenated with the weights of
# all the nodes in the sub-tree
def dfs(node, parent):
for to in graph[node]:
if (to == parent):
continue
dfs(to, node)
weight[node] += weight[to]
# Driver code
n = 6
# Weights of the nodes
weight[1] = "abcde"
weight[2] = "fghijkl"
weight[3] = "abcdefg"
weight[4] = "mnopqr"
weight[5] = "stuvwxy"
weight[6] = "zabcdef"
# Edges of the tree
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(3)
graph[2].append(4)
graph[1].append(5)
graph[5].append(6)
dfs(1, 1)
print(countTotalPangram(n))
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10C#
// C# implementation of
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static List []graph =
new List[100];
static String []weight =
new String[100];
// Function that returns if the
// String x is a pangram
static bool Pangram(String x)
{
Dictionary mp = new Dictionary();
int n = x.Length;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++)
{
if (mp.ContainsKey(x[i]))
{
mp[x[i]] = mp[x[i]] + 1;
}
else
{
mp.Add(x[i], 1);
}
}
if (mp.Count == 26)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Function to return the
// count of nodes which
// make pangram with the
// sub-tree nodes
static int countTotalPangram(int n)
{
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (Pangram(weight[i]))
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
// Function to perform dfs and
// update the nodes such that
// weight[i] will store the weight[i]
// concatenated with the weights of
// all the nodes in the sub-tree
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
foreach(int to in graph[node])
{
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
weight[node] += weight[to];
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 6;
// Weights of the nodes
weight[1] = "abcde";
weight[2] = "fghijkl";
weight[3] = "abcdefg";
weight[4] = "mnopqr";
weight[5] = "stuvwxy";
weight[6] = "zabcdef";
for(int i = 0;
i < graph.Length; i++)
graph[i] = new List();
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(3);
graph[2].Add(4);
graph[1].Add(5);
graph[5].Add(6);
dfs(1, 1);
Console.Write(countTotalPangram(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput 输出:
1
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(N * S)。
在dfs中,树的每个节点都处理一次,因此,如果树中总共有N个节点,则由于dfs而导致的复杂度为O(N)。同样,为了处理每个节点,将Pangram()函数用于复杂度为O(S)的每个节点,其中S是子树中所有权重字符串的长度之和,并且由于对每个节点都执行了此操作,因此这部分的总时间复杂度变为O(N * S)。因此,最终时间复杂度为O(N * S)。 - 辅助空间: O(1)。
不需要任何额外的空间,因此空间复杂度是恒定的。