无向图的欧拉路径和电路
欧拉路径是图中的一条路径,它只访问每条边一次。欧拉回路是在同一顶点开始和结束的欧拉路径。
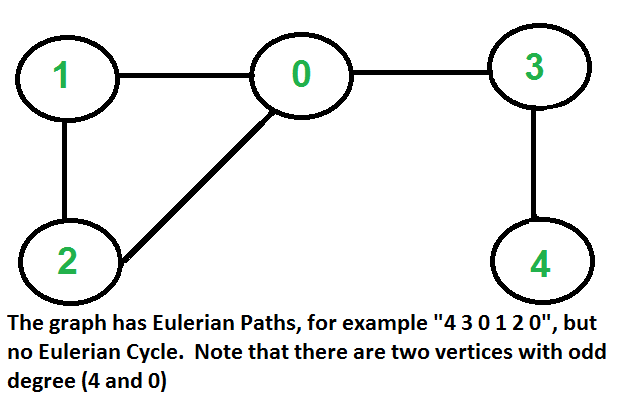
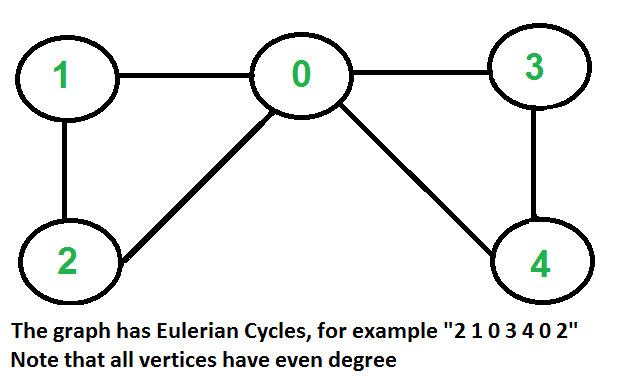
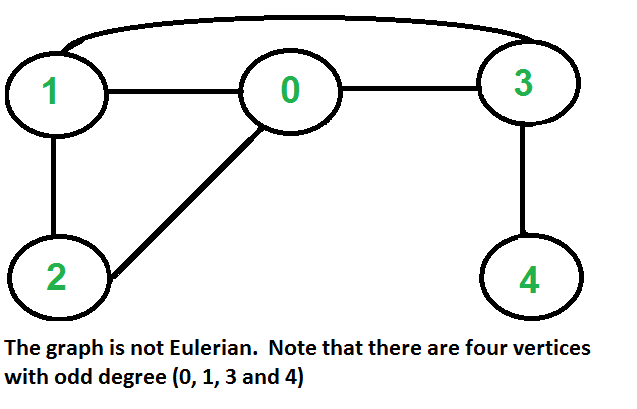
如何判断给定图是否为欧拉图?
问题与以下问题相同。 “是否可以在不从纸上拿起铅笔并且不不止一次地跟踪任何边缘的情况下绘制给定的图形”。
如果一个图有一个欧拉循环,则称为欧拉图;如果它有一条欧拉路径,则称为半欧拉图。该问题似乎类似于哈密顿路径,这是一般图的 NP 完全问题。幸运的是,我们可以在多项式时间内找出给定图是否具有欧拉路径。事实上,我们可以在 O(V+E) 时间内找到它。
以下是具有欧拉路径和循环的无向图的一些有趣属性。我们可以使用这些属性来判断一个图是否是欧拉图。
欧拉循环
如果满足以下两个条件,则无向图具有欧拉环。
....a)所有非零度数的顶点都是连接的。我们不关心度数为零的顶点,因为它们不属于欧拉循环或路径(我们只考虑所有边)。
....b)所有顶点的度数都是偶数。
欧拉路径
如果满足以下两个条件,则无向图具有欧拉路径。
....a) 与欧拉循环的条件 (a) 相同
....b)如果零个或两个顶点的度数为奇数,而所有其他顶点的度数为偶数。请注意,在无向图中只有一个度数为奇数的顶点是不可能的(在无向图中,所有度数的总和总是偶数)
请注意,没有边的图被认为是欧拉图,因为没有要遍历的边。
这是如何运作的?
在欧拉路径中,每访问一个顶点v,我们都会经过两条未访问的边,其中一个端点为v。因此,欧拉路径中的所有中间顶点的度数必须是偶数。对于欧拉循环,任何顶点都可以是中间顶点,因此所有顶点的度数必须是偶数。
C++
// A C++ program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// A class that represents an undirected graph
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // A dynamic array of adjacency lists
public:
// Constructor and destructor
Graph(int V) {this->V = V; adj = new list[V]; }
~Graph() { delete [] adj; } // To avoid memory leak
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not
int isEulerian();
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
bool isConnected();
// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();
void DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[]);
};
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w);
adj[w].push_back(v); // Note: the graph is undirected
}
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected.
// It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
bool Graph::isConnected()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool visited[V];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != 0)
break;
// If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if (i == V)
return true;
// Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
DFSUtil(i, visited);
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size() > 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/* The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) */
int Graph::isEulerian()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isConnected() == false)
return 0;
// Count vertices with odd degree
int odd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() & 1)
odd++;
// If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
if (odd > 2)
return 0;
// If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
// If odd count is 0, then eulerian
// Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph
return (odd)? 1 : 2;
}
// Function to run test cases
void test(Graph &g)
{
int res = g.isEulerian();
if (res == 0)
cout << "graph is not Eulerian\n";
else if (res == 1)
cout << "graph has a Euler path\n";
else
cout << "graph has a Euler cycle\n";
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
// Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
Graph g1(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
test(g1);
Graph g2(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
g2.addEdge(4, 0);
test(g2);
Graph g3(5);
g3.addEdge(1, 0);
g3.addEdge(0, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 1);
g3.addEdge(0, 3);
g3.addEdge(3, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
test(g3);
// Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
// connected in the form of cycle
Graph g4(3);
g4.addEdge(0, 1);
g4.addEdge(1, 2);
g4.addEdge(2, 0);
test(g4);
// Let us create a graph with all vertices
// with zero degree
Graph g5(3);
test(g5);
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
// This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list
// representation
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation
private LinkedList adj[];
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i=0; i i = adj[v].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are
// connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
boolean isConnected()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != 0)
break;
// If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if (i == V)
return true;
// Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
DFSUtil(i, visited);
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size() > 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/* The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) */
int isEulerian()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isConnected() == false)
return 0;
// Count vertices with odd degree
int odd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size()%2!=0)
odd++;
// If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
if (odd > 2)
return 0;
// If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
// If odd count is 0, then eulerian
// Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph
return (odd==2)? 1 : 2;
}
// Function to run test cases
void test()
{
int res = isEulerian();
if (res == 0)
System.out.println("graph is not Eulerian");
else if (res == 1)
System.out.println("graph has a Euler path");
else
System.out.println("graph has a Euler cycle");
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.test();
Graph g2 = new Graph(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
g2.addEdge(4, 0);
g2.test();
Graph g3 = new Graph(5);
g3.addEdge(1, 0);
g3.addEdge(0, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 1);
g3.addEdge(0, 3);
g3.addEdge(3, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
g3.test();
// Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
// connected in the form of cycle
Graph g4 = new Graph(3);
g4.addEdge(0, 1);
g4.addEdge(1, 2);
g4.addEdge(2, 0);
g4.test();
// Let us create a graph with all vertices
// with zero degree
Graph g5 = new Graph(3);
g5.test();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# Python program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
#Complexity : O(V+E)
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices # No. of vertices
self.graph = defaultdict(list) # default dictionary to store graph
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
self.graph[v].append(u)
# A function used by isConnected
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in self.graph[v]:
if visited[i] == False:
self.DFSUtil(i, visited)
'''Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are
connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
node with non-zero degree'''
def isConnected(self):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False]*(self.V)
# Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.graph[i]) > 1:
break
# If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if i == self.V-1:
return True
# Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
self.DFSUtil(i, visited)
# Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False and len(self.graph[i]) > 0:
return False
return True
'''The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) '''
def isEulerian(self):
# Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if self.isConnected() == False:
return 0
else:
# Count vertices with odd degree
odd = 0
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.graph[i]) % 2 != 0:
odd += 1
'''If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
If odd count is 0, then eulerian
If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph'''
if odd == 0:
return 2
elif odd == 2:
return 1
elif odd > 2:
return 0
# Function to run test cases
def test(self):
res = self.isEulerian()
if res == 0:
print("graph is not Eulerian")
elif res == 1:
print("graph has a Euler path")
else:
print("graph has a Euler cycle")
# Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
g1 = Graph(5)
g1.addEdge(1, 0)
g1.addEdge(0, 2)
g1.addEdge(2, 1)
g1.addEdge(0, 3)
g1.addEdge(3, 4)
g1.test()
g2 = Graph(5)
g2.addEdge(1, 0)
g2.addEdge(0, 2)
g2.addEdge(2, 1)
g2.addEdge(0, 3)
g2.addEdge(3, 4)
g2.addEdge(4, 0)
g2.test()
g3 = Graph(5)
g3.addEdge(1, 0)
g3.addEdge(0, 2)
g3.addEdge(2, 1)
g3.addEdge(0, 3)
g3.addEdge(3, 4)
g3.addEdge(1, 3)
g3.test()
# Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
# connected in the form of cycle
g4 = Graph(3)
g4.addEdge(0, 1)
g4.addEdge(1, 2)
g4.addEdge(2, 0)
g4.test()
# Let us create a graph with all vertices
# with zero degree
g5 = Graph(3)
g5.test()
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// A C# program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list
// representation
public class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation
private List []adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[v];
for (int i=0; i();
}
//Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w);// Add w to v's list.
adj[w].Add(v); //The graph is undirected
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v,bool []visited)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
foreach(int i in adj[v]){
int n = i;
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are
// connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
bool isConnected()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool []visited = new bool[V];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].Count != 0)
break;
// If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if (i == V)
return true;
// Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
DFSUtil(i, visited);
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].Count > 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/* The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) */
int isEulerian()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isConnected() == false)
return 0;
// Count vertices with odd degree
int odd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].Count%2!=0)
odd++;
// If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
if (odd > 2)
return 0;
// If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
// If odd count is 0, then eulerian
// Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph
return (odd==2)? 1 : 2;
}
// Function to run test cases
void test()
{
int res = isEulerian();
if (res == 0)
Console.WriteLine("graph is not Eulerian");
else if (res == 1)
Console.WriteLine("graph has a Euler path");
else
Console.WriteLine("graph has a Euler cycle");
}
// Driver method
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.test();
Graph g2 = new Graph(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
g2.addEdge(4, 0);
g2.test();
Graph g3 = new Graph(5);
g3.addEdge(1, 0);
g3.addEdge(0, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 1);
g3.addEdge(0, 3);
g3.addEdge(3, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
g3.test();
// Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
// connected in the form of cycle
Graph g4 = new Graph(3);
g4.addEdge(0, 1);
g4.addEdge(1, 2);
g4.addEdge(2, 0);
g4.test();
// Let us create a graph with all vertices
// with zero degree
Graph g5 = new Graph(3);
g5.test();
}
}
// This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 Javascript
输出:
graph has a Euler path
graph has a Euler cycle
graph is not Eulerian
graph has a Euler cycle
graph has a Euler cycle