学习一规则算法
先决条件:基于规则的分类器
学习一个规则:
这种方法在顺序学习算法中用于学习规则。它返回一个包含至少一些示例的规则(如图 1 所示)。然而,真正强大的是它能够在给定的属性之间创建关系,从而覆盖更大的假设空间。
For example:
IF Mother(y, x) and Female(y), THEN Daughter(x, y).
Here, any person can be associated with the variables x and y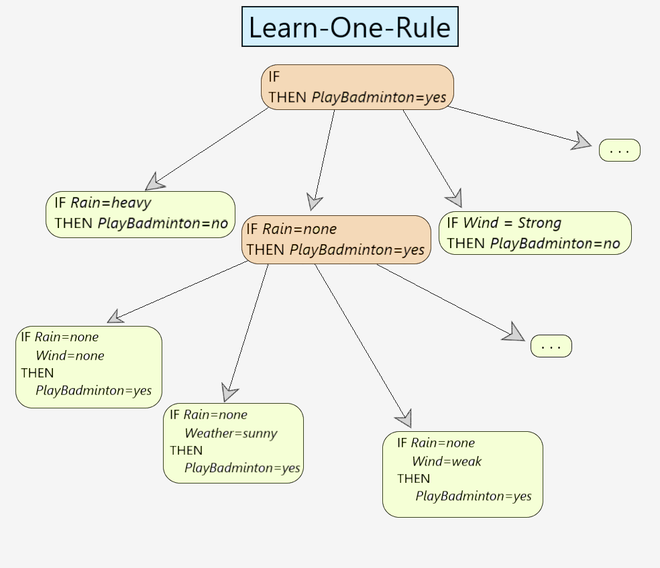
图 1:Learn-One-Rule 示例
学习一规则算法
Learn-One-Rule 算法遵循贪婪搜索范式,它以高精度搜索规则,但其覆盖率非常低。它对特定实例的所有正例进行分类。它返回一个涵盖一些示例的规则。
Learn-One-Rule(target_attribute, attributes, examples, k):
Pos = positive examples
Neg = negative examples
best-hypothesis = the most general hypothesis
candidate-hypothesis = {best-hypothesis}
while candidate-hypothesis:
//Generate the next more specific candidate-hypothesis
constraints_list = all constraints in the form "attribute=value"
new-candidate-hypothesis = all specializations of candidate-
hypothesis by adding all-constraints
remove all duplicates/inconsistent hypothesis from new-candidate-hypothesis.
//Update best-hypothesis
best_hypothesis = argmax(h∈CHs) Performance(h,examples,target_attribute)
//Update candidate-hypothesis
candidate-hypothesis = the k best from new-candidate-hypothesis
according to Performance.
prediction = most frequent value of target_attribute from examples that match best-hypothesis
IF best_hypothesis:
return prediction 它涉及计算每个候选假设的性能的 PERFORMANCE 方法。 (即假设与训练数据中的给定示例集的匹配程度。
Performance(NewRule,h):
h-examples = the set of rules that match h
return (h-examples)它从最通用的规则前提条件开始,然后贪婪地添加最能提高训练示例性能的变量。
学习一个规则示例
让我们通过一个例子来理解算法的工作: Day Weather Temp Wind Rain PlayBadminton D1 Sunny Hot Weak Heavy No D2 Sunny Hot Strong Heavy No D3 Overcast Hot Weak Heavy No D4 Snowy Cold Weak Light Yes D5 Snowy Cold Weak Light Yes D6 Snowy Cold Strong Light Yes D7 Overcast Mild Strong Heavy No D8 Sunny Hot Weak Light Yes
Step 1 - best_hypothesis = IF h THEN PlayBadminton(x) = Yes
Step 2 - candidate-hypothesis = {best-hypothesis}
Step 3 - constraints_list = {Weather(x)=Sunny, Temp(x)=Hot, Wind(x)=Weak, ......}
Step 4 - new-candidate-hypothesis = {IF Weather=Sunny THEN PlayBadminton=YES,
IF Weather=Overcast THEN PlayBadminton=YES, ...}
Step 5 - best-hypothesis = IF Weather=Sunny THEN PlayBadminton=YES
Step 6 - candidate-hypothesis = {IF Weather=Sunny THEN PlayBadminton=YES,
IF Weather=Sunny THEN PlayBadminton=YES...}
Step 7 - Go to Step 2 and keep doing it till the best-hypothesis is obtained.You can refer to Fig 1. for a better understanding of how the best-hypothesis is obtained. [Step 5 & 6]
Sequential Learning Algorithm 使用该算法,对其进行改进并增加假设空间的覆盖范围。可以修改它以接受指定感兴趣的目标值的参数。