无向树中的最长路径
给定一棵无向树,我们需要找到这棵树的最长路径,其中路径定义为节点序列。
例子:
Input : Below shown Tree using adjacency list
representation:
Output : 5
In below tree longest path is of length 5
from node 5 to node 7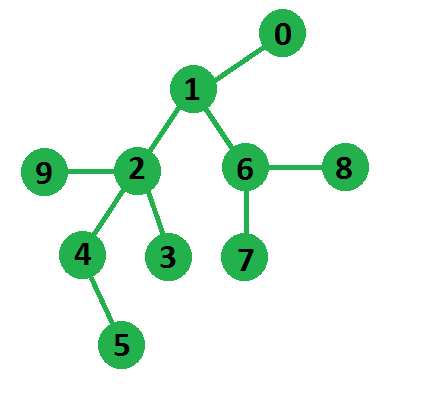
这个问题与n叉树的直径相同。我们在这里讨论了一个简单的解决方案。
在这篇文章中,讨论了一个有效的解决方案。我们可以使用两个 BFS 找到最长的路径。这个想法基于以下事实:如果我们从任何节点 x 开始 BFS,并找到一个与 x 距离最长的节点,它必须是最长路径的端点。可以用反证法来证明。所以我们的算法简化为简单的两个 BFS。第一个 BFS 找到最长路径的端点,第二个 BFS 从这个端点找到实际最长的路径。为了证明这个算法为什么有效,这里有一个很好的解释证明正确性:图论中树的直径算法
如上图所示,如果我们从节点 0 开始 BFS,距离它最远的节点将是节点 5,现在如果我们从节点 5 开始 BFS,距离最远的节点将是是node-7,最后,从node-5到node-7的路径将构成我们最长的路径。
C++
// C++ program to find longest path of the tree
#include
using namespace std;
// This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // Pointer to an array containing
// adjacency lists
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void addEdge(int v, int w);// function to add an edge to graph
void longestPathLength(); // prints longest path of the tree
pair bfs(int u); // function returns maximum distant
// node from u with its distance
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
adj[w].push_back(v); // Since the graph is undirected
}
// method returns farthest node and its distance from node u
pair Graph::bfs(int u)
{
// mark all distance with -1
int dis[V];
memset(dis, -1, sizeof(dis));
queue q;
q.push(u);
// distance of u from u will be 0
dis[u] = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
int t = q.front(); q.pop();
// loop for all adjacent nodes of node-t
for (auto it = adj[t].begin(); it != adj[t].end(); it++)
{
int v = *it;
// push node into queue only if
// it is not visited already
if (dis[v] == -1)
{
q.push(v);
// make distance of v, one more
// than distance of t
dis[v] = dis[t] + 1;
}
}
}
int maxDis = 0;
int nodeIdx;
// get farthest node distance and its index
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (dis[i] > maxDis)
{
maxDis = dis[i];
nodeIdx = i;
}
}
return make_pair(nodeIdx, maxDis);
}
// method prints longest path of given tree
void Graph::longestPathLength()
{
pair t1, t2;
// first bfs to find one end point of
// longest path
t1 = bfs(0);
// second bfs to find actual longest path
t2 = bfs(t1.first);
cout << "Longest path is from " << t1.first << " to "
<< t2.first << " of length " << t2.second;
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the example
Graph g(10);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 9);
g.addEdge(2, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 5);
g.addEdge(1, 6);
g.addEdge(6, 7);
g.addEdge(6, 8);
g.longestPathLength();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find longest path of the tree
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class LongestPathUndirectedTree {
// Utility Pair class for storing maximum distance
// Node with its distance
static class Pair {
T first; // maximum distance Node
V second; // distance of maximum distance node
//Constructor
Pair(T first, V second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list
static class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices
LinkedList[] adj; //Adjacency List
// Constructor
Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
// Initializing Adjacency List
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; ++i) {
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
}
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int s, int d) {
adj[s].add(d); // Add d to s's list.
adj[d].add(s); // Since the graph is undirected
}
// method returns farthest node and its distance from node u
Pair bfs(int u) {
int[] dis = new int[V];
// mark all distance with -1
Arrays.fill(dis, -1);
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(u);
// distance of u from u will be 0
dis[u] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int t = q.poll();
// loop for all adjacent nodes of node-t
for(int i = 0; i < adj[t].size(); ++i) {
int v = adj[t].get(i);
// push node into queue only if
// it is not visited already
if(dis[v] == -1) {
q.add(v);
// make distance of v, one more
// than distance of t
dis[v] = dis[t] + 1;
}
}
}
int maxDis = 0;
int nodeIdx = 0;
// get farthest node distance and its index
for(int i = 0; i < V; ++i) {
if(dis[i] > maxDis) {
maxDis = dis[i];
nodeIdx = i;
}
}
return new Pair(nodeIdx, maxDis);
}
// method prints longest path of given tree
void longestPathLength() {
Pair t1, t2;
// first bfs to find one end point of
// longest path
t1 = bfs(0);
// second bfs to find actual longest path
t2 = bfs(t1.first);
System.out.println("Longest path is from "+ t1.first
+ " to "+ t2.first +" of length "+t2.second);
}
}
// Driver code to test above methods
public static void main(String[] args){
// Create a graph given in the example
Graph graph = new Graph(10);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 2);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.addEdge(2, 9);
graph.addEdge(2, 4);
graph.addEdge(4, 5);
graph.addEdge(1, 6);
graph.addEdge(6, 7);
graph.addEdge(6, 8);
graph.longestPathLength();
}
}
// Added By Brij Raj Kishore C#
// C# program to find longest path of the tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Utility Pair class for storing
// maximum distance Node with its distance
public class Pair
{
// maximum distance Node
public T first;
// distance of maximum distance node
public V second;
// Constructor
public Pair(T first, V second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// This class represents a undirected graph
// using adjacency list
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
List[] adj; //Adjacency List
// Constructor
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
// Initializing Adjacency List
adj = new List[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
{
adj[i] = new List();
}
}
// function to add an edge to graph
public void addEdge(int s, int d)
{
adj[s].Add(d); // Add d to s's list.
adj[d].Add(s); // Since the graph is undirected
}
// method returns farthest node and
// its distance from node u
public Pair bfs(int u)
{
int[] dis = new int[V];
// mark all distance with -1
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dis[i] = -1;
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue(u);
// distance of u from u will be 0
dis[u] = 0;
while (q.Count != 0)
{
int t = q.Dequeue();
// loop for all adjacent nodes of node-t
for(int i = 0; i < adj[t].Count; ++i)
{
int v = adj[t][i];
// push node into queue only if
// it is not visited already
if(dis[v] == -1)
{
q.Enqueue(v);
// make distance of v, one more
// than distance of t
dis[v] = dis[t] + 1;
}
}
}
int maxDis = 0;
int nodeIdx = 0;
// get farthest node distance and its index
for(int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
{
if(dis[i] > maxDis)
{
maxDis = dis[i];
nodeIdx = i;
}
}
return new Pair(nodeIdx, maxDis);
}
// method prints longest path of given tree
public void longestPathLength()
{
Pair t1, t2;
// first bfs to find one end point of
// longest path
t1 = bfs(0);
// second bfs to find actual longest path
t2 = bfs(t1.first);
Console.WriteLine("longest path is from " + t1.first +
" to " + t2.first + " of length " + t2.second);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Create a graph given in the example
Graph graph = new Graph(10);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 2);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.addEdge(2, 9);
graph.addEdge(2, 4);
graph.addEdge(4, 5);
graph.addEdge(1, 6);
graph.addEdge(6, 7);
graph.addEdge(6, 8);
graph.longestPathLength();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Python3
# Python program to find the Longest Path of the Tree
# By Aaditya Upadhyay
from collections import deque
class Graph:
# Initialisation of graph
def __init__(self, vertices):
# No. of vertices
self.vertices = vertices
# adjacency list
self.adj = {i: [] for i in range(self.vertices)}
def addEdge(self, u, v):
# add u to v's list
self.adj[u].append(v)
# since the graph is undirected
self.adj[v].append(u)
# method return farthest node and its distance from node u
def BFS(self, u):
# marking all nodes as unvisited
visited = [False for i in range(self.vertices + 1)]
# mark all distance with -1
distance = [-1 for i in range(self.vertices + 1)]
# distance of u from u will be 0
distance[u] = 0
# in-built library for queue which performs fast operations on both the ends
queue = deque()
queue.append(u)
# mark node u as visited
visited[u] = True
while queue:
# pop the front of the queue(0th element)
front = queue.popleft()
# loop for all adjacent nodes of node front
for i in self.adj[front]:
if not visited[i]:
# mark the ith node as visited
visited[i] = True
# make distance of i , one more than distance of front
distance[i] = distance[front]+1
# Push node into the stack only if it is not visited already
queue.append(i)
maxDis = 0
# get farthest node distance and its index
for i in range(self.vertices):
if distance[i] > maxDis:
maxDis = distance[i]
nodeIdx = i
return nodeIdx, maxDis
# method prints longest path of given tree
def LongestPathLength(self):
# first DFS to find one end point of longest path
node, Dis = self.BFS(0)
# second DFS to find the actual longest path
node_2, LongDis = self.BFS(node)
print('Longest path is from', node, 'to', node_2, 'of length', LongDis)
# create a graph given in the example
G = Graph(10)
G.addEdge(0, 1)
G.addEdge(1, 2)
G.addEdge(2, 3)
G.addEdge(2, 9)
G.addEdge(2, 4)
G.addEdge(4, 5)
G.addEdge(1, 6)
G.addEdge(6, 7)
G.addEdge(6, 8)
G.LongestPathLength()Javascript
输出:
Longest path is from 5 to 7 of length 5