图的迭代深度优先遍历
图的深度优先遍历(或搜索)类似于树的深度优先遍历(DFS)。这里唯一的问题是,与树不同,图可能包含循环,因此一个节点可能会被访问两次。为避免多次处理节点,请使用布尔访问数组。
例子:
Input: n = 4, e = 6
0 -> 1, 0 -> 2, 1 -> 2, 2 -> 0, 2 -> 3, 3 -> 3
Output: DFS from vertex 1 : 1 2 0 3
Explanation:
DFS Diagram:
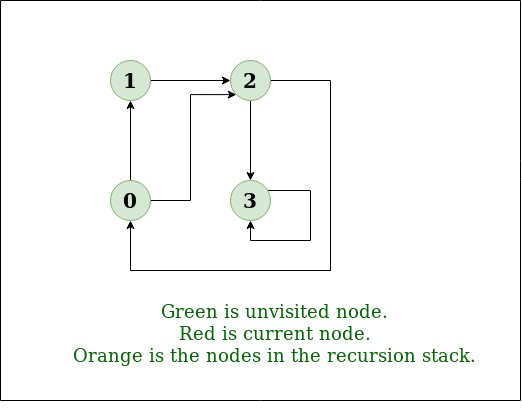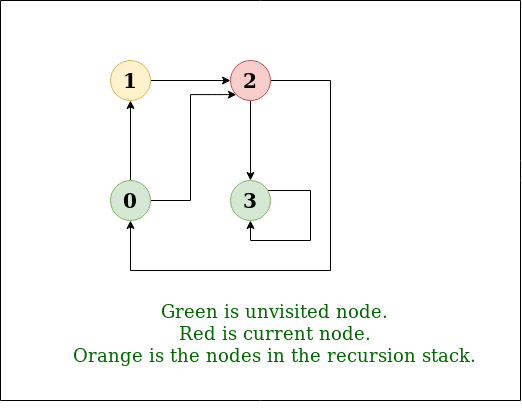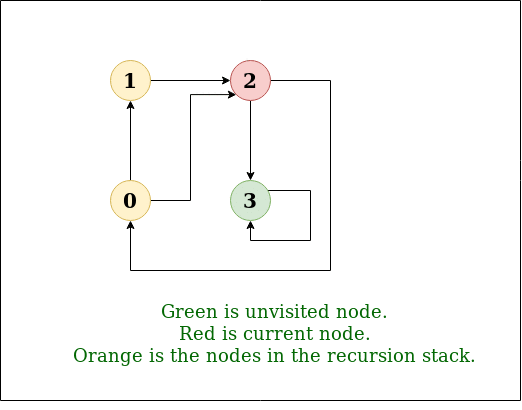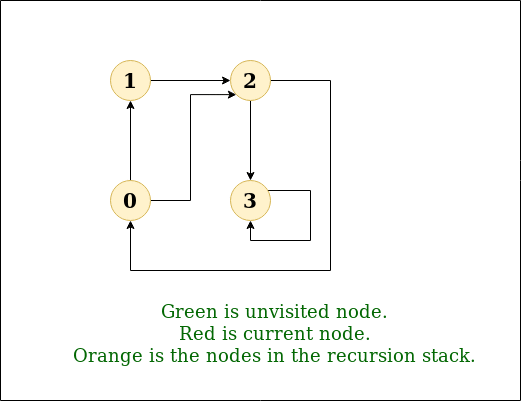
Input: n = 4, e = 6
2 -> 0, 0 -> 2, 1 -> 2, 0 -> 1, 3 -> 3, 1 -> 3
Output: DFS from vertex 2 : 2 0 1 3
Explanation:
DFS Diagram:
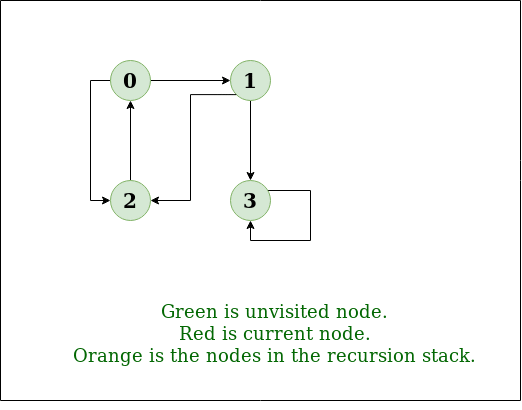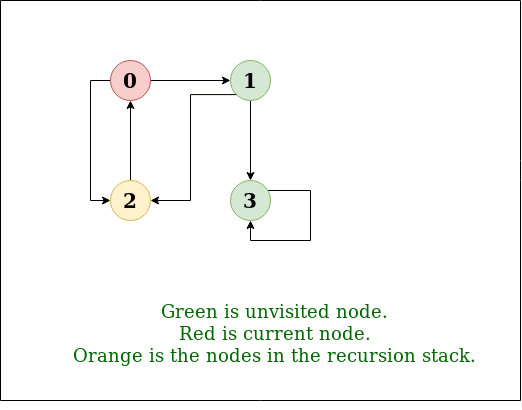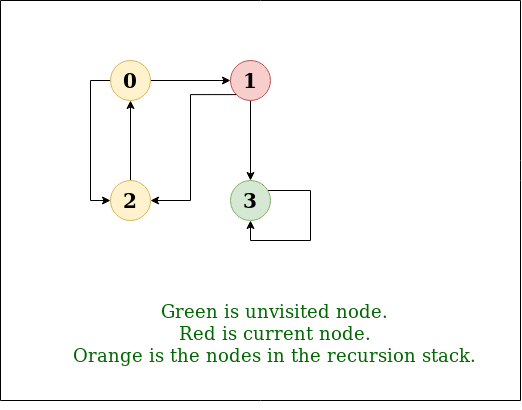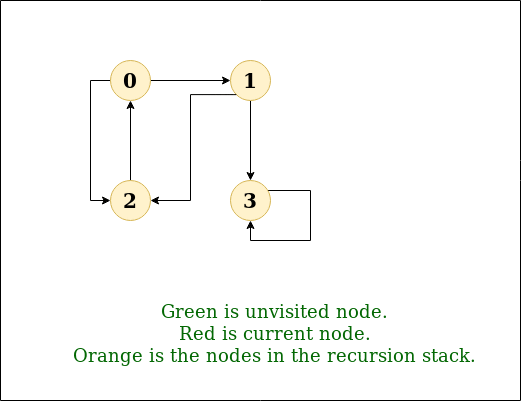
DFS 的递归实现已经讨论过:previous post。
解决方案:
- 方法:深度优先搜索是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图数据结构的算法。该算法从根节点开始(在图的情况下选择某个任意节点作为根节点)并在回溯之前沿着每个分支尽可能地探索。所以基本思路是从根或任意一个节点开始,标记该节点,移动到相邻的未标记节点,继续这个循环,直到没有未标记的相邻节点。然后回溯并检查其他未标记的节点并遍历它们。最后打印路径中的节点。
迭代 DFS 和递归 DFS 之间的唯一区别是递归堆栈被节点堆栈替换。 - 算法:
- 创建了一堆节点并访问了数组。
- 将根插入堆栈。
- 运行一个循环,直到堆栈不为空。
- 从堆栈中弹出元素并打印该元素。
- 对于当前节点的每个相邻且未访问的节点,标记该节点并将其插入堆栈。
- 迭代 DFS 的实现:这类似于BFS ,唯一的区别是队列被堆栈替换。
C++
// An Iterative C++ program to do DFS traversal from
// a given source vertex. DFS(int s) traverses vertices
// reachable from s.
#include
using namespace std;
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // adjacency lists
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void addEdge(int v, int w); // to add an edge to graph
void DFS(int s); // prints all vertices in DFS manner
// from a given source.
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
void Graph::DFS(int s)
{
// Initially mark all vertices as not visited
vector visited(V, false);
// Create a stack for DFS
stack stack;
// Push the current source node.
stack.push(s);
while (!stack.empty())
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
int s = stack.top();
stack.pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if (!visited[s])
{
cout << s << " ";
visited[s] = true;
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
for (auto i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
stack.push(*i);
}
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
int main()
{
Graph g(5); // Total 5 vertices in graph
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 4);
cout << "Following is Depth First Traversal\n";
g.DFS(0);
return 0;
} Java
//An Iterative Java program to do DFS traversal from
//a given source vertex. DFS(int s) traverses vertices
//reachable from s.
import java.util.*;
public class GFG
{
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
static class Graph
{
int V; //Number of Vertices
LinkedList[] adj; // adjacency lists
//Constructor
Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
//To add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
void DFS(int s)
{
// Initially mark all vertices as not visited
Vector visited = new Vector(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited.add(false);
// Create a stack for DFS
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// Push the current source node
stack.push(s);
while(stack.empty() == false)
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if(visited.get(s) == false)
{
System.out.print(s + " ");
visited.set(s, true);
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
Iterator itr = adj[s].iterator();
while (itr.hasNext())
{
int v = itr.next();
if(!visited.get(v))
stack.push(v);
}
}
}
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Total 5 vertices in graph
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 4);
System.out.println("Following is the Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS(0);
}
} Python3
# An Iterative Python program to do DFS traversal from
# a given source vertex. DFS(int s) traverses vertices
# reachable from s.
# This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
# list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self,V): # Constructor
self.V = V # No. of vertices
self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)] # adjacency lists
def addEdge(self,v, w): # to add an edge to graph
self.adj[v].append(w) # Add w to v’s list.
# prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
def DFS(self,s): # prints all vertices in DFS manner from a given source.
# Initially mark all vertices as not visited
visited = [False for i in range(self.V)]
# Create a stack for DFS
stack = []
# Push the current source node.
stack.append(s)
while (len(stack)):
# Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack[-1]
stack.pop()
# Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
# we need to print the popped item only
# if it is not visited.
if (not visited[s]):
print(s,end=' ')
visited[s] = True
# Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
# If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
# to the stack.
for node in self.adj[s]:
if (not visited[node]):
stack.append(node)
# Driver program to test methods of graph class
g = Graph(5); # Total 5 vertices in graph
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 4);
print("Following is Depth First Traversal")
g.DFS(0)
# This code is contributed by ankush_953C#
// An Iterative C# program to do DFS traversal from
// a given source vertex. DFS(int s) traverses vertices
// reachable from s.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
public class Graph
{
public int V; // Number of Vertices
public LinkedList[] adj; // adjacency lists
// Constructor
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// To add an edge to graph
public void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].AddLast(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
public void DFS(int s)
{
// Initially mark all vertices as not visited
Boolean []visited = new Boolean[V];
// Create a stack for DFS
Stack stack = new Stack();
// Push the current source node
stack.Push(s);
while(stack.Count > 0)
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack.Peek();
stack.Pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if(visited[s] == false)
{
Console.Write(s + " ");
visited[s] = true;
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
foreach(int v in adj[s])
{
if(!visited[v])
stack.Push(v);
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Total 5 vertices in graph
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 4);
Console.Write("Following is the Depth First Traversal\n");
g.DFS(0);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnasb Kundu Javascript
C++
// An Iterative C++ program to do DFS traversal from
// a given source vertex. DFS(int s) traverses vertices
// reachable from s.
#include
using namespace std;
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // adjacency lists
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void addEdge(int v, int w); // to add an edge to graph
void DFS(); // prints all vertices in DFS manner
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
void DFSUtil(int s, vector &visited);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
void Graph::DFSUtil(int s, vector &visited)
{
// Create a stack for DFS
stack stack;
// Push the current source node.
stack.push(s);
while (!stack.empty())
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
int s = stack.top();
stack.pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if (!visited[s])
{
cout << s << " ";
visited[s] = true;
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
for (auto i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
stack.push(*i);
}
}
// prints all vertices in DFS manner
void Graph::DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
vector visited(V, false);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
int main()
{
Graph g(5); // Total 5 vertices in graph
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
cout << "Following is Depth First Traversal\n";
g.DFS();
return 0;
} Java
//An Iterative Java program to do DFS traversal from
//a given source vertex. DFS() traverses vertices
//reachable from s.
import java.util.*;
public class GFG
{
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
static class Graph
{
int V; //Number of Vertices
LinkedList[] adj; // adjacency lists
//Constructor
Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
//To add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
void DFSUtil(int s, Vector visited)
{
// Create a stack for DFS
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// Push the current source node
stack.push(s);
while(stack.empty() == false)
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if(visited.get(s) == false)
{
System.out.print(s + " ");
visited.set(s, true);
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
Iterator itr = adj[s].iterator();
while (itr.hasNext())
{
int v = itr.next();
if(!visited.get(v))
stack.push(v);
}
}
}
// prints all vertices in DFS manner
void DFS()
{
Vector visited = new Vector(V);
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited.add(false);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (!visited.get(i))
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
System.out.println("Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
}
} Python3
# An Iterative Python3 program to do DFS
# traversal from a given source vertex.
# DFS(s) traverses vertices reachable from s.
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)]
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v].append(w) # Add w to v’s list.
# prints all not yet visited vertices
# reachable from s
def DFSUtil(self, s, visited):
# Create a stack for DFS
stack = []
# Push the current source node.
stack.append(s)
while (len(stack) != 0):
# Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack.pop()
# Stack may contain same vertex twice.
# So we need to print the popped item only
# if it is not visited.
if (not visited[s]):
print(s, end = " ")
visited[s] = True
# Get all adjacent vertices of the
# popped vertex s. If a adjacent has not
# been visited, then push it to the stack.
i = 0
while i < len(self.adj[s]):
if (not visited[self.adj[s][i]]):
stack.append(self.adj[s][i])
i += 1
# prints all vertices in DFS manner
def DFS(self):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False] * self.V
for i in range(self.V):
if (not visited[i]):
self.DFSUtil(i, visited)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
g = Graph(5) # Total 5 vertices in graph
g.addEdge(1, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 1)
g.addEdge(3, 4)
g.addEdge(4, 0)
print("Following is Depth First Traversal")
g.DFS()
# This code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// An Iterative C# program to do DFS traversal from
// a given source vertex. DFS() traverses vertices
// reachable from s.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph
{
public int V; // Number of Vertices
public List[] adj; // adjacency lists
// Constructor
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new List[V];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// To add an edge to graph
public void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
public void DFSUtil(int s, List visited)
{
// Create a stack for DFS
Stack stack = new Stack();
// Push the current source node
stack.Push(s);
while(stack.Count != 0)
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack.Peek();
stack.Pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if(visited[s] == false)
{
Console.Write(s + " ");
visited[s] = true;
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
foreach(int itr in adj[s])
{
int v = itr;
if(!visited[v])
stack.Push(v);
}
}
}
// prints all vertices in DFS manner
public void DFS()
{
List visited = new List(V);
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited.Add(false);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
Console.WriteLine("Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
输出:
Following is Depth First Traversal
0 3 2 1 4- 复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(V + E),其中 V 是顶点数,E 是图中的边数。
- 空间复杂度: O(V)。由于需要一个大小为 V 的额外访问数组。
上述解决方案的修改:请注意,上述实现仅打印从给定顶点可到达的顶点。例如,如果边 0-3 和 0-2 被删除,那么上面的程序将只打印 0。要打印图的所有顶点,请为每个未访问的顶点调用 DFS。
执行:
C++
// An Iterative C++ program to do DFS traversal from
// a given source vertex. DFS(int s) traverses vertices
// reachable from s.
#include
using namespace std;
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // adjacency lists
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void addEdge(int v, int w); // to add an edge to graph
void DFS(); // prints all vertices in DFS manner
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
void DFSUtil(int s, vector &visited);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
void Graph::DFSUtil(int s, vector &visited)
{
// Create a stack for DFS
stack stack;
// Push the current source node.
stack.push(s);
while (!stack.empty())
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
int s = stack.top();
stack.pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if (!visited[s])
{
cout << s << " ";
visited[s] = true;
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
for (auto i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
stack.push(*i);
}
}
// prints all vertices in DFS manner
void Graph::DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
vector visited(V, false);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
int main()
{
Graph g(5); // Total 5 vertices in graph
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
cout << "Following is Depth First Traversal\n";
g.DFS();
return 0;
}
Java
//An Iterative Java program to do DFS traversal from
//a given source vertex. DFS() traverses vertices
//reachable from s.
import java.util.*;
public class GFG
{
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
static class Graph
{
int V; //Number of Vertices
LinkedList[] adj; // adjacency lists
//Constructor
Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
//To add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
void DFSUtil(int s, Vector visited)
{
// Create a stack for DFS
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// Push the current source node
stack.push(s);
while(stack.empty() == false)
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if(visited.get(s) == false)
{
System.out.print(s + " ");
visited.set(s, true);
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
Iterator itr = adj[s].iterator();
while (itr.hasNext())
{
int v = itr.next();
if(!visited.get(v))
stack.push(v);
}
}
}
// prints all vertices in DFS manner
void DFS()
{
Vector visited = new Vector(V);
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited.add(false);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (!visited.get(i))
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
System.out.println("Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
}
}
Python3
# An Iterative Python3 program to do DFS
# traversal from a given source vertex.
# DFS(s) traverses vertices reachable from s.
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)]
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v].append(w) # Add w to v’s list.
# prints all not yet visited vertices
# reachable from s
def DFSUtil(self, s, visited):
# Create a stack for DFS
stack = []
# Push the current source node.
stack.append(s)
while (len(stack) != 0):
# Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack.pop()
# Stack may contain same vertex twice.
# So we need to print the popped item only
# if it is not visited.
if (not visited[s]):
print(s, end = " ")
visited[s] = True
# Get all adjacent vertices of the
# popped vertex s. If a adjacent has not
# been visited, then push it to the stack.
i = 0
while i < len(self.adj[s]):
if (not visited[self.adj[s][i]]):
stack.append(self.adj[s][i])
i += 1
# prints all vertices in DFS manner
def DFS(self):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False] * self.V
for i in range(self.V):
if (not visited[i]):
self.DFSUtil(i, visited)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
g = Graph(5) # Total 5 vertices in graph
g.addEdge(1, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 1)
g.addEdge(3, 4)
g.addEdge(4, 0)
print("Following is Depth First Traversal")
g.DFS()
# This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// An Iterative C# program to do DFS traversal from
// a given source vertex. DFS() traverses vertices
// reachable from s.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph
{
public int V; // Number of Vertices
public List[] adj; // adjacency lists
// Constructor
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new List[V];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// To add an edge to graph
public void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// prints all not yet visited vertices reachable from s
public void DFSUtil(int s, List visited)
{
// Create a stack for DFS
Stack stack = new Stack();
// Push the current source node
stack.Push(s);
while(stack.Count != 0)
{
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
s = stack.Peek();
stack.Pop();
// Stack may contain same vertex twice. So
// we need to print the popped item only
// if it is not visited.
if(visited[s] == false)
{
Console.Write(s + " ");
visited[s] = true;
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then push it
// to the stack.
foreach(int itr in adj[s])
{
int v = itr;
if(!visited[v])
stack.Push(v);
}
}
}
// prints all vertices in DFS manner
public void DFS()
{
List visited = new List(V);
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited.Add(false);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
Console.WriteLine("Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
输出:
Following is Depth First Traversal
0 1 2 3 4与递归遍历一样,迭代实现的时间复杂度为 O(V + E)。