卤代芳烃的反应
你知道卤代芳烃可以由海洋生物产生吗?海洋生物可以利用海水中的氯化物和溴化物来生产卤代芳烃。它们已被公认为提供多种治疗品质。因此,无论是人工的还是自然的,卤代芳烃都会发生各种反应。让我们更详细地了解卤代芳烃的概念反应!
卤代芳烃
Haloarenes are aromatic hydrocarbon halogen derivatives with the halogen atom bonded directly to a carbon atom of the aromatic ring. Aryl halides is another name for them. When a hydrogen atom linked to an aromatic ring is replaced with a halogen atom, haloarenes are formed.
Ar – H + X ⇢ Ar – X + H
卤代芳烃具有通式 Ar-X ,其中 Ar 表示芳基,X 表示卤素原子。
卤代芳烃的反应
卤代芳烃或芳基卤化物反应可分为三类:
- 亲电取代反应
- 亲核取代反应
- 与金属反应
卤代芳烃的亲电取代反应
寻找电子的物种被称为亲电体。在有机化合物中,亲电试剂在亲电取代过程中取代了另一个亲电试剂。苯环的亲电过程,如卤化、硝化、磺化和傅克反应,都是在卤代芳烃上进行的。我们将分别介绍每一个,但首先,让我们看看 Haloarenes 如何对亲电试剂的攻击作出反应:
- 由于卤素的吸电子倾向,苯环对亲电取代反应略微失活。
- 由于其不同的共振模式,环的邻位和对位比间位有更多的电子或负电荷。因此,卤代芳烃作为亲电取代反应的 o- 和 p- 指令起作用。
由于上述因素,卤代芳烃在亲电取代反应中的活性低于常规苯环。因此,与苯相比,这些反应更慢,需要更极端的条件。
- 卤化:卤代芳烃在溶剂存在下与氯反应生成卤代芳烃(例如氯化铁)。氯分子带有少量正电荷并趋于极性。结果,氯作为亲电子试剂,攻击化合物的富电子邻位和对位。

卤化
该反应将形成邻位和对位化合物。反应的主要结果将是对位异构体,而次要产物将是邻位异构体。在以下示例中,氯苯与路易斯酸相互作用以产生二卤代苯的邻位和对位替代物。
- 硝化作用:由于分子中存在两个带负电的氧原子,NO 2首先由硝酸生成,它是由硫酸的存在开始的; NO 2在N 上有一个亲电子中心。富电子的邻位和对位被NO 2攻击,产生对位异构体作为主要产物,邻位异构体作为次要产物。

硝化
磺化: SO 3在磺化过程中是亲电子试剂。在邻位和对位位置,它针对富含电子的卤代烯。反应生成对和邻氯苯磺酸,对异构体是主要产物,邻异构体是次要产物。

磺化
- 傅克反应:由于碳原子中存在正电荷,这种情况下的亲电子试剂是烷基和丙酮基团。有两种类型的傅克反应:
Friedel-Crafts 烷基化反应:

傅克烷基化
傅克酰化反应:

傅克酰化
卤代芳烃的亲核取代反应
对于卤代芳烃,亲核取代反应很棘手。然而,在某些条件下,卤代芳烃会经历亲核取代过程。以下是卤代芳烃在亲核取代反应字符减少或不反应的主要原因:
- 羟基起取代作用:卤代芳烃在300大气压下用氢氧化钠水溶液加热至623K时,卤原子被羟基取代,生成酚盐。当用稀盐酸酸化酚盐时,会产生苯酚。

- 共振效应:在卤代芳烃的情况下,苯环的 π - 电子与卤代芳烃结构中的卤原子共轭。由于这种共振,CX 键会形成部分双键。卤代芳烃比卤代烷更难部分双键断裂。结果,卤代芳烃难以被亲核试剂裂解,并且在亲核取代反应中具有较低的反应性。
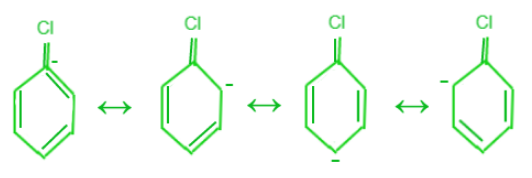
共振的例子
在 CX 键中,碳原子杂化的差异。在卤代芳烃的情况下,卤素基团的成员与sp 2杂化碳原子结合。另一方面,在卤代烷烃中,卤素与sp 3杂化碳原子结合。与 sp 3 C 相比, sp 2 C 具有更强的 s字符。因此,sp 2 C 比 sp 3 C 更具电负性。
因此,sp 2 C 更擅长从 CX 键中去除电子并将它们保持在靠近自身的位置。结果,卤代芳烃和卤代烷烃之间的键长更短。长度越短的键越强。例如,在卤代烷中,C-Cl 键长为 177 pm,而在卤代芳烃中为 169 pm。
卤代芳烃与金属的反应
金属以有限的方式与卤代芳烃发生反应。有两个主要反应:
- 拟合反应:芳基取代卤代芳烃中的卤原子。当金属钠在无水醚存在下加热时,会生成二芳基化合物。合适的反应就是我们所说的。

拟合反应
在该反应中,使用无水乙醚使卤代芳烃混合物与钠反应。二芳基是最终结果。
- Wurtz-Fitting 反应:当卤代芳烃的卤原子在钠存在下在卤代烷醚溶液中加热时,卤代芳烃的卤原子被烷基取代,从而形成高级芳烃。

Wurtz拟合反应
在无水醚和钠存在下,烷基卤化物的组合与芳基卤化物相互作用。烷基芳烃是成品。
示例问题
问题 1:定义卤代芳烃。
回答:
Haloarenes are aromatic hydrocarbon halogen derivatives with the halogen atom bonded directly to a carbon atom of the aromatic ring. Aryl halides is another name for them. When a hydrogen atom linked to an aromatic ring is replaced with a halogen atom, haloarenes are formed.
问题 2:什么导致卤代芳烃发生亲电取代?
回答:
Through the resonance effect, the halogen atom in haloarenes transfers electrons to the benzene nucleus, which is electron-deficient in comparison to the halogen atom. Electrophilic substitution reactions occur in haloarenes as a result of the electrophile attacking at both the ortho and para positions.
问题 3:为什么卤代芳烃的亲核取代如此困难?
回答:
In haloarenes, the C–X bond takes on a partial double bond character and shortens. It boosts the C–X bond’s strength and gives haloarenes more stability. Cleavage of C–X bonds in haloarenes is substantially more difficult than in haloalkanes because of this.
问题4:解释芳香亲核取代反应的机理。
回答:
The π – electrons migrate in such a way that the electron density in the benzene ring delocalizes at Ortho- and Para- positions as a nucleophile approaches and attacks the C-X bond. If an electron withdrawing group is present at the Ortho and Para locations of the benzene ring in this situation, it will withdraw the negative charge on the carbon atom, stabilizing the negative charge.
As a result, the presence of electron withdrawing groups like NO2 at the Ortho and Para positions aids the nucleophile’s attack. Furthermore, resonance as well as an electron withdrawing group like NO2 help to stabilize the carbocation.
The reaction will proceed in a sequence of fast and slow steps, resulting in the production of a high resonance stabilized sigma complex with a high resonance. Finally, when the negative charge delocalizes due to the elimination of the Cl bond, the π – electrons will be recovered. The final step is to form the product.
问题5:为什么卤代芳烃具有邻位对位效应?
回答:
Ortho para directing is haloarenes. Because the halogen atoms on the benzene ring in haloarenes are ortho and para directing groups on the benzene ring, this is the case. The electron density at the o– and p– positions of the ring increases slightly due to resonance. The o- and p-positions in haloarenes have greater electron density centers than the m-positions due to resonance.
问题 6:有哪些类型的傅克反应?
回答:
There are Two types of Friedel-Crafts Reactions :
- Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reactions
- Friedel-Crafts Acylation Reactions
Because of the positive charge present in the carbon atom, the electrophile in this circumstance is the alkyl and acetonic group.
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reactions:

Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
Friedel-Crafts Acylation Reactions:
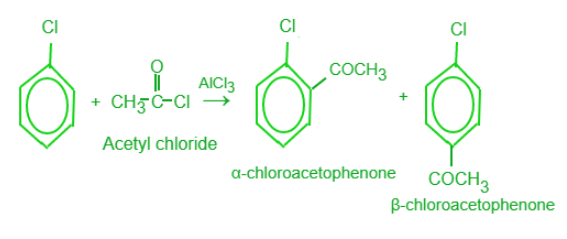
Friedel-Crafts Acylation