原子结构和性质
原子结构和量子力学历史的起源归功于德谟克利特。他是第一个提出物质由原子组成的人。整个化学反应领域、化学键、物理性质都与原子结构有关。原子结构的第一个科学理论是约翰道尔顿在 1800 年提出的。一旦发现了原子结构,它也为亚原子粒子的发现奠定了基础,亚原子粒子是构成物质结构的基本粒子。
元素的原子结构是指它的原子核和它的构成,它是由什么材料组成的。它还涉及存在于原子核周围的电子。构成物质原子结构的主要物质是质子、电子和中子。中子和质子位于原子的核心并构成原子核,原子核被属于原子的电子包围。元素的原子序数是该元素原子核中存在的质子总数。
Atoms which are neutral in terms of the charge, have equal number of protons and electrons. This makes the atom neutral because protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged. But atoms have the ability to lose or gain electrons in order to increase their own stability and the resulting entity is charged in nature and is called an ion.
没有两种元素具有相同数量的质子和电子,这使得每种元素的原子结构都不同。这是每个元素独特特征背后的主要原因。在 18 世纪和 19 世纪,世界各地的许多科学家都试图借助他们自己的原子模型来解释原子结构。每个这样的模型都有自己的优点和缺点。但它们都在现代原子模型的发展中发挥了巨大的作用。该领域最著名的贡献者是 JJ Thompson、John Dalton、Emest Rutherford 和 Neils Bohr。
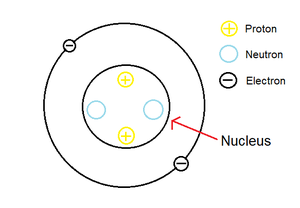
根据玻尔模型的氦原子。
Important Terminology
- Atom – The defining structure and basic units of matter of an element are called atoms. The term “atom” came from a Greek word that meant indivisible because earlier atom was thought to be the smallest things in the universe that could not be divided
- Atomic Structure – The structure of an atom comprising of a nucleus, in which the protons and neutrons are present. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus.
- Nucleus – A collection of particles called protons and neutrons is called Nucleus. Protons are positively charged and neutrons, are electrically neutral. Protons and neutrons are made up of particles called quarks. The chemical element of an atom is determined by the number of protons, or the atomic number, Z, of the nucleus.
- Proton – Positively charged particles found within atomic nuclei is given the name of Proton. Rutherford discovered proton in his famous cathode ray experiment that was conducted between 1911 and 1919. Protons are about 99.86% as massive as neutrons. The number of protons in an atom is unique for each element
- Electron – Electrons are very tiny compared to protons and neutrons, about1800 times smaller than either a proton or a neutron. Electrons are just 0.054% as massive as neutrons. Electrons were discovered in 1897 by Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson, a British physicist. Electrons have a negative charge and are electrically attracted to the positively charged protons
- Neutron – Rutherford theorized the neutron’s existence in 1920 and later discovered by Chadwick in 1932. Neutrons were found during experiments where atoms were shot at a thin sheet of beryllium. Subatomic particles with no charge were released – and were named as neutron. Neutrons are uncharged particles found within all atomic nuclei
- Isotopes – Members of same family of an element that all have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are named as isotopes. The number of protons in a nucleus determines the element’s atomic number on the Periodic Table. All the isotopes have unique properties, just like all family members have their own qualities.
道尔顿的原子论
约翰道尔顿是一位英国化学家,他认为每一种物质都是由原子组成的。此外,原子是不可分割和不可破坏的。他还提出,一种特定物质的所有原子都是相同的,但不同元素的原子具有不同的大小和质量。
根据道尔顿的原子理论,化学反应涉及原子的重排以形成产物。根据他的理论中提出的假设,原子结构是由原子组成的,它们是负责发生化学反应的最小粒子。
道尔顿理论的假设:
- 存在的每一种物质都是由原子构成的。
- 原子是不可分割的。
- 特定元素中只有一种原子。
- 原子具有恒定的质量,每个元素都会变化。
- 在化学反应中,原子发生重排
- 原子既不能被创造也不能被摧毁,只能从一种形式转变为另一种形式。
道尔顿的原子理论能够成功地解释化学反应的定律,即质量守恒定律、常数性质定律、多比例定律和倒数比例定律。
道尔顿原子论的缺点
- 该理论无法解释同位素的存在。
- 没有提供关于原子结构的适当解释。
- 后来发现原子是可分的,而道尔顿关于原子不可分的说法被证明是错误的。
原子构成粒子的发现使人们对化学有了更好的认识,这些构成粒子被称为亚原子粒子。
汤姆森的原子模型
约瑟夫·约翰·汤姆森爵士也是一位英国化学家,因发现电子而闻名,他也因此获得了诺贝尔奖。他进行了阴极射线实验以发明电子。在这个实验中,取了一个有两个开口的玻璃管。一个开口用于真空泵,另一个开口用于吸入,通过该开口将要填充在管中的气体推入。使用真空泵,部分真空泵被保持在玻璃室内。在电极的帮助下,连接了一个高压电源。简而言之,阴极和阳极放置在玻璃管内。
当允许电流在阴极和阳极之间流动时进行以下观察。
- 当高压电源接通并接通时,光线从阴极向阳极传输。在 ZnS 屏幕上观察到荧光点,这证实了射线被透射的事实。这些射线被命名为“阴极射线”。
- 当外部电场投射到管上时,光线会偏向正极。但是在没有电场的情况下,光线会回到直线上。
- 但是当转子叶片固定在阴极射线的路径上时,射线似乎在旋转。这证明了阴极射线是由一些具有一定质量的粒子组成的。
- 利用所有证据,汤姆森得出结论,阴极射线由称为电子的带负电粒子组成。
- 通过在阴极射线上施加电场和磁场,求出电荷质量比 (e/m)。电子的 e/m 为 17588 × 10 11 e/bg
Mullikin 做了一个油滴实验,使用 e/m 比找到电子的电荷。他发现电子的电荷 = 1.6 x 10 -16 C 和电子质量 = 9.1093 × 10 -31 kg。汤姆森将原子的结构描述为一个带正电的球体,其中固定有带负电的电子。该模型的流行名称是“李子布丁模型”,因为它可以被观察为李子布丁盘,其中带正电的原子表示布丁,李子片代表电子。
汤姆森模型失败的原因是这个模型对原子的稳定性并不清楚。该模型无法适应未来发现的其他亚原子粒子。
阿尔法射线散射实验和卢瑟福原子理论
作为 JJ Thomson 的学生的卢瑟福发现了另一种亚原子粒子,称为核。这一发现使原子结构发生了巨大变化。汤普森在他的实验中所做的观察被卢瑟福用来提出他的原子结构理论。
卢瑟福在他的实验中使用了放射性现象。他使用放射性物质溴化镭(RaBr)。 RaBr 发射 α 粒子,这是一种辐射形式。在装置中放置了一块薄薄的金金属板。然后将α粒子轰击在这张纸上。为了观察颗粒的偏转,使用硫化锌 (ZnS) 筛网并将其放置在金箔后面。卢瑟福进一步开发了一种探测器来计算放射性粒子的数量。最初,他记录了 RaBr 的计数率,因为他记录了每分钟发射的 α 粒子的计数。
卢瑟福模型的观察
卢瑟福做了以下观察并得出结论:
- 大多数α粒子穿过薄片。这意味着原子的大部分空间是空的。
- 另一个观察结果是,一些 α 粒子向各个方向偏转了一点。这导致了正电荷不是均匀分布在整个原子中的结论。
- 很少有 α 粒子沿着它们行进的路径偏转回来。这是因为电荷相互排斥。看到这个卢瑟福得出结论,原子中的正电荷存在于非常小的体积中。
- 不仅是带正电的粒子,而且大量的质量也集中在一个非常小的体积中。卢瑟福将这个区域命名为 Nucleus。
- 卢瑟福还提出了电子存在于轨道周围的论点,就像太阳系中的行星一样。电子带负电,它们围绕原子核旋转。
- 由于电子和原子核分别带负电荷和正电荷,因此电子和原子核由静电引力保持。
卢瑟福模型的结论
从上述所有观察中得出结论,卢瑟福提出了他的原子结构,该结构具有以下性质 -
- 原子核位于原子的中心,电荷和质量的最大值只集中在那里。
- 原子本质上是球形的。
- 电子以圆形轨道围绕原子核旋转。
卢瑟福模型的局限性
就像其他原子模型一样,卢瑟福的模型也有很多不足之处。
- 为了围绕原子核旋转,它们必须消耗能量,而且还要抵抗来自原子核的强大吸引力。电子会消耗大量能量,最终它们会失去全部能量并落入原子核。这引发了关于原子稳定性的严重问题。
- 如果电子围绕原子核连续旋转,那么它们发射的光谱应该是连续光谱,但我们观察到的是线光谱。
亚原子粒子
质子
- 质子带正电荷。此电荷为 1e,约为 1.602 × 10 -19
- 质子的质量约为 1.672 × 10 -24
- 质子比电子重 1800 多倍。
- 元素原子中的质子总数和元素的原子序数总是相等的。
中子
- 中子的质量几乎与质子的质量相似,即 1.674 × 10 -24
- 中子始终是电中性粒子,不带任何电荷。
- 一种元素的同位素具有相同数量的质子,但它们各自的原子核中的质子数量不同。
电子
- 一个电子的电荷为-1e,约为-1.602 × 10 -19
- 电子的质量约为 9.1 × 10 -31 。
- 与原子的质量相比,电子的质量几乎可以忽略不计,因此在计算原子的质量时会忽略电子的质量。
同位素的原子结构
所有组件都以原子核子的名称组合在一起。它可以是中子或质子。每个元素的质子数都是唯一的,由其唯一的原子序数表示。一个元素可以有多个原子结构,但具有不同数量的核子。元素的这些变体具有不同数量的核子。这些变体被称为元素的同位素。这导致同位素具有相同数量的质子但不同数量的中子。
为了描述同位素的结构,元素的符号与同位素的原子序数和质量数一起使用。举个例子,氢有 3 种同位素,分别是氚、氘和氚。同位素的稳定性不同。半衰期也不同。但它们通常具有相似的化学行为,因为它们具有相同的电子结构。
玻尔的原子论
玻尔在 1915 年提出了他的模型,它是应用最广泛的原子模型,它基于普朗克的量子化理论。玻尔的理论适用于修改后的原子结构。它解释了电子总是只在固定的轨道上移动,它们并不存在于原子中的任何地方。玻尔还解释说,每个轨道都是一个固定的能级。轨道也称为壳。卢瑟福只解释了原子核。玻尔对该模型进行了更改,并添加了电子和能级。
玻尔模型是一个带正电的小原子核,被负电子包围,它们在轨道上移动。玻尔发现,电子与原子核的距离越大,其能量越大。
假设:
- 原子内部的电子存在于称为“静止轨道”的离散轨道中。
- 量子数用于表示这些壳的能级。
- 电子可以通过吸收能量进入更高的能级,并通过失去或释放一些能量进入更低的能级。
- 只有当电子停留在自己的轨道上时,才不会发生能量的吸收或发射。
- 电子仅在这些静止轨道中旋转。
- 静止轨道的能量被量化。
玻尔原子论的局限性:
- 它仅适用于单电子物质,例如 H、He+、Li2+、Be3+、……。
- 当使用更精确的光谱仪观察氢的发射光谱时,每条谱线都被视为多条较小的离散谱线的组合。
- 玻尔的理论无法解释斯塔克和塞曼效应。
示例问题
问题1:元素周期表的优点是什么?
回答:
In the periodic table, elements are arranged in a tabular form. This makes it is easy to remember the properties of elements if one knows the position of the element. Also the compounds formed by the elements are predictable if the position of the element is known. Periodic table made it easy and systematic to study chemistry
问题2:如果一个原子中的电子数和质子数相等,那么为什么说元素的原子序数与电子数相同是错误的?
回答:
It is wrong to say that the atomic number of the element is the same as the number of electrons because an atom can lose or gain electrons, so the number of electrons keeps changing and they are never constant. Whereas the number of protons never changes for an element. This is why atomic number is taken from number of protons.
问题3:电子贡献负电荷,质子贡献正电荷。一个原子两者都有,但为什么没有电荷?
回答:
As per Thomson’s model of an atom, the number of electrons and the number of protons are equal in an atom. Electrons are negatively charged and protons are positively charged, hence the + and – charges are neutralized by each other that making atoms neutral as a whole
问题四:为什么卢瑟福的模型不能解释原子的稳定性?
回答:
According to Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory, when charged particles are accelerated, they should emit electromagnetic radiation. Similarly, an electron in its orbit moves at a very high velocity and it will emit radiation; the orbit will then continue to shrink and the electron ultimately falls into the nucleus which does not happen in an atom.
问题5:道尔顿的原子论有什么缺陷?
回答:
There were multiple flaws found in dalton’s atomic theory. The biggest flaw was that atoms are not the elementary particles of matter, but they are further divided into three main categories known as electrons, protons, and neutrons. But they are the smallest entities that take part in a chemical reaction. The discovery of isotopes further led to a crucial flaw in this theory. Initially, it was said that the same elements have similar atoms, but isotopes proved that atoms in some elements can have variable densities and masses. Similarly, isobar’s discovery denied the fact that atoms are different for different elements. The whole number ratio theory was also found incorrect as it was not observed in complex compounds.