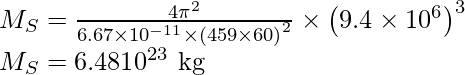卫星结合能
人类在生命的早期就知道所有的物质物品都有一种被地球吸引的自然趋势。任何抛出的东西都会掉到地上,上山比下山更累,上面的云雨落到地上,还有几个额外的例子。
地球的卫星是围绕地球运行的天体。它们的运动类似于行星围绕太阳运行的轨道,因此开普勒建立的行星运动规则同样有效并适用于它们。地球围绕地球的卫星轨道是圆形或椭圆形。月球是地球唯一的天然卫星。由于技术进步,包括印度在内的许多国家已经能够发射人造地球卫星,用于电信、地球物理学和气象学等领域。
什么是万有引力?
万有引力,或简称为引力,是将两个物体吸引在一起的力。宇宙中的所有物体都以一定的力量相互吸引,但由于物体之间的距离很远,这种力量在大多数情况下都太微弱而无法注意到。此外,虽然重力的范围是无限的,但随着物体移动得更远,这种效果会减弱。
引力势能:以某种姿势储存在体内的能量称为势能。如果一个粒子的位置由于作用在其上的力而发生变化,则其势能的变化等于该力对物体所做的功。重力势能是由重力产生的物体的势能。卫星与地球之间的势能表达式可以表示为:
PE = -GMm / r
卫星结合能或轨道卫星能量
Binding Energy is the minimal amount of energy that must be delivered to the satellite in order to free of the planet’s gravitational attraction or the gravitational influence of the planet.
术语“结合能”是指将卫星与地球结合的能量。卫星和行星之间的引力将被这种结合能克服。
考虑一颗围绕地球沿圆形路径旋转的卫星。地球与卫星之间的万有引力提供了必要的向心力,使卫星保持在稳定的圆形轨道上旋转。卫星在绕地球运行时有两种类型的机械能。由于它的轨道运动,存在动能,并且由于它在地球的引力场中的位置势能存在能量。
卫星结合能的推导
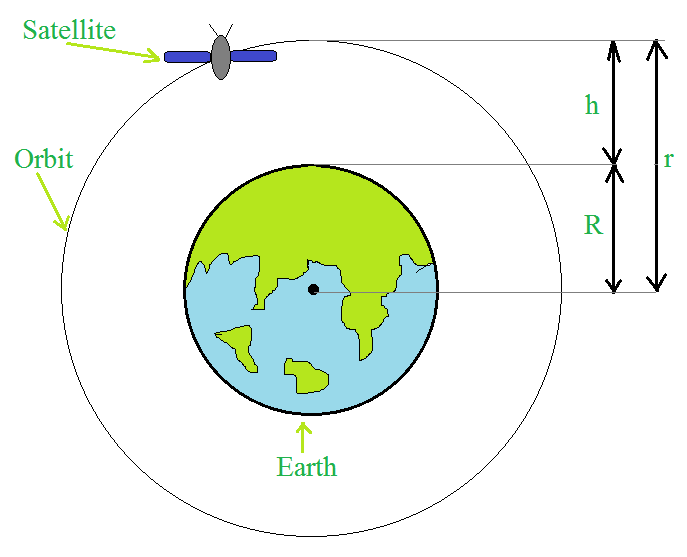
地球表面上方的卫星。
设,地球质量为 M,卫星质量为 m,地球半径为 R,卫星距地表高度为 h,卫星圆轨道半径为 r 或(R+h),卫星的临界速度为 v。
向心力等于重力,因为它提供了圆周运动所需的向心力,即
其中 G 是万有引力常数。
所以,动能可以写成,
现在,卫星和地球之间的势能可以给出为,
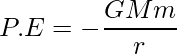
这里的负号表示作用在卫星和地球之间的力是有吸引力的。 .然而,KE 的大小是 PE 的一半,因此总 E 将是动能和势能的总和。
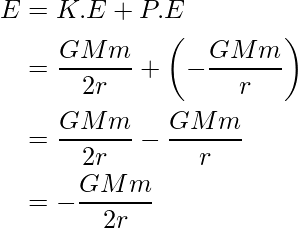
上面的表达式是卫星在一个稳定的圆形轨道上绕地球旋转的结合能。
静止在地球表面的卫星结合能的表达式。
设静止卫星的质量为 m,因此动能为零。
现在,势能可以表示为,
![]()
总E将是动能和势能之和,
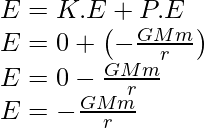
这里的负号表示作用在卫星和地球之间的力是有吸引力的。
地球卫星
地球卫星是围绕地球运行的天体。天体的运动很像围绕太阳运行的行星的运动,因此开普勒的行星运动定律也适用于它们。一般来说,地球的卫星轨道是圆形或椭圆形的。月球是地球唯一的天然卫星,轨道近乎圆形,时间周期约为27.3天,几乎相当于月球绕自转的周期。
让一颗卫星在距离地球中心 (R E + h) 的圆形轨道上,其中 R E是地球的半径。如果 m 是卫星的质量,则卫星的速度由下式给出
![]()
在每个轨道上,卫星以速度 V 移动距离 2π(R E + h)。它的时间周期 T 由下式给出
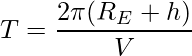
代入上式中V的值,
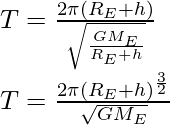
失重
地球吸引物体的力称为它的重量。当我们站在一个表面上时,我们会意识到自己的重量,因为表面会施加相反的力让我们保持静止。当我们使用悬挂在固定位置(例如天花板)的弹簧秤来确定物体的重量时,同样的原理也适用。除非受到与重力相反的力,否则物体会下落。弹簧正是将此力施加在物体上。这是因为物体的万有引力将弹簧向下拉了一点,然后弹簧对物体施加垂直向上的力。
想象一下,天平的顶端不再连接到房间的顶部天花板。物体以及弹簧的两端以相同的 g 加速度移动。弹簧没有伸长,也没有对物体施加任何向上的力,物体由于重力而在 g 处下落。因为弹簧根本没有伸长,所以弹簧秤的读数为零。因为物体上没有向上的力,如果是人,他或她不会感觉到自己的重量。因此,当一个物体自由落体时,它是失重的,这种现象称为失重。

围绕地球运行的卫星的每一部分和每一个地块都有一个朝向地球中心的加速度,该加速度等于地球在该位置的重力加速度值。结果,卫星内部的一切都在自由落体。就好像一个人从高处坠落到地面一样。结果,卫星内的人类没有重力感。因为重力为人类定义了垂直方向,所以他们没有水平或垂直方向;所有的方向对他们来说都是一样的。宇航员乘坐卫星漂浮在太空中的图像证明了这一点。
样题
问题 1:一颗 400 kg 的卫星在绕地球半径为 2R E的圆形轨道上。将它转移到半径为 4R E的圆形轨道需要多少能量?动能和势能有什么变化?
解决方案:
Given,
The mass of the satellite is 400 kg.
The initial radius of the orbit is 2RE.
The final radius of the orbit is 4RE.
The expression for the binding energy is,
![]() ,
,
So, the binding energy of the satellite at a radius of orbit 2RE is
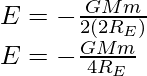
so, the binding energy of the satellite at a radius of orbit 4RE is
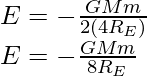
The change in the total energy binding energy is
![]()
Substitute the initial and final energy in the above expression,
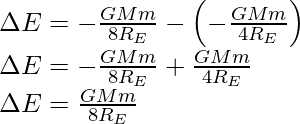
Rearrange the expression and substitute all the values,
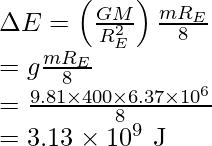
The kinetic energy is reduced and equal to minus of ∆E,
![]()
And the change in potential energy is twice the change in the binding energy,
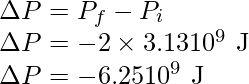
问题2:定义卫星的结合能并推导出其表达式。
解决方案:
Binding Energy is the minimal amount of energy that must be delivered to the satellite in order to free of the planet’s gravitational attraction or the gravitational influence of the planet. The term “binding energy” refers to the energy that binds the satellite to the Earth. This energy will overcome the gravitational force of attraction between the satellite and the Earth.
Let, the mass of the earth is M, the mass of the satellite is m, the radius of the earth is R, the height of the satellite from the earth surface is h, the radius of the circular orbit of the satellite is r or (R+h), and the critical velocity of the satellite is v.
The gravitational force provides the necessary centripetal force required for the circular motion. So, a centripetal force equal to gravitational force i.e.
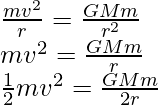
where G is the Universal gravitational constant.
So, the kinetic energy can be written as,
![]()
Now, the potential energy between satellite and the earth can be given as,
![]()
Here the negative sign represents the force that acts between the satellite and earth is attractive. . However, the magnitude of the K.E is half the P.E, so that the total E will be the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy.
The above expression is the binding energy of the satellite revolving around the earth in a stable circular orbit.
问题 3:什么是牛顿万有引力定律?
解决方案:
Every particle in the universe attracts all other particles with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their distance.
According to the law a force acting along the line connecting the two points attracts every other point mass, . The force is proportional to the product of the two masses, and it is inversely proportional to the square of their distance.
![]()
where F is the gravitational force acting between two objects, M and m are the masses of the objects, r is the distance between the centers of their masses, and G is the gravitational constant.
问题 4:陈述开普勒行星运动定律。
解决方案:
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion state that:
- The Sun is at one of the elliptical orbits’ focal points, which all planets follow.
- The radius vector drawn from the Sun to a planet covers the same area in the same amount of time. Because of this the gravitational force of the planet is central, so angular momentum is conserved.
- The square of a planet’s orbital period is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of the planet’s elliptical orbit. The period T and radius R of a planet’s circular orbit around the Sun are related by
![]()
where Ms is the mass of the Sun. Most planets have nearly circular orbits about the Sun. For elliptical orbits, the above equation is valid if R is replaced by the semi-major axis, a.
问题 5:火星有两颗卫星,火卫一和德尔莫斯。火卫一的周期为 7 小时 39 分钟,轨道半径为 9.4 × 10 3公里。计算火星的质量。
解决方案:
Given,
Time is equal to 7 hours, 39 minutes i.e. 459 min and this is equal to (459×60) sec.
An orbital radius is 9.4 ×103 km i.e. 9.4 ×106 m.
According to Kepler’s laws
![]()
Rearrange the above expression,
![]()
Substitute the values in the above expression,