用Java实现 Strassen 算法
Strassen 算法用于平方矩阵的乘法,即矩阵的阶数应为 (N x N)。 Strassen 算法基于分而治之的技术。简单来说,它用于矩阵乘法。 Strassen 的矩阵乘法方法是一种典型的分治算法。但是,让我们再次了解分治法的背后是什么,并考虑如下示例来实现它例如:假设 A 和 B 是两个矩阵,则结果矩阵 C 使得
Matrix C = Matrix A * Matrix B
现在考虑矩阵的数学计算是可以得出为什么施特拉森矩阵的实现起作用的结论。假设两个矩阵相乘,那么该方法将是
- 输入两个矩阵。
- 检查矩阵乘法的兼容性,仅当第一个矩阵的行数等于第二个矩阵的列数时才成立。
- 将矩阵相乘并将两个矩阵的乘积分配给另一个称为结果矩阵的矩阵。
- 打印结果矩阵。
在上面的方法中,得出了两个假设来说明为什么需要 Strassen 算法发挥作用
- 首先,算法的时间复杂度是 O(n 3 ),太高了。
- 其次,两个以上矩阵相乘不仅会增加程序的混乱度和复杂度,也会相应地增加时间复杂度。
目的:
Volker Strassen 是一个名字,他发表了他的算法来证明一般矩阵乘法的时间复杂度 O(n 3 ) 不是最优的。于是发表了Strassen的矩阵链乘法,降低了时间复杂度。该算法比标准矩阵乘法更快,并且在日常世界中计算大量大型矩阵乘法时非常有用。
矩阵乘法的施特拉森算法
步骤 1:取三个矩阵假设 A、B、C,其中 C 是合成矩阵,A 和 B 是要使用施特拉森方法相乘的矩阵。

Step 2:将A、B、C矩阵分成四个(n/2)×(n/2)矩阵,分别取第一部分如下图
第 3 步:使用以下公式求解矩阵的第 1 部分
M1:=(A1+A3)×(B1+B2)
M2:=(A2+A4)×(B3+B4)
M3:=(A1−A4)×(B1+A4)
M4:=A1×(B2−B4)
M5:=(A3+A4)×(B1)
M6:=(A1+A2)×(B4)
M7:=A4×(B3−B1)
Then,
P:=M2+M3−M6−M7
Q:=M4+M6
R:=M5+M7
S:=M1−M3−M4−M5第 4 步:在求解第一部分后,计算第二、第三和第四以及最终输出,结果生成一个乘法矩阵,如上图所示。
步骤 5:打印结果矩阵。
执行:
例子
Java
// Java Program to Implement Strassen Algorithm
// Class Strassen matrix multiplication
public class GFG {
// Method 1
// Function to multiply matrices
public int[][] multiply(int[][] A, int[][] B)
{
// Order of matrix
int n = A.length;
// Creating a 2D square matrix with size n
// n is input from the user
int[][] R = new int[n][n];
// Base case
// If there is only single element
if (n == 1)
// Returning the simple multiplication of
// two elements in matrices
R[0][0] = A[0][0] * B[0][0];
// Matrix
else {
// Step 1: Dividing Matrix into parts
// by storing sub-parts to variables
int[][] A11 = new int[n / 2][n / 2];
int[][] A12 = new int[n / 2][n / 2];
int[][] A21 = new int[n / 2][n / 2];
int[][] A22 = new int[n / 2][n / 2];
int[][] B11 = new int[n / 2][n / 2];
int[][] B12 = new int[n / 2][n / 2];
int[][] B21 = new int[n / 2][n / 2];
int[][] B22 = new int[n / 2][n / 2];
// Step 2: Dividing matrix A into 4 halves
split(A, A11, 0, 0);
split(A, A12, 0, n / 2);
split(A, A21, n / 2, 0);
split(A, A22, n / 2, n / 2);
// Step 2: Dividing matrix B into 4 halves
split(B, B11, 0, 0);
split(B, B12, 0, n / 2);
split(B, B21, n / 2, 0);
split(B, B22, n / 2, n / 2);
// Using Formulas as described in algorithm
// M1:=(A1+A3)×(B1+B2)
int[][] M1
= multiply(add(A11, A22), add(B11, B22));
// M2:=(A2+A4)×(B3+B4)
int[][] M2 = multiply(add(A21, A22), B11);
// M3:=(A1−A4)×(B1+A4)
int[][] M3 = multiply(A11, sub(B12, B22));
// M4:=A1×(B2−B4)
int[][] M4 = multiply(A22, sub(B21, B11));
// M5:=(A3+A4)×(B1)
int[][] M5 = multiply(add(A11, A12), B22);
// M6:=(A1+A2)×(B4)
int[][] M6
= multiply(sub(A21, A11), add(B11, B12));
// M7:=A4×(B3−B1)
int[][] M7
= multiply(sub(A12, A22), add(B21, B22));
// P:=M2+M3−M6−M7
int[][] C11 = add(sub(add(M1, M4), M5), M7);
// Q:=M4+M6
int[][] C12 = add(M3, M5);
// R:=M5+M7
int[][] C21 = add(M2, M4);
// S:=M1−M3−M4−M5
int[][] C22 = add(sub(add(M1, M3), M2), M6);
// Step 3: Join 4 halves into one result matrix
join(C11, R, 0, 0);
join(C12, R, 0, n / 2);
join(C21, R, n / 2, 0);
join(C22, R, n / 2, n / 2);
}
// Step 4: Return result
return R;
}
// Method 2
// Function to subtract two matrices
public int[][] sub(int[][] A, int[][] B)
{
//
int n = A.length;
//
int[][] C = new int[n][n];
// Iterating over elements of 2D matrix
// using nested for loops
// Outer loop for rows
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// Inner loop for columns
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
// Subtracting corresponding elements
// from matrices
C[i][j] = A[i][j] - B[i][j];
// Returning the resultant matrix
return C;
}
// Method 3
// Function to add two matrices
public int[][] add(int[][] A, int[][] B)
{
//
int n = A.length;
// Creating a 2D square matrix
int[][] C = new int[n][n];
// Iterating over elements of 2D matrix
// using nested for loops
// Outer loop for rows
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// Inner loop for columns
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
// Adding corresponding elements
// of matrices
C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[i][j];
// Returning the resultant matrix
return C;
}
// Method 4
// Function to split parent matrix
// into child matrices
public void split(int[][] P, int[][] C, int iB, int jB)
{
// Iterating over elements of 2D matrix
// using nested for loops
// Outer loop for rows
for (int i1 = 0, i2 = iB; i1 < C.length; i1++, i2++)
// Inner loop for columns
for (int j1 = 0, j2 = jB; j1 < C.length;
j1++, j2++)
C[i1][j1] = P[i2][j2];
}
// Method 5
// Function to join child matrices
// into (to) parent matrix
public void join(int[][] C, int[][] P, int iB, int jB)
{
// Iterating over elements of 2D matrix
// using nested for loops
// Outer loop for rows
for (int i1 = 0, i2 = iB; i1 < C.length; i1++, i2++)
// Inner loop for columns
for (int j1 = 0, j2 = jB; j1 < C.length;
j1++, j2++)
P[i2][j2] = C[i1][j1];
}
// Method 5
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Display message
System.out.println(
"Strassen Multiplication Algorithm Implementation For Matrix Multiplication :\n");
// Create an object of Strassen class
// in he main function
GFG s = new GFG();
// Size of matrix
// Considering size as 4 in order to illustrate
int N = 4;
// Matrix A
// Custom input to matrix
int[][] A = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 4, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 5, 6, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 2, 5, 6 } };
// Matrix B
// Custom input to matrix
int[][] B = { { 1, 0, 5, 1 },
{ 1, 2, 0, 2 },
{ 0, 3, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 1, 2 } };
// Matrix C computations
// Matrix C calling method to get Result
int[][] C = s.multiply(A, B);
// Display message
System.out.println(
"\nProduct of matrices A and B : ");
// Iterating over elements of 2D matrix
// using nested for loops
// Outer loop for rows
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Inner loop for columns
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
// Printing elements of resultant matrix
// with whitespaces in between
System.out.print(C[i][j] + " ");
// New line once the all elements
// are printed for specific row
System.out.println();
}
}
}Strassen Multiplication Algorithm Implementation For Matrix Multiplication :
Product of matrices A and B :
7 21 15 22
8 8 21 12
12 17 28 22
8 31 16 31 施特拉森方法的时间复杂度
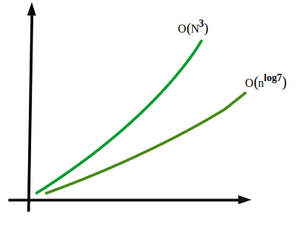
通过分析,时间复杂度函数可以写为:
T(N) = 7T(N/2) + O(N2)通过使用主定理解决这个问题,我们得到:
T(n)=O(nlog7)因此,矩阵乘法的施特拉森算法的时间复杂度推导为:
O(nlog7) = O (n2.81)O(n 3 ) 与 O(n 2.81)