二叉树的迭代对角遍历
考虑在节点之间通过的斜率 -1 线。给定一棵二叉树,打印二叉树中属于同一行的所有对角线元素。
Input : Root of below tree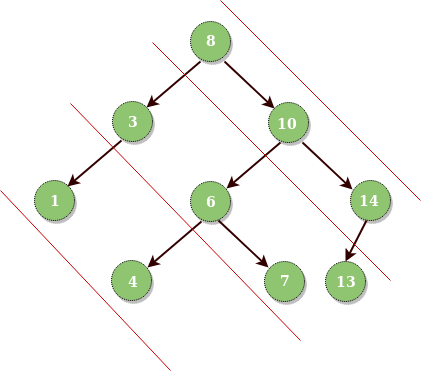
Output :
Diagonal Traversal of binary tree :
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4我们在下面的帖子中讨论了递归解决方案。
二叉树的对角遍历
在这篇文章中,讨论了迭代解决方案。这个想法是使用队列来仅存储当前节点的左子节点。打印当前节点的数据后,将当前节点设为其右子节点(如果存在)。
分隔符NULL用于标记下一个对角线的开始。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
/* C++ program to construct string from binary tree*/
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
child and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node */
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
void diagonalPrint(Node* root)
{
// base case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// inbuilt queue of Treenode
queue q;
// push root
q.push(root);
// push delimiter
q.push(NULL);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// if current is delimiter then insert another
// for next diagonal and cout nextline
if (temp == NULL) {
// if queue is empty return
if (q.empty())
return;
// output nextline
cout << endl;
// push delimiter again
q.push(NULL);
}
else {
while (temp) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
// if left child is present
// push into queue
if (temp->left)
q.push(temp->left);
// current equals to right child
temp = temp->right;
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
} Java
// Java program to con string from binary tree
import java.util.*;
class solution
{
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
// child and a pointer to right child
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
};
// Helper function that allocates a new node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
static void diagonalPrint(Node root)
{
// base case
if (root == null)
return;
// inbuilt queue of Treenode
Queue q= new LinkedList();
// add root
q.add(root);
// add delimiter
q.add(null);
while (q.size()>0) {
Node temp = q.peek();
q.remove();
// if current is delimiter then insert another
// for next diagonal and cout nextline
if (temp == null) {
// if queue is empty return
if (q.size()==0)
return;
// output nextline
System.out.println();
// add delimiter again
q.add(null);
}
else {
while (temp!=null) {
System.out.print( temp.data + " ");
// if left child is present
// add into queue
if (temp.left!=null)
q.add(temp.left);
// current equals to right child
temp = temp.right;
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(8);
root.left = newNode(3);
root.right = newNode(10);
root.left.left = newNode(1);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(14);
root.right.right.left = newNode(13);
root.left.right.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right.right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
}
}
//contributed by Arnab Kundu Python3
# Python3 program to construct string from binary tree
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.val = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print diagonal view
def diagonalprint(root):
# base case
if root is None:
return
# queue of treenode
q = []
# Append root
q.append(root)
# Append delimiter
q.append(None)
while len(q) > 0:
temp = q.pop(0)
# If current is delimiter then insert another
# for next diagonal and cout nextline
if not temp:
# If queue is empty then return
if len(q) == 0:
return
# Print output on nextline
print(' ')
# append delimiter again
q.append(None)
else:
while temp:
print(temp.val, end = ' ')
# If left child is present
# append into queue
if temp.left:
q.append(temp.left)
# current equals to right child
temp = temp.right
# Driver Code
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.left.right.left = Node(4)
root.left.right.right = Node(7)
diagonalprint(root)
# This code is contributed by Praveen kumarC#
// C# program to con string from binary tree
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG
{
// A binary tree node has data,
// pointer to left child and
// a pointer to right child
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
};
// Helper function that
// allocates a new node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// Iterative function to print diagonal view
static void diagonalPrint(Node root)
{
// base case
if (root == null)
return;
// inbuilt queue of Treenode
Queue q = new Queue();
// Enqueue root
q.Enqueue(root);
// Enqueue delimiter
q.Enqueue(null);
while (q.Count > 0)
{
Node temp = (Node) q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
// if current is delimiter then insert another
// for next diagonal and cout nextline
if (temp == null)
{
// if queue is empty return
if (q.Count == 0)
return;
// output nextline
Console.WriteLine();
// Enqueue delimiter again
q.Enqueue(null);
}
else
{
while (temp != null)
{
Console.Write( temp.data + " ");
// if left child is present
// Enqueue into queue
if (temp.left != null)
q.Enqueue(temp.left);
// current equals to right child
temp = temp.right;
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = newNode(8);
root.left = newNode(3);
root.right = newNode(10);
root.left.left = newNode(1);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(14);
root.right.right.left = newNode(13);
root.left.right.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right.right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduJavascript
Java
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
//Node
class Node{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
//Constructor for initializing the value of the node along with
//left and right pointers
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class DiagonalTraversal {
//root node
Node root = null;
//function to print in diagonal order
void traverse() {
//if the tree is empty, do not have to print
//anything
if(root == null)
return;
//if root is not empty, point curr node to the
//root node
Node curr = root;
//Maintain a queue to store left child
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
//continue till the queue is empty and curr is null
while(!q.isEmpty() || curr!=null) {
//if curr is null
//1. print the data of the curr node
//2. if left child is present, add it to the queue
//3. Move curr pointer to the right
if(curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.data+" ");
if(curr.left != null)
q.add(curr.left);
curr = curr.right;
}
//if curr is null, remove a node from the queue
//and point it to curr node
else {
curr = q.remove();
}
}
}
//Driver function
public static void main(String args[]) {
DiagonalTraversal tree = new DiagonalTraversal();
/* 8
/ \
3 10
/ \ \
1 6 14
/ \ /
4 7 13 */
//construction of the tree
tree.root = new Node(8);
tree.root.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.right = new Node(10);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(14);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
//function call
tree.traverse();
}
}
//This method is contributed by Likhita AVL C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
// Constructor for initializing the value
// of the node along with left and right pointers
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class DiagonalTraversal{
// Root node
Node root = null;
// Function to print in diagonal order
void traverse()
{
// If the tree is empty, do not have to print
// anything
if (root == null)
return;
// If root is not empty, point curr node to the
// root node
Node curr = root;
// Maintain a queue to store left child
Queue q = new Queue();
// Continue till the queue is empty
// and curr is null
while (q.Count != 0 || curr != null)
{
// If curr is null
// 1. print the data of the curr node
// 2. if left child is present, add it to the queue
// 3. Move curr pointer to the right
if (curr != null)
{
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
if (curr.left != null)
q.Enqueue(curr.left);
curr = curr.right;
}
// If curr is null, remove a node from
// the queue and point it to curr node
else
{
curr = q.Dequeue();
}
}
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
DiagonalTraversal tree = new DiagonalTraversal();
/* 8
/ \
3 10
/ \ \
1 6 14
/ \ /
4 7 13 */
// Construction of the tree
tree.root = new Node(8);
tree.root.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.right = new Node(10);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(14);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
// Function call
tree.traverse();
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127 Javascript
输出:
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4方法:不使用分隔符
就像水平顺序遍历一样,使用队列。需要进行少量修改。
if(curr.left != null) -> add it to the queue
and move curr pointer to right of curr.
if curr = null, then remove a node from queue.执行:
Java
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
//Node
class Node{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
//Constructor for initializing the value of the node along with
//left and right pointers
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class DiagonalTraversal {
//root node
Node root = null;
//function to print in diagonal order
void traverse() {
//if the tree is empty, do not have to print
//anything
if(root == null)
return;
//if root is not empty, point curr node to the
//root node
Node curr = root;
//Maintain a queue to store left child
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
//continue till the queue is empty and curr is null
while(!q.isEmpty() || curr!=null) {
//if curr is null
//1. print the data of the curr node
//2. if left child is present, add it to the queue
//3. Move curr pointer to the right
if(curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.data+" ");
if(curr.left != null)
q.add(curr.left);
curr = curr.right;
}
//if curr is null, remove a node from the queue
//and point it to curr node
else {
curr = q.remove();
}
}
}
//Driver function
public static void main(String args[]) {
DiagonalTraversal tree = new DiagonalTraversal();
/* 8
/ \
3 10
/ \ \
1 6 14
/ \ /
4 7 13 */
//construction of the tree
tree.root = new Node(8);
tree.root.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.right = new Node(10);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(14);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
//function call
tree.traverse();
}
}
//This method is contributed by Likhita AVL
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
// Constructor for initializing the value
// of the node along with left and right pointers
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class DiagonalTraversal{
// Root node
Node root = null;
// Function to print in diagonal order
void traverse()
{
// If the tree is empty, do not have to print
// anything
if (root == null)
return;
// If root is not empty, point curr node to the
// root node
Node curr = root;
// Maintain a queue to store left child
Queue q = new Queue();
// Continue till the queue is empty
// and curr is null
while (q.Count != 0 || curr != null)
{
// If curr is null
// 1. print the data of the curr node
// 2. if left child is present, add it to the queue
// 3. Move curr pointer to the right
if (curr != null)
{
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
if (curr.left != null)
q.Enqueue(curr.left);
curr = curr.right;
}
// If curr is null, remove a node from
// the queue and point it to curr node
else
{
curr = q.Dequeue();
}
}
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
DiagonalTraversal tree = new DiagonalTraversal();
/* 8
/ \
3 10
/ \ \
1 6 14
/ \ /
4 7 13 */
// Construction of the tree
tree.root = new Node(8);
tree.root.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.right = new Node(10);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(14);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
// Function call
tree.traverse();
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127
Javascript
输出
8 10 14 3 6 7 13 1 4 ?list=PLqM7alHXFySHCXD7r1J0ky9Zg_GBB1dbk