钾和钙——原子结构、化学性质、用途
原子是参与化学反应的元素或化合物的最小部分。它们由称为质子、中子和电子的微小粒子组成。希腊哲学家德谟克利特是第一个使用原子一词的人。
原子的结构是由约翰道尔顿于 1808 年在他出版的一本书中发现的。他也被称为“原子论之父”。它们是由一个原子核和一个或多个轨道上的电子组成的微小粒子。原子核由带正电的质子和带负电的中子组成。一个原子的质子和中子的质量大致相同。围绕原子核的原子轨道描述了电子的位置和波状行为。现在,在本文中,我们将讨论钾和钙的情况。
钾
Potassium is the first element in the periodic table’s fourth period. The name potassium is derived from the mineral Potash. For hundreds of years, the element has been used. It, along with lithium, rubidium, sodium, caesium, and francium, is an alkali metal. Potassium has an atomic mass of 39.098 atomic mass units. It is represented by the letter ‘K.’
钾被评为地球表面发现的第七丰富的元素。它主要存在于巧妙的岩石和矿物沉积物中。钾天然存在于离子盐中。发现它溶解在 0.04%(重量)的海水中。钾是热和电的良导体。它是一种极其活跃的金属,在自然界中从未发现过游离态;相反,它总是存在于与其他元素的化合物中。
以下是钾的总结细节:Symbol K Atomic number 19 Atomic Mass 39.098 a.m.u. Group I Period 4 Block s State Solid (at 20 °C) Electronic configuration [Ar] 4s1 Melting point 63.5 °C or 336 K Boiling point 759 °C or 1032 K Density 0.89 g cm-3 Key isotope 39K
钾的同位素:钾具有三种同位素,分别称为钾 39、40 和 41。钾 40 是一种放射性元素,可能存在于岩石、植物和动物中。它用于确定对象的年龄。这种同位素衰变为氩同位素。
钾的原子结构
原子核由 19 个质子和 21 个中子组成。原子核由 19 个电子束缚,在外壳(环)中有一个高度不稳定的电子。元素的化学和物理特性由其外层电子的稳定性决定。

图:钾的原子结构
电子配置如下:Shells K L M N No. of electrons 2 8 8 1
钾的物理性质是:
- 钾是碱金属。
- 它是一种高反应性元素,不会以自由状态存在。
- 它是一种柔软的银白色金属。
- 钾的密度小于水的密度(0.89 g/cm 3 )。因此,它可以漂浮在水面上。 2
- 它本质上具有延展性。
- 钾的熔点为 63.5 °C,沸点为 759 °C。
钾的化学性质是:
- 与水反应放出氢气。该反应是挥发性的,并可能引起爆炸。
2K +2H 2 O ⇢ 2KOH + H 2 ⇡
- 它与氮、磷、硫和氟具有高度反应性。
- 与稀硫酸反应迅速溶解,放出钾离子和氢气。
2K +H 2 SO 4 ⇢ 2K + + SO 4 + H 2 ⇡
- 钾与卤素反应形成卤化钾。
2K+ Cl 2 ⇢ 2KCl
钾的用途是:
- 钾在我们的日常生活中被广泛使用,其中一些如下所述:
- 工业使用钾来制造肥皂、洗涤剂、染料、火药等。
- 钾用于肌肉收缩。
- 过量的钾饮食有助于降低血压并预防中风。
- 碳酸钾用于生产玻璃。
- 它对肥料的需求量很大。
- 也可用作热交换介质,用于核电站。
Interesting Facts
- Potassium was the first metal to get isolated by electrolysis.
- It was suspected in 1702 that potassium is a distinct element that combines with the same anions to produce similar salts and was proven in 1807 by using electrolysis.
- It plays a vital role in the functioning of living cells and its deficiency or excess amount can cause abnormal heart rhythm and other various electrocardiographic abnormalities.
钙
Calcium, with atomic number 20, is denoted by the symbol Ca in the periodic table. Calcium (Ca) is an essential mineral that helps our bones stay strong and capable of bearing our weight. Calcium is also employed by our nervous system to aid in the transmission of impulses throughout our bodies.
钙被评为地球表面发现的第五丰富的元素。它在电离时产生阳离子钙的最外层包含两个价电子。地球上最常见的钙化合物是碳酸钙。石膏、无水石膏、萤石等也是钙的一些来源。
以下是钙的总结细节:Symbol Ca Atomic number 20 Atomic mass 40.08 g/mol Group II Period 4 Block s State Solid (at 20 °C) Electronic configuration [Ar] 4s 2 Melting point 842 °C Boiling point 1482 °C
钙的同位素:钙有五种天然稳定的同位素——钙 40、钙 42、钙 43、钙 44 和钙 46。
钙的原子结构
原子核中有 20 个质子和 20 个中子。有 20 个电子占据可接近的电子壳(环)。元素的化学和物理特性取决于其外部(价)电子的稳定性。

图:钙的原子结构
钙原子的电子构型由下式给出:Shells K L M N Number of electrons 2 8 8 2
钙的物理性质是:
- 钙在游离状态下不会自然产生。
- 它用作铝、铅、铜和其他贱金属的合金剂。
- 它是一种软金属。
- 钙是良导体。
- 它本质上具有延展性和延展性。
- 钙的熔点为 842°C,沸点为
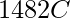
钙的化学性质是:
- 碳酸氢钙的溶解形式存在于硬水中。
CaCO 3 + CO 2 ⇢ Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 + H 2 O
- 当钙与空气接触时,它会形成一层氮化物和氧化物涂层。
2Ca + O 2 ⇢ 2CaO
3Ca + N 2 ⇢ Ca 3 N 2
- 钙的化合物对酸具有高度反应性。
CaCO 3 + HCl ⇢ CaCl 2 + HO + CO 2 ⇡
钙的用途
- 钙可用于多种用途。其中一些在下面提到;
- 钙有助于维持强壮的骨骼以执行许多必要的功能。
- 神经需要在大脑和身体的每个部位之间传递信息。
- 在金属萃取过程中可用作还原剂。
- 它还用作生产某些金属的合金剂。
- 连接酸钙用作食品添加剂。
- 碳化钙用于生产塑料和乙炔气。
Interesting Facts
- Calcium hydroxyl phosphate is the principal inorganic element of teeth and bones.
- Calcium is important for both animal and plant life. We can find 2% of the calcium in the human body.
- Lack of calcium in the blood can cause a disease called “Hypocalcemia” also known as calcium deficiency in the human body. It can also lead to dental changes, alterations in the brain, etc
示例问题
问题 1:我们最常服用的钾是哪种形式?
解决方案:
Humans take several forms of potassium but the most common one is potassium chloride. The minimum intake is about 4.7 mg in average.
问题2:为什么要使用钾肥?
解决方案:
Potassium fertilizers are also named potash fertilizer. It is obtained from the burned away wood, mines, and the ocean. It is highly used as fertilizer because it helps in the growth of plants as well as the movement of stomata.
问题3:如何自然地从水中去除钙?
解决方案:
Calcium is naturally found in water as it may get dissolved from limestone, marble, gypsum, etc. Calcium in the water determines its hardness. We can treat water by adding some sodium carbonate or washing soda in it which will break down the calcium present in it.
问题 4:钙的生物用途是什么?
解决方案:
The biological use of calcium is to provide strength and structure to the skeleton. It is very significant for the maintenance of bones and teeth.
问题5:过量使用钾有什么影响?
解决方案:
Some of the common side effects of potassium are nausea, stomach pain, discomfort, vomiting, and abnormal heart rate.
问题6:钾在工业领域的用途是什么?
解决方案:
Potassium is used in industries as a raw material to manufacture potassium metal as well as it is also used in the soap industry as a water softening agent instead of sodium chloride.
问题 7:为什么乳制品对我们的饮食至关重要?
解决方案:
Dairy products are highly rich in calcium. Hence, it is essential for our diet as calcium helps in strengthening our bones.