图的深度优先搜索或 DFS
图的深度优先遍历(或搜索)类似于树的深度优先遍历。这里唯一的问题是,与树不同,图可能包含循环(一个节点可能会被访问两次)。为避免多次处理节点,请使用布尔访问数组。
例子:
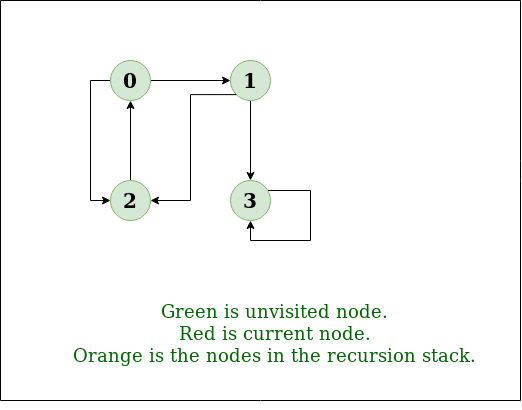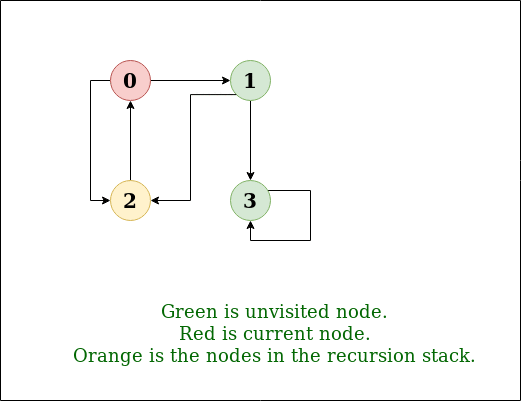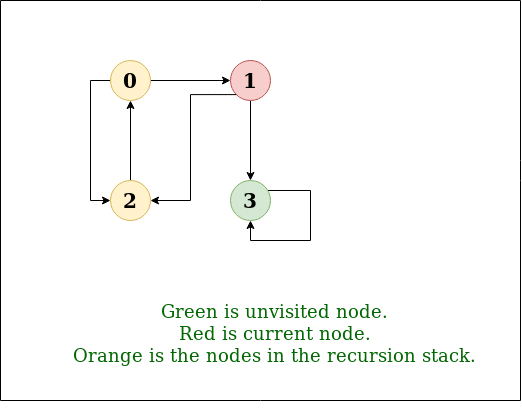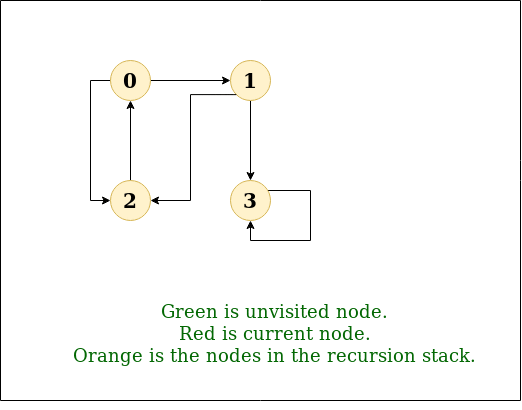
Input: n = 4, e = 6
0 -> 1, 0 -> 2, 1 -> 2, 2 -> 0, 2 -> 3, 3 -> 3
Output: DFS from vertex 1 : 1 2 0 3
Explanation:
DFS Diagram:
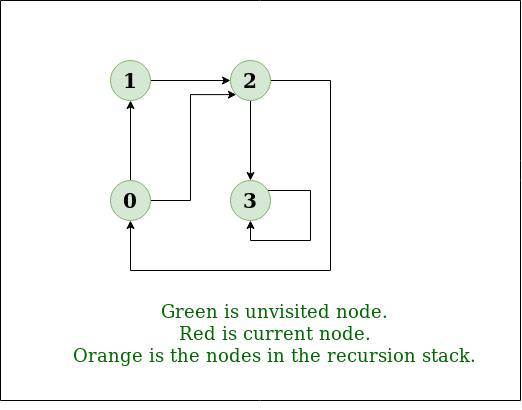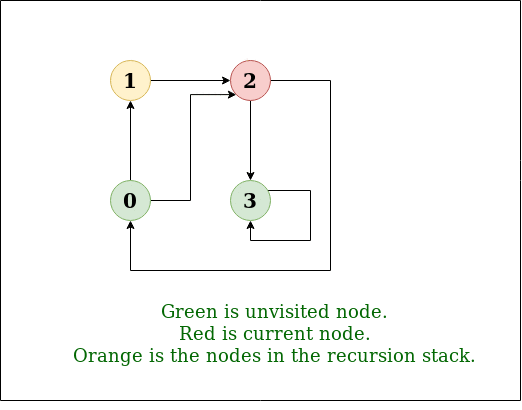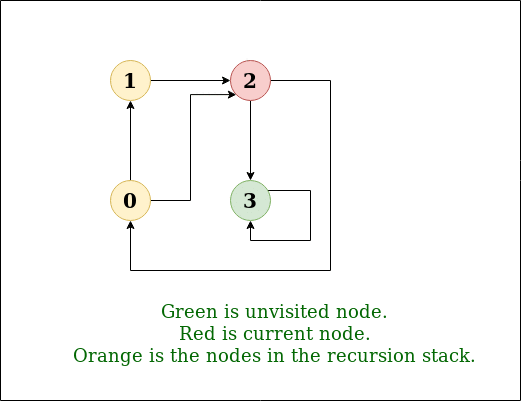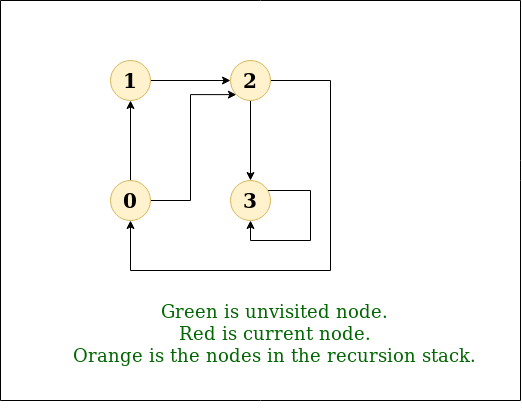
Input: n = 4, e = 6
2 -> 0, 0 -> 2, 1 -> 2, 0 -> 1, 3 -> 3, 1 -> 3
Output: DFS from vertex 2 : 2 0 1 3
Explanation:
DFS Diagram:
先决条件:
有关深度优先遍历的所有应用,请参阅此帖子。
方法:
深度优先搜索是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图数据结构的算法。该算法从根节点开始(在图的情况下选择某个任意节点作为根节点)并在回溯之前沿着每个分支尽可能地探索。所以基本思路是从根或任意一个节点开始,标记该节点,移动到相邻的未标记节点,继续这个循环,直到没有未标记的相邻节点。然后回溯并检查其他未标记的节点并遍历它们。最后,打印路径中的节点。
算法:
创建一个递归函数,该函数接受节点的索引和访问过的数组。
- 将当前节点标记为已访问并打印该节点。
- 遍历所有相邻和未标记的节点,并以相邻节点的索引调用递归函数。
执行:
下面是简单的深度优先遍历的实现。 C++ 实现使用图的邻接表表示。 STL 的列表容器用于存储相邻节点的列表。
C++
// C++ program to print DFS traversal from
// a given vertex in a given graph
#include
using namespace std;
// Graph class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph {
public:
map visited;
map > adj;
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// DFS traversal of the vertices
// reachable from v
void DFS(int v);
};
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
void Graph::DFS(int v)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and
// print it
visited[v] = true;
cout << v << " ";
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent
// to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFS(*i);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g;
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
cout << "Following is Depth First Traversal"
" (starting from vertex 2) \n";
g.DFS(2);
return 0;
}
// improved by Vishnudev C Java
// Java program to print DFS
// mtraversal from a given given
// graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph {
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for
// Adjacency List Representation
private LinkedList adj[];
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v's list.
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v, boolean visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
System.out.print(v + " ");
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this
// vertex
Iterator i = adj[v].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do DFS traversal.
// It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void DFS(int v)
{
// Mark all the vertices as
// not visited(set as
// false by default in java)
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
// Call the recursive helper
// function to print DFS
// traversal
DFSUtil(v, visited);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
System.out.println(
"Following is Depth First Traversal "
+ "(starting from vertex 2)");
g.DFS(2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# Python3 program to print DFS traversal
# from a given given graph
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph using
# adjacency list representation
class Graph:
# Constructor
def __init__(self):
# default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# A function used by DFS
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as visited
# and print it
visited.add(v)
print(v, end=' ')
# Recur for all the vertices
# adjacent to this vertex
for neighbour in self.graph[v]:
if neighbour not in visited:
self.DFSUtil(neighbour, visited)
# The function to do DFS traversal. It uses
# recursive DFSUtil()
def DFS(self, v):
# Create a set to store visited vertices
visited = set()
# Call the recursive helper function
# to print DFS traversal
self.DFSUtil(v, visited)
# Driver code
# Create a graph given
# in the above diagram
g = Graph()
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 3)
print("Following is DFS from (starting from vertex 2)")
g.DFS(2)
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# program to print DFS traversal
// from a given graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph {
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for
// Adjacency List Representation
private List[] adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[ v ];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Function to Add an edge into the graph
void AddEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w); // Add w to v's list.
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v, bool[] visited)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
// and print it
visited[v] = true;
Console.Write(v + " ");
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
List vList = adj[v];
foreach(var n in vList)
{
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do DFS traversal.
// It uses recursive DFSUtil()
void DFS(int v)
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
// (set as false by default in c#)
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
// Call the recursive helper function
// to print DFS traversal
DFSUtil(v, visited);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.AddEdge(0, 1);
g.AddEdge(0, 2);
g.AddEdge(1, 2);
g.AddEdge(2, 0);
g.AddEdge(2, 3);
g.AddEdge(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(
"Following is Depth First Traversal "
+ "(starting from vertex 2)");
g.DFS(2);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
// This code is contributed by techno2mahi Javascript
C++
// C++ program to print DFS
// traversal for a given given
// graph
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph {
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v);
public:
map visited;
map > adj;
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// prints DFS traversal of the complete graph
void DFS();
};
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
cout << v << " ";
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i);
}
// The function to do DFS traversal. It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void Graph::DFS()
{
// Call the recursive helper function to print DFS
// traversal starting from all vertices one by one
for (auto i : adj)
if (visited[i.first] == false)
DFSUtil(i.first);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g;
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 9);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(9, 3);
cout << "Following is Depth First Traversal \n";
g.DFS();
return 0;
}
// improved by Vishnudev C Java
// Java program to print DFS
// traversal from a given given
// graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph {
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for
// Adjacency List Representation
private LinkedList adj[];
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v's list.
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v, boolean visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
System.out.print(v + " ");
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this
// vertex
Iterator i = adj[v].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do DFS traversal. It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited(set as
// false by default in java)
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
// Call the recursive helper function to print DFS
// traversal starting from all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
if (visited[i] == false)
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
System.out.println(
"Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
'''Python program to print DFS traversal for complete graph'''
from collections import defaultdict
# this class represents a directed graph using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
# Constructor
def __init__(self):
# default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# Function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# A function used by DFS
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited.add(v)
print(v,end=" ")
# recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for neighbour in self.graph[v]:
if neighbour not in visited:
self.DFSUtil(neighbour, visited)
# The function to do DFS traversal. It uses recursive DFSUtil
def DFS(self):
# create a set to store all visited vertices
visited = set()
# call the recursive helper function to print DFS traversal starting from all
# vertices one by one
for vertex in self.graph:
if vertex not in visited:
self.DFSUtil(vertex, visited)
# Driver code
# create a graph given in the above diagram
print("Following is Depth First Traversal \n")
g = Graph()
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 3)
g.DFS()
# Improved by Dheeraj KumarC#
// C# program to print DFS
// traversal from a given given
// graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
public class Graph {
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for
// Adjacency List Representation
private List[] adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[ v ];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w); // Add w to v's list.
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v, bool[] visited)
{
// Mark the current
// node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
Console.Write(v + " ");
// Recur for all the
// vertices adjacent to this
// vertex
foreach(int i in adj[v])
{
int n = i;
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do
// DFS traversal. It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited(set as
// false by default in java)
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
// Call the recursive helper
// function to print DFS
// traversal starting from
// all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
if (visited[i] == false)
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(
"Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 Javascript
输出:
Following is Depth First Traversal (starting from vertex 2)
2 0 1 3复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(V + E),其中 V 是顶点数,E 是图中的边数。
- 空间复杂度: O(V),因为需要一个额外访问的大小为 V 的数组。
处理断开连接的图:
- 解决方案:
这将通过处理极端案例来实现。
上面的代码仅遍历从给定源顶点可到达的顶点。从给定顶点可能无法到达所有顶点,如在断开连接图中。要对此类图进行完整的 DFS 遍历,请在 DFS 之后从所有未访问的节点运行 DFS。
递归函数保持不变。 - 算法:
- 创建一个递归函数,该函数接受节点的索引和访问过的数组。
- 将当前节点标记为已访问并打印该节点。
- 遍历所有相邻和未标记的节点,并以相邻节点的索引调用递归函数。
- 从 0 到顶点数循环,检查该节点是否在之前的 DFS 中未被访问,用当前节点调用递归函数。
执行:
C++
// C++ program to print DFS
// traversal for a given given
// graph
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph {
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v);
public:
map visited;
map > adj;
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// prints DFS traversal of the complete graph
void DFS();
};
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
cout << v << " ";
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i);
}
// The function to do DFS traversal. It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void Graph::DFS()
{
// Call the recursive helper function to print DFS
// traversal starting from all vertices one by one
for (auto i : adj)
if (visited[i.first] == false)
DFSUtil(i.first);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g;
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 9);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(9, 3);
cout << "Following is Depth First Traversal \n";
g.DFS();
return 0;
}
// improved by Vishnudev C
Java
// Java program to print DFS
// traversal from a given given
// graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph {
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for
// Adjacency List Representation
private LinkedList adj[];
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v's list.
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v, boolean visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
System.out.print(v + " ");
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this
// vertex
Iterator i = adj[v].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do DFS traversal. It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited(set as
// false by default in java)
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
// Call the recursive helper function to print DFS
// traversal starting from all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
if (visited[i] == false)
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
System.out.println(
"Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija
Python3
'''Python program to print DFS traversal for complete graph'''
from collections import defaultdict
# this class represents a directed graph using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
# Constructor
def __init__(self):
# default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# Function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# A function used by DFS
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited.add(v)
print(v,end=" ")
# recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for neighbour in self.graph[v]:
if neighbour not in visited:
self.DFSUtil(neighbour, visited)
# The function to do DFS traversal. It uses recursive DFSUtil
def DFS(self):
# create a set to store all visited vertices
visited = set()
# call the recursive helper function to print DFS traversal starting from all
# vertices one by one
for vertex in self.graph:
if vertex not in visited:
self.DFSUtil(vertex, visited)
# Driver code
# create a graph given in the above diagram
print("Following is Depth First Traversal \n")
g = Graph()
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 3)
g.DFS()
# Improved by Dheeraj Kumar
C#
// C# program to print DFS
// traversal from a given given
// graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
public class Graph {
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for
// Adjacency List Representation
private List[] adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[ v ];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w); // Add w to v's list.
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v, bool[] visited)
{
// Mark the current
// node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
Console.Write(v + " ");
// Recur for all the
// vertices adjacent to this
// vertex
foreach(int i in adj[v])
{
int n = i;
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do
// DFS traversal. It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited(set as
// false by default in java)
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
// Call the recursive helper
// function to print DFS
// traversal starting from
// all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
if (visited[i] == false)
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(
"Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
输出:
Following is Depth First Traversal
0 1 2 3 9复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(V + E),其中 V 是顶点数,E 是图中的边数。
- 空间复杂度: O(V),因为需要一个额外访问的大小为 V 的数组。
https://youtu.be/Y40bRyPQQr0
- DFS 的应用。
- 图的广度优先遍历
- 最近关于 DFS 的文章