Day-Stout-Warren 算法平衡给定的二叉搜索树
给定一个不平衡的二叉搜索树(BST),任务是在线性时间内将其转换为平衡的 BST,并且不使用辅助空间。
例子:
Input: 5
/ \
1 10
\
20
\
35
Output: 20
/ \
5 35
/ \
1 10
Input: 10
/
5
/
2
/
1
Output: 5
/ \
2 10
/
1
方法:此场景中使用的算法是Day-Stout-Warren 算法。形成的平衡树将是一棵完全二叉树。请按照以下步骤执行算法。
- Step 1 :利用右旋的概念,通过中序遍历,将给定的BST转换成链表(右链表)。这种形式的 BST 被称为骨干或藤蔓。这个阶段的运行时间是线性的,不需要额外的空间。
该函数的编码方式是,它执行所有所需的右旋转以展平 BST,并在最后返回 BST 中的节点数。 - 第 2 步:使用公式h = log2(N+1) [N 是节点总数] 计算BST 的高度,其中所有级别将被完全填充。并使用高度计算可以适合该高度的节点数m = pow(2, h)-1 。 [h 是高度,直到所有级别都被节点完全填充]
N 和 m的差值 (diff) 是平衡完全二叉树最后一级的节点数量。 - 然后将第一步中获得的藤蔓从其根部左旋不同时间。然后将上述修改后的树左旋转 m/2, m/4, m/8 。 . .根据算法,直到 m 大于 0 的次数
插图:
Illustration-1: Here the given tree is a left skewed BST
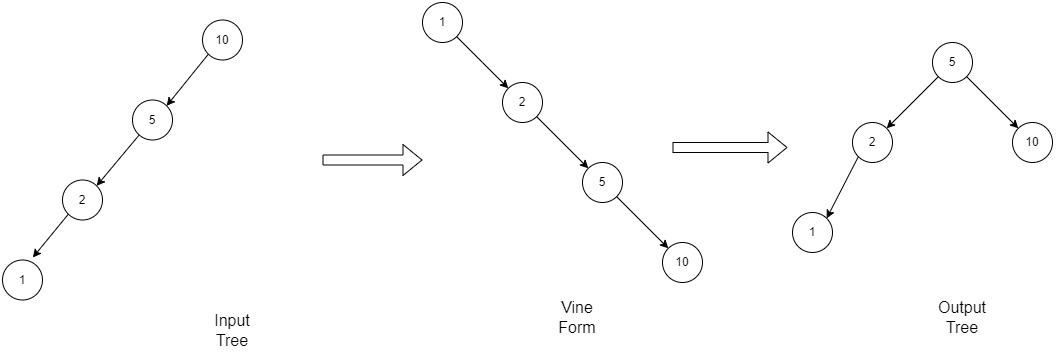
Example-1
Illustration-2: Here it is a non-skewed but unbalanced BST
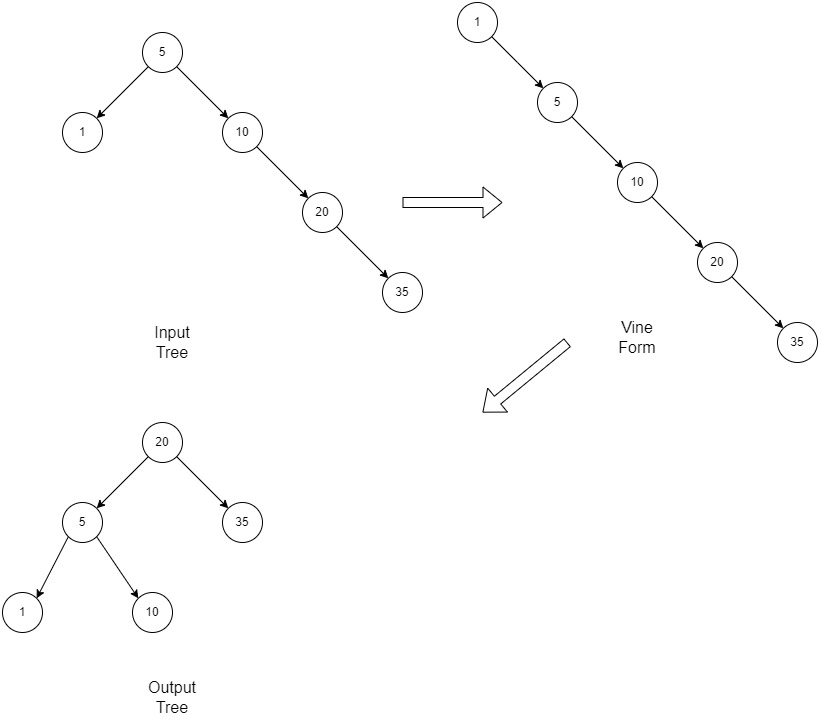
Example-2
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ code to balance BST using DSW algorithm.
#include
using namespace std;
// Defining the structure for TreeNode.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode()
: val(0)
, left(NULL)
, right(NULL)
{
}
TreeNode(int x)
: val(x)
, left(NULL)
, right(NULL)
{
}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left,
TreeNode* right)
: val(x)
, left(left)
, right(right)
{
}
};
// Function to convert input BST
// to right linked list
// known as vine or backbone.
int bstToVine(TreeNode* grand)
{
int count = 0;
// Make tmp pointer to traverse
// and right flatten the given BST.
TreeNode* tmp = grand->right;
// Traverse until tmp becomes NULL
while (tmp) {
// If left exist for node
// pointed by tmp then
// right rotate it.
if (tmp->left) {
TreeNode* oldTmp = tmp;
tmp = tmp->left;
oldTmp->left = tmp->right;
tmp->right = oldTmp;
grand->right = tmp;
}
// If left dont exists
// add 1 to count and
// traverse further right to
// flatten remaining BST.
else {
count++;
grand = tmp;
tmp = tmp->right;
}
}
return count;
}
// Function to compress given tree
// with its root as grand->right.
void compress(TreeNode* grand, int m)
{
// Make tmp pointer to traverse
// and compress the given BST.
TreeNode* tmp = grand->right;
// Traverse and left-rotate root m times
// to compress given vine form of BST.
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
TreeNode* oldTmp = tmp;
tmp = tmp->right;
grand->right = tmp;
oldTmp->right = tmp->left;
tmp->left = oldTmp;
grand = tmp;
tmp = tmp->right;
}
}
// Function to implement the algorithm
TreeNode* balanceBST(TreeNode* root)
{
// create dummy node with value 0
TreeNode* grand = new TreeNode(0);
// assign the right of dummy node as our input BST
grand->right = root;
// get the number of nodes in input BST and
// simultaneously convert it into right linked list.
int count = bstToVine(grand);
// gets the height of tree in which all levels
// are completely filled.
int h = log2(count + 1);
// get number of nodes until second last level
int m = pow(2, h) - 1;
// Left rotate for excess nodes at last level
compress(grand, count - m);
// Left rotation till m becomes 0
// Step is done as mentioned in algo to
// make BST balanced.
for (m = m / 2; m > 0; m /= 2) {
compress(grand, m);
}
// return the balanced tree
return grand->right;
}
// Function to print preorder traversal
// of Binary tree.
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
if (!root)
return;
cout << root->val << " ";
preorderTraversal(root->left);
preorderTraversal(root->right);
return;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(10);
root->left = new TreeNode(5);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->left->left->left
= new TreeNode(1);
// Function call to implement
// Day-Stout-Warren algorithm
root = balanceBST(root);
// To print the preorder traversal of BST
preorderTraversal(root);
return 0;
} Javascript
5 2 1 10 时间复杂度: O(N) 其中 N 是 BST 中的节点总数
辅助空间: O(1)