ML——候选消除算法
候选消除算法在给定假设空间 H 和一组示例 E 的情况下逐步构建版本空间。实例一一添加;每个示例都可能通过删除与示例不一致的假设来缩小版本空间。候选消除算法通过为每个新示例更新一般和特定边界来实现这一点。
- 您可以将其视为 Find-S 算法的扩展形式。
- 考虑正面和负面的例子。
- 实际上,这里使用正例作为 Find-S 算法(基本上它们是从规范中概括出来的)。
- 而反例是从泛化形式指定的。
使用的术语:
- 概念学习:概念学习基本上是机器的学习任务(Learn by Train 数据)
- 一般假设:不指定特征来学习机器。
- G = {'?', '?','?','?'...}:属性个数
- 特定假设:指定学习机器的特征(特定特征)
- S= {'pi','pi','pi'...}:pi 的数量取决于属性的数量。
- 版本空间:介于一般假设和特定假设之间。它不仅编写了一个假设,而且还基于训练数据集编写了一组所有可能的假设。
算法:
Step1: Load Data set
Step2: Initialize General Hypothesis and Specific Hypothesis.
Step3: For each training example
Step4: If example is positive example
if attribute_value == hypothesis_value:
Do nothing
else:
replace attribute value with '?' (Basically generalizing it)
Step5: If example is Negative example
Make generalize hypothesis more specific.
例子:
考虑下面给出的数据集:
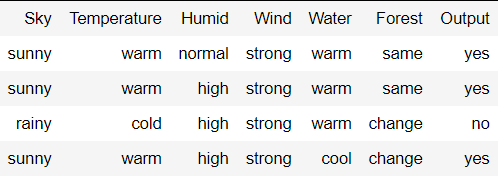
算法步骤:
Initially : G = [[?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?],
[?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?]]
S = [Null, Null, Null, Null, Null, Null]
For instance 1 : <'sunny','warm','normal','strong','warm ','same'> and positive output.
G1 = G
S1 = ['sunny','warm','normal','strong','warm ','same']
For instance 2 : <'sunny','warm','high','strong','warm ','same'> and positive output.
G2 = G
S2 = ['sunny','warm',?,'strong','warm ','same']
For instance 3 : <'rainy','cold','high','strong','warm ','change'> and negative output.
G3 = [['sunny', ?, ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, 'warm', ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?],
[?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, ?, ?, ?, ?, 'same']]
S3 = S2
For instance 4 : <'sunny','warm','high','strong','cool','change'> and positive output.
G4 = G3
S4 = ['sunny','warm',?,'strong', ?, ?]
At last, by synchronizing the G4 and S4 algorithm produce the output.
输出 :
G = [['sunny', ?, ?, ?, ?, ?], [?, 'warm', ?, ?, ?, ?]]
S = ['sunny','warm',?,'strong', ?, ?]