基于规则的分类器——机器学习
基于规则的分类器只是另一种类型的分类器,它通过使用各种“if..else”规则来做出类决策。这些规则很容易解释,因此这些分类器通常用于生成描述性模型。与“if”一起使用的条件称为先行条件,每个规则的预测类别称为结果。
基于规则的分类器的特性:
- 覆盖率:满足特定规则的先行条件的记录的百分比。
- 基于规则的分类器生成的规则通常不是相互排斥的,即许多规则可以覆盖相同的记录。
- 由基于规则的分类器生成的规则可能不是详尽无遗的,即可能存在任何规则未涵盖的一些记录。
- 它们创建的决策边界是线性的,但它们可能比决策树复杂得多,因为许多规则是针对同一记录触发的。
一个明显的问题,在知道规则不是相互排斥的后想到的问题是,如果不同的规则和不同的结果覆盖了记录,将如何决定类。
上述问题有两种解决方案:
- 任何一个规则都可以排序,即将触发的最高优先级规则对应的类作为最终类。
- 否则,我们可以根据每个类的权重为每个类分配投票,即规则保持无序。
例子:
以下是将蘑菇分类为可食用或有毒的数据集:
| Class | Cap Shape | Cap Surface | Bruises | Odour | Stalk Shape | Population | Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| edible | flat | scaly | yes | anise | tapering | scattered | grasses |
| poisonous | convex | scaly | yes | pungent | enlargening | several | grasses |
| edible | convex | smooth | yes | almond | enlargening | numerous | grasses |
| edible | convex | scaly | yes | almond | tapering | scattered | meadows |
| edible | flat | fibrous | yes | anise | enlargening | several | woods |
| edible | flat | fibrous | no | none | enlargening | several | urban |
| poisonous | conical | scaly | yes | pungent | enlargening | scattered | urban |
| edible | flat | smooth | yes | anise | enlargening | numerous | meadows |
| poisonous | convex | smooth | yes | pungent | enlargening | several | urban |
Rules:
- 气味 = 刺激性和栖息地 = 城市 -> 等级 = 有毒
- 瘀伤 = 是 -> 等级 = 可食用:此规则涵盖负面和正面记录。
如何生成规则:
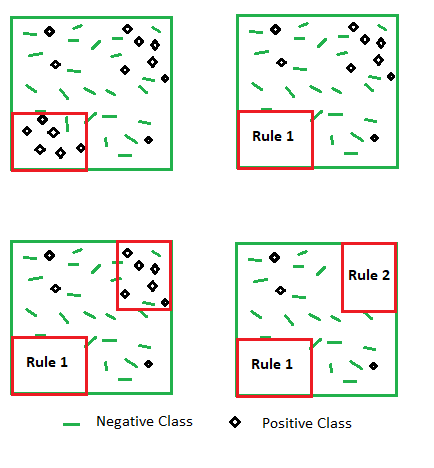
顺序规则生成。
可以使用一般到特定的方法或特定到一般的方法生成规则。在从一般到特定的方法中,从没有前因的规则开始,并不断向其添加条件,直到我们看到评估指标的重大改进。而对于另一个,我们继续从涵盖非常具体案例的规则中删除条件。评估指标可以是准确性、信息增益、似然比等。
增量生成模型的算法:
下面给出的算法生成一个具有无序规则和有序类的模型,即我们可以在生成规则的同时决定优先考虑哪个类。
A <-Set of attributes
T <-Set of training records
Y <-Set of classes
Y' <-Ordered Y according to relevance
R <-Set of rules generated, initially to an empty list
for each class y in Y'
while the majority of class y records are not covered
generate a new rule for class y, using methods given above
Add this rule to R
Remove the records covered by this rule from T
end while
end for
Add rule {}->y' where y' is the default class
对记录进行分类:
下面描述的分类算法假设规则是无序的并且类是加权的。
R <-Set of rules generated using training Set
T <-Test Record
W <-class name to Weight mapping, predefined, given as input
F <-class name to Vote mapping, generated for each test record, to be calculated
for each rule r in R
check if r covers T
if so then add W of predicted_class to F of predicted_class
end for
Output the class with the highest calculated vote in F
注意:规则集也可以通过修剪(简化)其他已经生成的模型(如决策树)来间接创建。