给定L = {l 1 ,l 2 ,………,l n }的欧几里得平面上’n’条直线的集合。第i个线由公式的形式给出一个I X + B I Y = C I。找出可使用集合L中的线形成的三角形的数量。请注意,没有两对线在同一点相交。
注意:此问题并未提及线不能平行,这使得该问题难以解决。
例子:
Input: a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4}
b[] = {2, 4, 5, 5}
c[] = {5, 7, 8, 6}
Output: 2
The number of triangles that can be formed are: 2
Input: a[] = {1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
b[] = {2, 4, 6, 3, 6, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25}
c[] = {3, 5, 11, 10, 9, 17, 13, 11, 7, 3}
Output: 30
The number of triangles that can be formed are: 30
天真的算法
天真的算法可以描述为:
- 从集合L中拾取3条任意线。
- 现在检查是否可以使用所选的3条线来形成三角形。通过检查它们中没有一个是成对并行的,可以很容易地做到这一点。
- 如果可以形成三角形,则增加计数器。
时间复杂度:有n个C 3三联线。对于每个三元组,我们必须进行3次比较以检查是否有2条线不平行,这意味着可以在O(1)时间内完成检查。这使得幼稚算法为O(n 3 )。
高效算法
这也可以在O(n log n)中实现。高效算法背后的逻辑描述如下。
我们将集合L分为多个子集。子集的形成基于斜率,即特定子集中的所有线具有相同的斜率,即它们彼此平行。
让我们考虑三组(假设A,B和C)。对于特定的集合(例如A),属于该集合的线都彼此平行。如果我们有A,B和C,则可以从每组中选择一条线以获得三角形,因为这些线都不是平行的。通过制作子集,我们确保不会同时拾取两条平行的线。
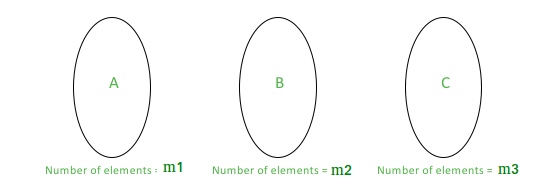
现在,如果我们只有这三个子集,
Number of triangles = (Number of ways to pick a line from A) *
(Number of ways to pick a line from B) *
(Number of ways to pick a line from C)
= m1*m2*m3
Here m1 is count of elements with first slope (in Set A)
Here m2 is count of elements with first slope (in Set B)
Here m3 is count of elements with first slope (in Set C)
同样,如果我们有4个子集,我们可以扩展此逻辑以得到,
三角形数量= m1 * m2 * m3 + m1 * m2 * m4 + m1 * m3 * m4 + m2 * m3 * m4
对于大于3的子集数,如果我们有’k’个子集,则我们的任务是查找一次取3个子集的元素数之和。这可以通过维护一个count数组来完成。我们创建一个计数数组,其中count i表示平行线的第i个子集的计数。
We one by one compute following values.
sum1 = m1 + m2 + m3 .....
sum2 = m1*m2 + m1*m3 + ... + m2*m3 + m2*m4 + ...
sum3 = m1*m2*m3 + m1*m2*m4 + ...... m2*m3*m4 + ....
sum3 gives our final answer
C++
// C++ program to find the number of
// triangles that can be formed
// using a set of lines in Euclidean
// Plane
#include
using namespace std;
#define EPSILON numeric_limits::epsilon()
// double variables can't be checked precisely
// using '==' this function returns true if
// the double variables are equal
bool compareDoubles(double A, double B)
{
double diff = A-B;
return (diff Java
// Java program to find the number of
// triangles that can be formed
// using a set of lines in Euclidean
// Plane
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static double EPSILON = 1.0842e-19;
// Double variables can't be checked precisely
// using '==' this function returns true if
// the double variables are equal
static boolean compareDoubles(double A, double B)
{
double diff = A - B;
return (diff < EPSILON) &&
(-diff < EPSILON);
}
// This function returns the number of
// triangles for a given set of lines
static int numberOfTringles(int []a, int []b,
int []c, int n)
{
// Slope array stores the slope of lines
Vector slope = new Vector<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
slope.add((double)(a[i] * 1.0) / b[i]);
// Slope array is sorted so that all lines
// with same slope come together
Collections.sort(slope);
// After sorting slopes, count different
// slopes. k is index in count[].
int []count = new int [n];
int k = 0;
// Count of current slope
int this_count = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (compareDoubles((double)slope.get(i),
(double)slope.get(i - 1)))
this_count++;
else
{
count[k++] = this_count;
this_count = 1;
}
}
count[k++] = this_count;
// Calculating sum1 (Sum of all slopes)
// sum1 = m1 + m2 + ...
int sum1 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
sum1 += count[i];
// Calculating sum2. sum2 = m1*m2 + m2*m3 + ...
int sum2 = 0;
// Needed for sum3
int temp[] = new int [n];
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
temp[i] = count[i] * (sum1 - count[i]);
sum2 += temp[i];
}
sum2 /= 2;
// Calculating sum3 which gives the
// final answer
// m1 * m2 * m3 + m2 * m3 * m4 + ...
int sum3 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
sum3 += count[i] * (sum2 - temp[i]);
sum3 /= 3;
return sum3;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Lines are stored as arrays of a, b
// and c for 'ax+by=c'
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int b[] = { 2, 4, 5, 5 };
int c[] = { 5, 7, 8, 6 };
// n is the number of lines
int n = a.length;
System.out.println("The number of triangles " +
"that can be formed are: " +
numberOfTringles(a, b, c, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher C#
// C# program to find the number of
// triangles that can be formed
// using a set of lines in Euclidean
// Plane
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG{
static double EPSILON = 1.0842e-19;
// Double variables can't be checked precisely
// using '==' this function returns true if
// the double variables are equal
static bool compareDoubles(double A, double B)
{
double diff = A - B;
return (diff < EPSILON) &&
(-diff < EPSILON);
}
// This function returns the number of
// triangles for a given set of lines
static int numberOfTringles(int []a, int []b,
int []c, int n)
{
// Slope array stores the slope of lines
List slope = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
slope.Add((double)(a[i] * 1.0) / b[i]);
// Slope array is sorted so that all lines
// with same slope come together
slope.Sort();
// After sorting slopes, count different
// slopes. k is index in count[].
int []count = new int [n];
int k = 0;
// Count of current slope
int this_count = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (compareDoubles((double)slope[i],
(double)slope[i - 1]))
this_count++;
else
{
count[k++] = this_count;
this_count = 1;
}
}
count[k++] = this_count;
// Calculating sum1 (Sum of all slopes)
// sum1 = m1 + m2 + ...
int sum1 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
sum1 += count[i];
// Calculating sum2. sum2 = m1*m2 + m2*m3 + ...
int sum2 = 0;
// Needed for sum3
int []temp = new int [n];
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
temp[i] = count[i] * (sum1 - count[i]);
sum2 += temp[i];
}
sum2 /= 2;
// Calculating sum3 which gives
// the final answer
// m1 * m2 * m3 + m2 * m3 * m4 + ...
int sum3 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
sum3 += count[i] * (sum2 - temp[i]);
sum3 /= 3;
return sum3;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// lines are stored as arrays of a, b
// and c for 'ax+by=c'
int []a = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int []b = { 2, 4, 5, 5 };
int []c = { 5, 7, 8, 6 };
// n is the number of lines
int n = a.Length;
Console.WriteLine("The number of triangles " +
"that can be formed are: " +
numberOfTringles(a, b, c, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher 输出:
The number of triangles that can be formed are: 2
时间复杂度:代码中的所有循环均为O(n)。因此,该实现方式中的时间复杂度由用于对斜率阵列进行排序的排序函数驱动。这使得算法为O(nlogn)。