Java中的数学类方法与示例|设置 2
Java.math 类及其方法 |设置 1 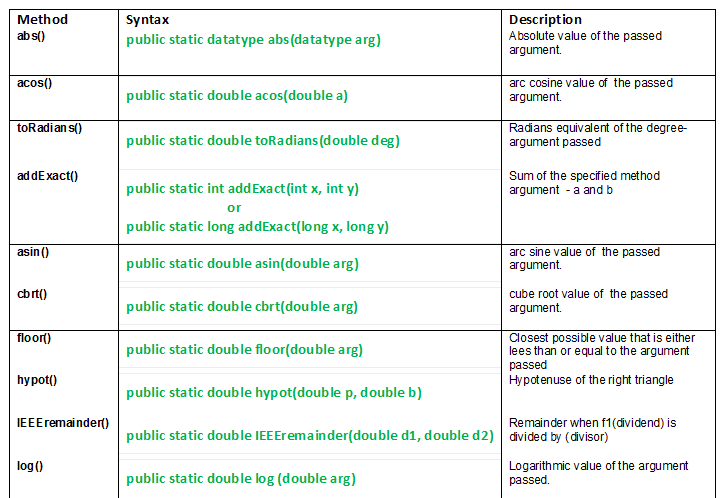
本文讨论的Java.math 类方法:
- abs() : Java.math.abs()方法返回传递的任何类型参数的绝对值。此方法可以处理所有数据类型。
- 特例 :
- 如果参数为正零或负零,则结果为正零。
- 如果参数是无限的,则结果是正无穷大。
- 结果是 NaN,如果传递的参数是 NaN。
句法:
public static datatype abs(datatype arg) Parameters: arg - the argument whose absolute value we need Returns: absolute value of the passed argument. - acos() : Java.math.acos()方法返回传递参数的反余弦值。
反余弦是传递的参数的反余弦。
acos(arg) = cos -1 of arg
特殊情况:如果参数为 NaN 或其绝对值大于 1,则结果为 NaN。
句法:public static double acos(double a) Parameters: a - the argument whose arc cosine value we need. argument is taken as radian Returns: arc cosine value of the argument. - toRadians() : Java.math.toRadians(double deg)方法将参数(度)转换为弧度。
特殊点:数学类通常将弧度作为输入,这在现实生活中的应用非常不同,因为角度通常以度数表示。
句法:public static double toRadians(double deg) Parameters: deg - degree angle needs to be in radian. Returns: radians equivalent of the degree-argument passed.什么是 NaN 论点?
一个保持双精度类型的非数字 (NaN) 值的常量。它相当于 Double.longBitsToDouble(0x7ff8000000000000L) 返回的值。Java代码解释了 Math 类中的 abs()、acos()、toRadians() 方法。
// Java program explaining Math class methods // abs(), acos(), toRadians() import java.math.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) { // Declaring the variables int Vali = -1; float Valf = .5f; // Printing the values System.out.println("Initial value of int : "+Vali); System.out.println("Initial value of int : "+Valf); // Use of .abs() method to get the absoluteValue int Absi = Math.abs(Vali); float Absf = Math.abs(Valf); System.out.println("Absolute value of int : "+Absi); System.out.println("Absolute value of int : "+Absf); System.out.println(""); // Use of acos() method // Value greater than 1, so passing NaN double Acosi = Math.acos(60); System.out.println("acos value of Acosi : "+Acosi); double x = Math.PI; // Use of toRadian() method x = Math.toRadians(x); double Acosj = Math.acos(x); System.out.println("acos value of Acosj : "+Acosj); } }输出:
Initial value of int : -1 Initial value of int : 0.5 Absolute value of int : 1 Absolute value of int : 0.5 acos value of Acosi : NaN acos value of Acosj : 1.5159376794536454 - addExact() : Java.math.addExact(int a, int b)方法返回传递参数的总和。
特殊点:如果Result溢出一个int或long(根据传递的参数),该方法抛出ArithmeticException。
句法:public static int addExact(int x, int y) or public static long addExact(long x, long y) Parameters: a - first value b - second value Returns: Sum of the specified method arguments - a and b. - asin() : Java.math.asin()方法返回传递的方法参数的反正弦值。返回的角度在 -pi/2 到 pi/2 的范围内。
反正弦是传递的参数的反正弦。
asin(arg) = arg 的正弦-1
特例 :- 结果为 NaN,如果参数为 NaN 或其绝对值大于 1。
- 如果参数为零,则结果为零。
句法:
public static double asin(double arg) Parameters: arg - argument passed. Returns: arc sine of the argument passed. - cbrt() : Java.math.cbrt()方法返回传递参数的立方根。
特别点:- 如果参数为 NaN,则结果为 NaN。
- 如果参数是无限的,则结果是与参数相同符号的无穷大。
- 如果参数为零,则结果为零。
句法:
public static double cbrt(double arg) Parameters: arg - argument passed. Returns: cube root of the argument passedJava代码解释了 Math 类中的 addExact()、asin()、cbrt() 方法。
// Java program explaining Math class methods // addExact(), asin(), cbrt() import java.math.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 1, b = 8; // get the result of addExact method int radd = Math.addExact(a,b); System.out.println("Using addExact() : "+radd); System.out.println(""); // Use of acos() method // Value greater than 1, so passing NaN double Asini = Math.asin(radd); System.out.println("asin value of Asini : "+Asini); double x = Math.PI; // Use of toRadian() method x = Math.toRadians(x); double Asinj = Math.asin(x); System.out.println("asin value of Asinj : "+Asinj); System.out.println(""); // Use of cbrt() method double cbrtval = Math.cbrt(216); System.out.println("cube root : "+cbrtval); } }输出:
Using addExact() : 9 acos value of Asini : NaN acos value of Asinj : 0.054858647341251204 cube root : 6.0 - floor() : Java.math.floor()方法返回参数的下限值,即最接近的整数值,小于或等于传递的参数。
例如:101.23 的底值 = 101
要点:如果传递一个 NaN 或无限参数,则会产生相同的参数。Syntax: public static double floor(double arg) Parameters: arg - the argument whose floor value we need Returns:closest possible value that is either less than or equal to the argument passed - hypot () : Java.math.hypot(double p, double b)方法在传递 traingle 的底和垂直作为参数时返回直角三角形的斜边。
斜边 = [垂直2 + 底2 ] 1/2很重要的一点 :
- 如果任一参数是无限的,则结果是正无穷大。
- 如果任一参数为 NaN 且任一参数都不是无限的,则结果为 NaN。
Syntax: public static double hypot(double p, double b) Parameters: p - perpendicular of the right triangle b - base of the right triangle Returns: hypotenuse of the right triangle - IEEEremainder() : Java.math.IEEERemainder(double d1, double d2)方法通过对 IEEE 754 标准的两个参数应用余数运算来返回余数。
余值 = d1 – d2 * n
在哪里,
n = d1/d2 最接近的精确值Syntax: public static double IEEEremainder(double d1,double d2) Parameters: d1 - dividend d2 - divisor Returns: remainder when f1(dividend) is divided by(divisor) - log() : Java.math.log()方法返回传递参数的对数值。
Syntax: public static double log(double arg) Parameters: arg - argument passed. Returns: logarithmic value of the argument passed.Java代码解释了 Math 类中的 floor()、hypot()、IEEEremainder()、log() 方法。
// Java program explaining MATH class methods // floor(), hypot(), IEEEremainder(), log() import java.lang.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) { // Use of floor method double f1 = 30.56, f2 = -56.34; f1 =Math.floor(f1); System.out.println("Floor value of f1 : "+f1); f2 =Math.floor(f2); System.out.println("Floor value of f2 : "+f2); System.out.println(""); // Use of hypot() method double p = 12, b = -5; double h = Math.hypot(p, b); System.out.println("Hypotenuse : "+h); System.out.println(""); // Use of IEEEremainder() method double d1 = 105, d2 = 2; double r = Math.IEEEremainder(d1,d2); System.out.println("Remainder : "+r); System.out.println(""); // Use of log() method double l = 10; l = Math.log(l); System.out.println("Log value of 10 : "+l); } }输出:
Floor value of f1 : 30.0 Floor value of f2 : -57.0 Hypotenuse : 13.0 Remainder : 1.0 Log value of 10 : 2.302585092994046Java.math 类及其方法 |设置 3