Android – Jetpack Compose 中的互操作性
在 Jetpack compose 中创建 UI 很有趣,但如果我们想在我们的应用程序中编写一些 Jetpack compose 尚不支持的功能(如谷歌地图、admob)或一些尚未支持的第三方库,它可能会成为障碍迁移到 Compose。幸运的是,Jetpack Compose 支持各种互操作性 API ,以利用 Jetpack compose 中的传统视图,反之亦然。在本文中,我们将在我们的可组合中使用传统的 android视图。
先决条件:
- Jetpack Compose 的知识。
- Kotlin 知识
- 了解Android的View。
我们将首先编写一个增加计数器按钮的简单撰写应用程序。
分步实施
第 1 步:创建一个新项目
首先在 Android Studio 中创建一个新的 compose 项目。打开 Android Studio 并创建一个新的 compose 项目。
第 2 步:使用 MainActivity.kt 文件
创建一个可组合函数并编写以下代码来制作计数器。
Kotlin
@Composable
fun InteroperabilityExample() {
// A count state variable
var counter by remember {
mutableStateOf(0)
}
// Column
Column(
Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
// center the children
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center
) {
// Text Composable showing current counter
Text("Counter in Compose= $counter")
Text(text = "This text is a composable")
// Button to change the counter
Button(onClick = { counter++ }) {
Text(text = "Compose button to increase counter")
}
}
}Kotlin
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
JetpackComposeInteropTheme(darkTheme = false) {
Surface(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
color = MaterialTheme.colors.background
) {
// Out Composable function
InteroperabilityExample()
}
}
}
}
}XML
Kotlin
AndroidView(
actory = { context ->
// Linear layout in view system
LinearLayout(context).apply {
// setting orientation to vertical
orientation = LinearLayout.VERTICAL
// adding text view to layout
// using [addView] provided by [ViewGroup]
addView(
// TextView from View system
// creating text view and using apply
// scope function to add properties to text view
TextView(context).apply {
// setting text
text = "This is a Traditional text view "
// aligning text to center
textAlignment = TextView.TEXT_ALIGNMENT_CENTER
// setting text color
setTextColor(resources.getColor(R.color.black))
})
// adding text to display Counter
addView(
// Another textView from View System
TextView(context).apply {
// setting text
text = "Counter in view = $counter"
// assign Id to text view
id = R.id.counter1
// aligning text to center
textAlignment = TextView.TEXT_ALIGNMENT_CENTER
// setting text color
setTextColor(resources.getColor(R.color.black))
})
// Add another view to layout : Button
addView(
android.widget.Button(context).apply {
// setting text
text = "Traditional button to increase counter"
// setting text color
setTextColor(resources.getColor(R.color.white))
// set background color
setBackgroundColor(resources.getColor(R.color.purple_500))
// some padding to button
setPadding(20, 20, 20, 20)
// on click listener
setOnClickListener {
counter++
}
})
}
},
// The callback to be invoked after the layout is inflated.
update = {
// update counter when count changes
it.findViewById(R.id.counter1).text = "Counter is $counter"
},
// we can use modifier in AndroidView
// setting green border
modifier = Modifier.border(3.dp, Color.Green)
) 并从设置的内容中调用这个可组合的
科特林
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
JetpackComposeInteropTheme(darkTheme = false) {
Surface(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
color = MaterialTheme.colors.background
) {
// Out Composable function
InteroperabilityExample()
}
}
}
}
}
当我们运行这个应用程序时,我们会看到一个简单的计数器应用程序,当我们单击按钮时它会增加计数器
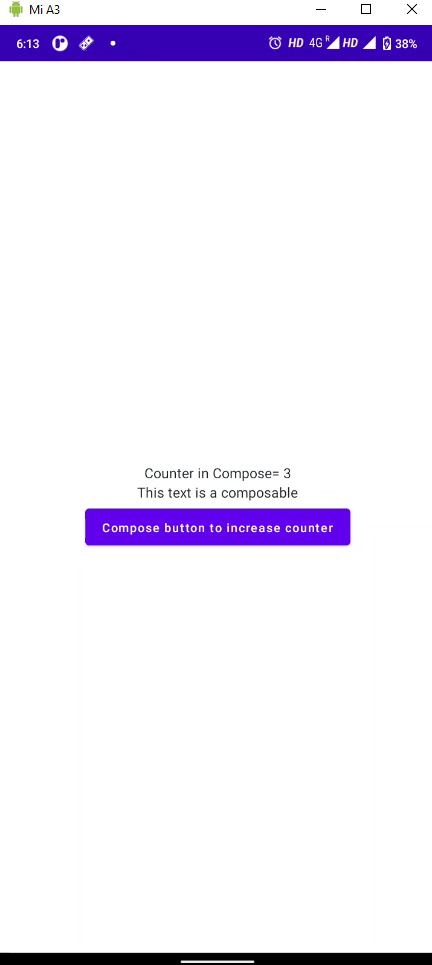
现在我们将在这个可组合函数中添加传统视图并增加相同的计数器。在此之前,我们需要创建ids.xml以使用 id 引用视图来更新 Textview 中的数据。展开 res > values 并右键单击它, new > Value Resource file并创建一个名为ids.xml的文件,然后将其写入即可。
XML
在 Button Composable 下方添加此代码以在 Composable 中添加 View
科特林
AndroidView(
actory = { context ->
// Linear layout in view system
LinearLayout(context).apply {
// setting orientation to vertical
orientation = LinearLayout.VERTICAL
// adding text view to layout
// using [addView] provided by [ViewGroup]
addView(
// TextView from View system
// creating text view and using apply
// scope function to add properties to text view
TextView(context).apply {
// setting text
text = "This is a Traditional text view "
// aligning text to center
textAlignment = TextView.TEXT_ALIGNMENT_CENTER
// setting text color
setTextColor(resources.getColor(R.color.black))
})
// adding text to display Counter
addView(
// Another textView from View System
TextView(context).apply {
// setting text
text = "Counter in view = $counter"
// assign Id to text view
id = R.id.counter1
// aligning text to center
textAlignment = TextView.TEXT_ALIGNMENT_CENTER
// setting text color
setTextColor(resources.getColor(R.color.black))
})
// Add another view to layout : Button
addView(
android.widget.Button(context).apply {
// setting text
text = "Traditional button to increase counter"
// setting text color
setTextColor(resources.getColor(R.color.white))
// set background color
setBackgroundColor(resources.getColor(R.color.purple_500))
// some padding to button
setPadding(20, 20, 20, 20)
// on click listener
setOnClickListener {
counter++
}
})
}
},
// The callback to be invoked after the layout is inflated.
update = {
// update counter when count changes
it.findViewById(R.id.counter1).text = "Counter is $counter"
},
// we can use modifier in AndroidView
// setting green border
modifier = Modifier.border(3.dp, Color.Green)
)
现在,当您运行此应用程序时,您将看到下面的 View System 中的 LinearLayout、TextView、Button 组成 Text 和 Button。

当您单击任何按钮时,它将增加相同的计数器并更新 Composable 和 TextView。

使用 AndroidView,我们还可以在我们的撰写应用程序中添加诸如谷歌地图、Admob 之类的库。