反向链式法则
积分是微积分理论的重要组成部分。它们在计算任意复杂函数的面积和体积时非常有用,否则这些函数很难计算,并且通常是函数所包围的面积或体积的错误近似值。积分是微分的反面,这就是为什么它们被称为反导数。有标准函数的积分公式,但这些公式通常不会扩展到函数变得复杂的情况。一种这样的规则是替换规则。让我们详细研究一下这个规则。
反向链式法则
导数的链式法则允许计算涉及一个或多个标准基本函数的非常复杂的函数的导数。对于此类场景中的集成,有多种技巧或方法可以简化计算。对于某些特殊类别的函数,使用反向链式法则。此规则也称为“替换规则”或“ u 替换规则” 。要使用此规则,函数应具有以下形式,
∫f(g(x))g'(x)dx
请注意,在给定形式的函数中,函数g(x) 及其导数 g'(x) 都存在。此类功能的一些示例是
∫cos(x 2 ).2xdx
在这种情况下,g(x) = x 2, f(x) = cos(x) 和 g'(x) = 2x。现在要使用替换规则计算此类函数的积分,需要稍作修改。考虑这些函数的一般形式:
∫f(g(x))g'(x)dx
设 u = g(x),对 x 求微分,
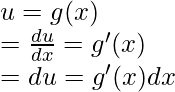
在前面的等式中使用这个结果,
∫f(u)du
现在这个积分可以通过将 u 的值代入最终结果来计算和完成。
∫f(g(x))g'(x)dx = ∫f(u)du, where u = g(x)
使用反向链式法则计算积分
必须在给定的积分函数中寻找可能的函数及其导数。想到的自然问题是如何知道正确的替换。没有确定正确替换的规则。识别正确替换的直觉是通过实践培养的。
示例 1:计算 ∫cos(x 2 ).2xdx 的积分。
回答:
F(x) = ∫cos(x2).2xdx
Look for a function, and it’s derivative in the whole function. In this case,
g(x) = x2 and g'(x) = 2x
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = x2
⇒ du = 2xdx
F(x) = ∫cos(u)du
⇒F(x) = sin(u) + C
⇒F(x) = sin(x2) + C
现在考虑一种不同类型的积分:
示例 2:计算 ∫tan(x)dx 的积分。
回答:
F(x) = ∫tan(x)dx
This can be re-written as,
![]()
Notice, here g(x) = cos(x) and g'(x) = -sin(x)
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = cos(x)
⇒ du = -sin(x)dx
⇒ -du = sin(x)dx
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ F(x) = -ln(u) + C
⇒ F(x) = -ln(cos(x)) + C
使用反向链规则时要避免的错误
从原始积分函数中选择“u”函数时应该小心。如果不仔细选择,积分可能会变得过于复杂而不是简化自身。此外,在某些情况下,u 函数不会立即可见。以下列表列出了在使用反向链规则解决整体问题时应牢记的一些事项。
1. For applying the reverse chain rule, the integral must be re-written in the form,
w(u(x)).u'(x)
Where the u-function is the inner function of the composite factor.
2. While integrating the composite function, the outer function should only be integrated after properly substituting the u-function and its derivatives.
3. Sometimes, in some situations, the integral must be divided/multiplied by some constant factors of variables or the function may need rearranging. For example,
F = ∫tan(x)dx
In this case, the u-function is not completely clear. So, tan(x) is rewritten in terms of sin(x) and cos(x).
F = ![]()
Now it is clear that cos(x) is the u-function.
示例问题
问题 1:计算∫cos(e x ).e x dx 的积分。
回答:
F(x) = ∫cos(ex).exdx
Look for a function, and it’s derivative in the whole function. In this case,
g(x) = ex and g'(x) = ex
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = ex
⇒ du = exdx
F(x) = ∫cos(u)du
⇒F(x) = sin(u) + C
⇒F(x) = sin(ex) + C
问题 2:计算 ∫(6x + 4) 6 .6dx 的积分。
回答:
F(x) = ∫(6x + 4)6.6dx.
Look for a function, and it’s derivative in the whole function. In this case,
g(x) = 6x + 4 and g'(x) = 6
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = 6x + 4
⇒ du = 6dx
F(x) = ∫u6du
⇒F(x) = ![]() + C
+ C
⇒F(x) = ![]() + C
+ C
问题 3:计算 ∫(x 2 + 1) 3 .2xdx 的积分。
回答:
F(x) = ∫(x2 + 1)3.2xdx.
Look for a function, and it’s derivative of that function in the original function. In this case,
g(x) = x2 + 1 and g'(x) = 2x
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = x2 + 1
⇒ du = 2xdx
F(x) = ∫u3du
⇒F(x) = 4![]() + C
+ C
⇒F(x) = ![]() + C
+ C
问题 4:计算积分![]() .
.
回答:
F(x) = ![]()
Look for a function, and it’s a derivative of that function in the original function. In this case,
g(x) = x2 + 1 and g'(x) = 2x
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = x2 + 1
⇒ du = 2xdx
F(x) = ![]()
⇒F(x) = ![]()
⇒F(x) = ![]()
问题 5:计算积分![]() .
.
回答:
F(x) = ![]()
Look for a function, and it’s a derivative of that function in the original function. In this case,
g(x) = x + 3 and g'(x) = 1
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = x + 3
⇒ du = dx
F(x) = ![]()
⇒F(x) = ![]()
⇒F(x) = ln(x + 3) + C
问题 6:计算积分![]()
回答:
F(x) = ![]()
Look for a function, and it’s derivative in the whole function. In this case,
g(x) = ln(x) and g'(x) = ![]()
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = ln(x)dx
⇒ du = ![]()
F(x) = ∫u2du
⇒F(x) = ![]() + C
+ C
⇒F(x) = ![]() + C
+ C
问题 7:计算 ∫sin(1-x)cos(1-x)dx 的积分
回答:
F(x) = ∫sin(1-x)cos(1-x)dx
This function can be re-written as,
F(x) = ![]()
Look for a function, and it’s derivative in the whole function. In this case,
g(x) = 2(x -1) and g'(x) = 2
Substituting, u = g(x)
⇒ u = 2(x – 1)
⇒ du = 2dx
F(x) = ![]()
⇒F(x) = ![]() + C
+ C
⇒F(x) = ![]() + C
+ C