图G =(V,E)中的母顶点是顶点v,因此从v开始的路径可以通过从v开始的路径到达G中的所有其他顶点。
例子:
Input: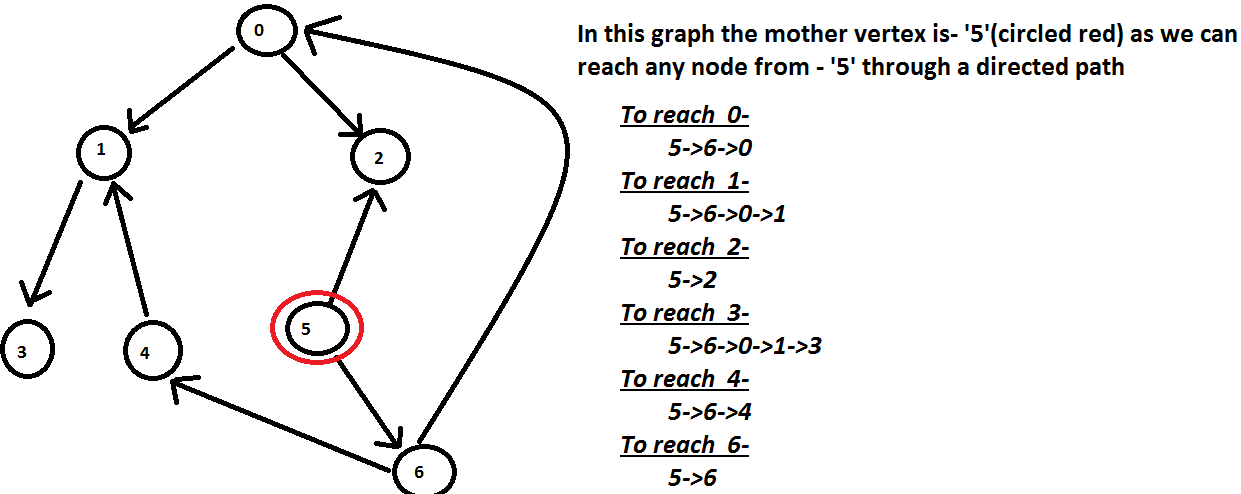
Output:
5
方法:
我们可以使用“深度优先搜索”方法解决此问题。为了进一步优化我们的方法,我们将使用有效的解决方案。
下面的解决方案也使用“深度优先搜索”来解决此问题,但是它仅执行一次“深度优先搜索周期”,并且一旦找到母顶点,就会停止执行。
- 在执行深度优先搜索时,我们有一个位掩码数组,代表每个顶点的位掩码。在执行期间,此位掩码数组将传递到所有顶点。
- 每个顶点都以这样一种方式修改其专用位掩码:可以从该顶点访问包括顶点在内的所有设置位,包括当前顶点。
- 在每次迭代中,我们通过检查当前顶点位掩码值(如果设置了代表所有顶点的位)来检查是否可以从该顶点访问所有顶点。如果可以从该顶点访问所有顶点,则它将中断执行并找到母顶点作为当前顶点。
- 如果已经从Vertex-1访问了Vertex-2,并且较早已经访问了Vertex-2,则Vertex-1通过对Vertex-2位掩码执行“或”操作来更新其位掩码。
时间复杂度: O(V + E)
上述想法如何运作?
让这种方法支持最多具有32个顶点的图。可以扩展此方法以支持更多数量的顶点,但是此处最多处理32个顶点。
- 创建了一个由32个位掩码组成的位掩码数组。数组的第0个索引表示Vertex-0的位掩码,而数组的第一个索引表示Vertex-1的位掩码,依此类推。
- 使用深度优先搜索算法访问图的所有顶点,并将相同的位掩码数组传递到所有顶点。相应地设置了位掩码值,以表示可以从该顶点访问的所有顶点。
- 设置与相邻顶点相对应的位索引,包括自己的位索引。相邻顶点的位掩码也将重复相同的操作,并将其返回给Vertex-1。
- 顶点1将继续对其位掩码的所有邻居的返回值执行“或”运算,以表示可以从顶点1访问的所有顶点。
- 请注意,如果Vertex-2是Vertex-1的邻居,并且已经从另一个邻居顶点访问过,那么它将不会再次访问其邻居的顶点,并将其位掩码返回到第一个节点。
- 每次迭代将检查是否将与当前顶点对应的位掩码的所有位都设置为1。如果将当前顶点均值的所有位都设置为1,则意味着可以从当前顶点访问所有顶点,并且当前顶点是的母顶点。该图。
以下是我们上述方法的实现:
// C++ code to find Mother
// Vertex using Bitmask
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Graph {
int V;
// Store in descending order
set >* adjList;
};
Graph* CreateGraph(int N)
{
Graph* g = new Graph();
g->V = N;
g->adjList
= new set >[N];
return g;
}
void AddEdge(
Graph* g, int src, int dest)
{
g->adjList[src].insert(dest);
}
void PrintGraph(Graph* g)
{
set >::iterator it;
for (int i = 0; i < g->V; i++) {
for (it = g->adjList[i].begin();
it != g->adjList[i].end();
it++) {
cout << "There is an edge from "
<< i << " to "
<< *it << endl;
}
}
}
bool IsEdge(Graph* g, int src, int dest)
{
if (g->adjList[src].find(dest)
!= g->adjList[src].end()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
int MotherVertexUtil(
Graph* g, int index,
int* mask, int* m_vertex)
{
// If mother vertex is already found
// then simply return with existing
// mask of the vertex index
if (*m_vertex != -1) {
return mask[index];
}
// if this vertex is already visited,
// return the bit-mask
// value of this vertex.
if (mask[index] != 0) {
return mask[index];
}
int tmpmask = 0;
// Set the bit corresponding
// to vertex index in tmpmask
tmpmask |= (1 << index);
for (int i = 0; i < g->V; i++) {
if ((index != i)
&& IsEdge(g, index, i)) {
// Set bits corresponding to all
// vertex which can be visite
// by this vertex by ORing
// the return value by util function
// Vertex is not visited
if (mask[i] == 0) {
int retmask
= MotherVertexUtil(
g, i, mask, m_vertex);
tmpmask |= retmask;
}
// Vertex is already visited
else {
tmpmask |= mask[i];
}
// Check if current vertex is
// mother vertex or mother vertex
// is already found
if (tmpmask == (pow(2, g->V) - 1)) {
// If all bits of a mask is set
// it means current vertex
// is mother vertex
if (*m_vertex == -1) {
*m_vertex = index;
}
return tmpmask;
}
}
}
// populate tmpmask as final
// bit mask of the vertex
mask[index] |= tmpmask;
return mask[index];
}
int MotherVertex(Graph* g)
{
int v = g->V;
int* mask = new int(v);
// Initially bit mask
// for all vertex will be 0
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
mask[i] = 0;
}
// DFS traversal is used to check
// for the mother vertex
// All set bits (of bitmask of a vertex)
// represent the current vertex index
// and index of vertices which could be
// visited from the current vertex.
/* Example:
If a vertex index is 3
then and vertex 5, 7 and 10
can be visited from this vertex
then final bit mask of this vertex
would be
00000000000000000000010010101000
(bits 3, 5, 7 and 10 are set) */
// tmpmask is used to store
// the final bitmask of the vertex.
int tmpmask = 0;
// flag to check if
// mother vertex is found
int m_vertex = -1;
for (int index = 0; index < v; index++) {
// set the bit corresponding
// to vertex index in tmpmask
tmpmask = (1 << index);
// mask for a vertex is 0
// means it has not yet
// visited so visit this vertex
if (mask[index] == 0) {
int retmask
= MotherVertexUtil(
g, index,
mask, &m_vertex);
// set bits corresponding to all
// vertices which can be visited
// from this vertex by ORing
// the return value by util function
tmpmask |= retmask;
}
// check if current vertex is
// mother vertex or mother vertex
// is already found
// If all bits of a mask is set
// it means current vertex
// is mother vertex
if (tmpmask == (pow(2, v) - 1)) {
// current vertex is mother vertex
if (m_vertex == -1) {
m_vertex = index;
}
break;
}
// populate tmpmask as final bit
// mask of the vertex
mask[index] |= tmpmask;
}
return m_vertex;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Graph* g = CreateGraph(7);
AddEdge(g, 0, 2);
AddEdge(g, 0, 1);
AddEdge(g, 1, 3);
AddEdge(g, 4, 1);
AddEdge(g, 5, 2);
AddEdge(g, 5, 6);
AddEdge(g, 6, 0);
AddEdge(g, 6, 4);
PrintGraph(g);
int m_vertex = MotherVertex(g);
if (m_vertex == -1) {
cout << "Mother vertex is not"
<< " existing in this graph"
<< endl;
}
else {
cout << "Mother vertex is: "
<< m_vertex << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
There is an edge from 0 to 2
There is an edge from 0 to 1
There is an edge from 1 to 3
There is an edge from 4 to 1
There is an edge from 5 to 6
There is an edge from 5 to 2
There is an edge from 6 to 4
There is an edge from 6 to 0
Mother vertex is: 5
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。