Diffie-Hellman 算法的实现
背景
椭圆曲线密码学 (ECC)是一种公钥密码学方法,它基于有限域上椭圆曲线的代数结构。与非 ECC 加密相比,ECC 需要更小的密钥来提供等效的安全性(256 位 ECC 安全性与 3072 位 RSA 加密具有等效的安全性)。
为了更好地理解椭圆曲线密码学,了解椭圆曲线的基础知识非常重要。椭圆曲线是由以下形式的方程定义的平面代数曲线
![]()
其中“a”是 x 的系数,“b”是方程的常数
曲线是非奇异的;也就是说,它的图没有尖点或自交点(当 Co-efficient 场的特征等于 2 或 3 时)。
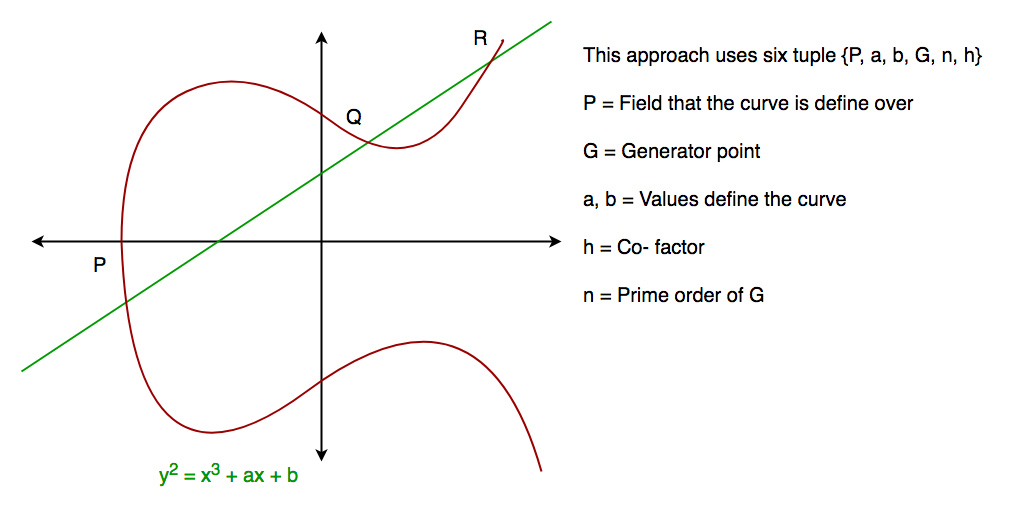
一般来说,椭圆曲线如下图所示。当绘制一条与曲线相交的直线时,椭圆曲线几乎可以相交 3 个点。如我们所见,椭圆曲线关于 x 轴对称。该属性在算法中起着关键作用。
Diffie-Hellman 算法
Diffie-Hellman 算法用于建立一个共享秘密,该秘密可用于秘密通信,同时使用椭圆曲线在公共网络上交换数据以生成点并使用参数获取密钥。
- 为了算法的简单和实际实现,我们将只考虑 4 个变量,一个素数 P 和 G(P 的原始根)以及两个私有值 a 和 b。
- P 和 G 都是公开可用的数字。用户(比如 Alice 和 Bob)选择私有值 a 和 b,他们生成一个密钥并公开交换它。对方收到密钥并生成密钥,之后他们有相同的密钥进行加密。
分步说明 Key generated = Key generated = Generated Secret Key = Generated Secret Key = Algebraically, it can be shown that Alice Bob Public Keys available = P, G Public Keys available = P, G Private Key Selected = a Private Key Selected = b ![]()
![]()
Exchange of generated keys takes place Key received = y key received = x ![]()
![]()
![]()
Users now have a symmetric secret key to encrypt
例子:
Step 1: Alice and Bob get public numbers P = 23, G = 9
Step 2: Alice selected a private key a = 4 and
Bob selected a private key b = 3
Step 3: Alice and Bob compute public values
Alice: x =(9^4 mod 23) = (6561 mod 23) = 6
Bob: y = (9^3 mod 23) = (729 mod 23) = 16
Step 4: Alice and Bob exchange public numbers
Step 5: Alice receives public key y =16 and
Bob receives public key x = 6
Step 6: Alice and Bob compute symmetric keys
Alice: ka = y^a mod p = 65536 mod 23 = 9
Bob: kb = x^b mod p = 216 mod 23 = 9
Step 7: 9 is the shared secret.执行:
C
/* This program calculates the Key for two persons
using the Diffie-Hellman Key exchange algorithm */
#include
#include
// Power function to return value of a ^ b mod P
long long int power(long long int a, long long int b,
long long int P)
{
if (b == 1)
return a;
else
return (((long long int)pow(a, b)) % P);
}
//Driver program
int main()
{
long long int P, G, x, a, y, b, ka, kb;
// Both the persons will be agreed upon the
// public keys G and P
P = 23; // A prime number P is taken
printf("The value of P : %lld\n", P);
G = 9; // A primitive root for P, G is taken
printf("The value of G : %lld\n\n", G);
// Alice will choose the private key a
a = 4; // a is the chosen private key
printf("The private key a for Alice : %lld\n", a);
x = power(G, a, P); // gets the generated key
// Bob will choose the private key b
b = 3; // b is the chosen private key
printf("The private key b for Bob : %lld\n\n", b);
y = power(G, b, P); // gets the generated key
// Generating the secret key after the exchange
// of keys
ka = power(y, a, P); // Secret key for Alice
kb = power(x, b, P); // Secret key for Bob
printf("Secret key for the Alice is : %lld\n", ka);
printf("Secret Key for the Bob is : %lld\n", kb);
return 0;
} Java
// This program calculates the Key for two persons
// using the Diffie-Hellman Key exchange algorithm
class GFG{
// Power function to return value of a ^ b mod P
private static long power(long a, long b, long p)
{
if (b == 1)
return a;
else
return (((long)Math.pow(a, b)) % p);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long P, G, x, a, y, b, ka, kb;
// Both the persons will be agreed upon the
// public keys G and P
// A prime number P is taken
P = 23;
System.out.println("The value of P:" + P);
// A primitive root for P, G is taken
G = 9;
System.out.println("The value of G:" + G);
// Alice will choose the private key a
// a is the chosen private key
a = 4;
System.out.println("The private key a for Alice:" + a);
// Gets the generated key
x = power(G, a, P);
// Bob will choose the private key b
// b is the chosen private key
b = 3;
System.out.println("The private key b for Bob:" + b);
// Gets the generated key
y = power(G, b, P);
// Generating the secret key after the exchange
// of keys
ka = power(y, a, P); // Secret key for Alice
kb = power(x, b, P); // Secret key for Bob
System.out.println("Secret key for the Alice is:" + ka);
System.out.println("Secret key for the Bob is:" + kb);
}
}
// This code is contributed by raghav14Python3
from random import randint
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Both the persons will be agreed upon the
# public keys G and P
# A prime number P is taken
P = 23
# A primitive root for P, G is taken
G = 9
print('The Value of P is :%d'%(P))
print('The Value of G is :%d'%(G))
# Alice will choose the private key a
a = 4
print('The Private Key a for Alice is :%d'%(a))
# gets the generated key
x = int(pow(G,a,P))
# Bob will choose the private key b
b = 3
print('The Private Key b for Bob is :%d'%(b))
# gets the generated key
y = int(pow(G,b,P))
# Secret key for Alice
ka = int(pow(y,a,P))
# Secret key for Bob
kb = int(pow(x,b,P))
print('Secret key for the Alice is : %d'%(ka))
print('Secret Key for the Bob is : %d'%(kb))Javascript
输出:
The value of P : 23
The value of G : 9
The private key a for Alice : 4
The private key b for Bob : 3
Secret key for the Alice is : 9
Secret Key for the Bob is : 9