通过在非相邻顶点(角)之间绘制对角线来形成凸多边形的三角剖分,以使对角线永不相交。问题在于以最小的成本找到三角剖分的成本。三角剖分的成本是其组成三角形的权重之和。每个三角形的重量是其周长(所有边的长度之和)
请参阅以下示例(从此源获取)。
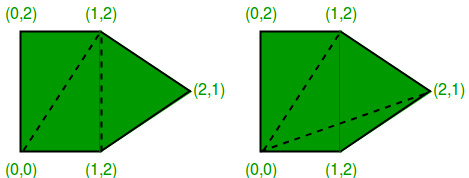
同一凸五边形的两个三角剖分。左侧的三角剖分的成本为8 +2√2+2√5(大约15.30),右侧的三角剖分的成本为4 +2√2+4√5(大约15.77)。
此问题具有递归子结构。想法是将多边形分为三个部分:单个三角形,左侧的子多边形和右侧的子多边形。我们尝试像这样进行所有可能的划分,并找到使三角形的成本加上两个子多边形的三角剖分的成本最小的方法。
Let Minimum Cost of triangulation of vertices from i to j be minCost(i, j)
If j < i + 2 Then
minCost(i, j) = 0
Else
minCost(i, j) = Min { minCost(i, k) + minCost(k, j) + cost(i, k, j) }
Here k varies from 'i+1' to 'j-1'
Cost of a triangle formed by edges (i, j), (j, k) and (k, i) is
cost(i, j, k) = dist(i, j) + dist(j, k) + dist(k, i)以下是上述幼稚递归公式的实现。
C++
// Recursive implementation for minimum cost convex polygon triangulation
#include
#include
#define MAX 1000000.0
using namespace std;
// Structure of a point in 2D plane
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
// Utility function to find minimum of two double values
double min(double x, double y)
{
return (x <= y)? x : y;
}
// A utility function to find distance between two points in a plane
double dist(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return sqrt((p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) +
(p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y));
}
// A utility function to find cost of a triangle. The cost is considered
// as perimeter (sum of lengths of all edges) of the triangle
double cost(Point points[], int i, int j, int k)
{
Point p1 = points[i], p2 = points[j], p3 = points[k];
return dist(p1, p2) + dist(p2, p3) + dist(p3, p1);
}
// A recursive function to find minimum cost of polygon triangulation
// The polygon is represented by points[i..j].
double mTC(Point points[], int i, int j)
{
// There must be at least three points between i and j
// (including i and j)
if (j < i+2)
return 0;
// Initialize result as infinite
double res = MAX;
// Find minimum triangulation by considering all
for (int k=i+1; k Java
// Class to store a point in the Euclidean plane
class Point
{
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// Utility function to return the distance between two
// vertices in a 2-dimensional plane
public double dist(Point p)
{
// The distance between vertices `(x1, y1)` & `(x2,
// y2)` is `√((x2 − x1) ^ 2 + (y2 − y1) ^ 2)`
return Math.sqrt((this.x - p.x) * (this.x - p.x)
+ (this.y - p.y) * (this.y - p.y));
}
}
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate the weight of optimal
// triangulation of a convex polygon represented by a
// given set of vertices `vertices[i..j]`
public static double MWT(Point[] vertices, int i, int j)
{
// If the polygon has less than 3 vertices,
// triangulation is not possible
if (j < i + 2)
{
return 0;
}
// keep track of the total weight of the minimum
// weight triangulation of `MWT(i,j)`
double cost = Double.MAX_VALUE;
// consider all possible triangles `ikj` within the
// polygon
for (int k = i + 1; k <= j - 1; k++)
{
// The weight of a triangulation is the length
// of perimeter of the triangle
double weight = vertices[i].dist(vertices[j])
+ vertices[j].dist(vertices[k])
+ vertices[k].dist(vertices[i]);
// choose the vertex `k` that leads to the
// minimum total weight
cost = Double.min(cost,
weight + MWT(vertices, i, k)
+ MWT(vertices, k, j));
}
return cost;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// vertices are given in clockwise order
Point[] vertices
= { new Point(0, 0), new Point(2, 0),
new Point(2, 1), new Point(1, 2),
new Point(0, 1) };
System.out.println(MWT(vertices,
0, vertices.length - 1));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Priiyadarshini KumariPython3
# Recursive implementation for minimum
# cost convex polygon triangulation
from math import sqrt
MAX = 1000000.0
# A utility function to find distance
# between two points in a plane
def dist(p1, p2):
return sqrt((p1[0] - p2[0])*(p1[0] - p2[0]) + \
(p1[1] - p2[1])*(p1[1] - p2[1]))
# A utility function to find cost of
# a triangle. The cost is considered
# as perimeter (sum of lengths of all edges)
# of the triangle
def cost(points, i, j, k):
p1 = points[i]
p2 = points[j]
p3 = points[k]
return dist(p1, p2) + dist(p2, p3) + dist(p3, p1)
# A recursive function to find minimum
# cost of polygon triangulation
# The polygon is represented by points[i..j].
def mTC(points, i, j):
# There must be at least three points between i and j
# (including i and j)
if (j < i + 2):
return 0
# Initialize result as infinite
res = MAX
# Find minimum triangulation by considering all
for k in range(i + 1, j):
res = min(res, (mTC(points, i, k) + \
mTC(points, k, j) + \
cost(points, i, k, j)))
return round(res, 4)
# Driver code
points = [[0, 0], [1, 0], [2, 1], [1, 2], [0, 2]]
n = len(points)
print(mTC(points, 0, n-1))
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10C
// A Dynamic Programming based program to find minimum cost of convex
// polygon triangulation
#include
#include
#define MAX 1000000.0
using namespace std;
// Structure of a point in 2D plane
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
// Utility function to find minimum of two double values
double min(double x, double y)
{
return (x <= y)? x : y;
}
// A utility function to find distance between two points in a plane
double dist(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return sqrt((p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) +
(p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y));
}
// A utility function to find cost of a triangle. The cost is considered
// as perimeter (sum of lengths of all edges) of the triangle
double cost(Point points[], int i, int j, int k)
{
Point p1 = points[i], p2 = points[j], p3 = points[k];
return dist(p1, p2) + dist(p2, p3) + dist(p3, p1);
}
// A Dynamic programming based function to find minimum cost for convex
// polygon triangulation.
double mTCDP(Point points[], int n)
{
// There must be at least 3 points to form a triangle
if (n < 3)
return 0;
// table to store results of subproblems. table[i][j] stores cost of
// triangulation of points from i to j. The entry table[0][n-1] stores
// the final result.
double table[n][n];
// Fill table using above recursive formula. Note that the table
// is filled in diagonal fashion i.e., from diagonal elements to
// table[0][n-1] which is the result.
for (int gap = 0; gap < n; gap++)
{
for (int i = 0, j = gap; j < n; i++, j++)
{
if (j < i+2)
table[i][j] = 0.0;
else
{
table[i][j] = MAX;
for (int k = i+1; k < j; k++)
{
double val = table[i][k] + table[k][j] + cost(points,i,j,k);
if (table[i][j] > val)
table[i][j] = val;
}
}
}
}
return table[0][n-1];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
Point points[] = {{0, 0}, {1, 0}, {2, 1}, {1, 2}, {0, 2}};
int n = sizeof(points)/sizeof(points[0]);
cout << mTCDP(points, n);
return 0;
} 输出:
15.3006上面的问题类似于矩阵链乘法。以下是mTC(points [],0,4)的递归树。
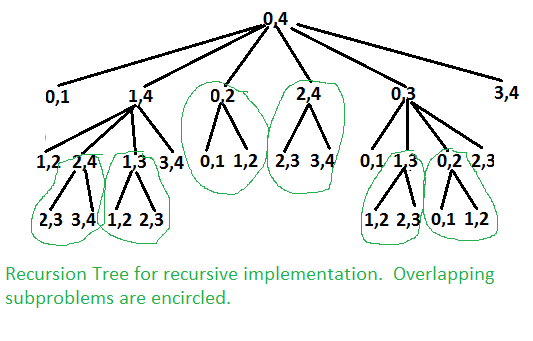
在上面的递归树中可以很容易地看出问题有很多重叠的子问题。由于该问题具有以下两个属性:最优子结构和子问题重叠,因此可以使用动态编程有效地解决它。
以下是动态编程解决方案的C++实现。
C
// A Dynamic Programming based program to find minimum cost of convex
// polygon triangulation
#include
#include
#define MAX 1000000.0
using namespace std;
// Structure of a point in 2D plane
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
// Utility function to find minimum of two double values
double min(double x, double y)
{
return (x <= y)? x : y;
}
// A utility function to find distance between two points in a plane
double dist(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return sqrt((p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) +
(p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y));
}
// A utility function to find cost of a triangle. The cost is considered
// as perimeter (sum of lengths of all edges) of the triangle
double cost(Point points[], int i, int j, int k)
{
Point p1 = points[i], p2 = points[j], p3 = points[k];
return dist(p1, p2) + dist(p2, p3) + dist(p3, p1);
}
// A Dynamic programming based function to find minimum cost for convex
// polygon triangulation.
double mTCDP(Point points[], int n)
{
// There must be at least 3 points to form a triangle
if (n < 3)
return 0;
// table to store results of subproblems. table[i][j] stores cost of
// triangulation of points from i to j. The entry table[0][n-1] stores
// the final result.
double table[n][n];
// Fill table using above recursive formula. Note that the table
// is filled in diagonal fashion i.e., from diagonal elements to
// table[0][n-1] which is the result.
for (int gap = 0; gap < n; gap++)
{
for (int i = 0, j = gap; j < n; i++, j++)
{
if (j < i+2)
table[i][j] = 0.0;
else
{
table[i][j] = MAX;
for (int k = i+1; k < j; k++)
{
double val = table[i][k] + table[k][j] + cost(points,i,j,k);
if (table[i][j] > val)
table[i][j] = val;
}
}
}
}
return table[0][n-1];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
Point points[] = {{0, 0}, {1, 0}, {2, 1}, {1, 2}, {0, 2}};
int n = sizeof(points)/sizeof(points[0]);
cout << mTCDP(points, n);
return 0;
}
输出:
15.3006