平均变化率表示一个变量相对于另一变量的总变化的总变化。瞬时变化率或导数测量一个变量相对于另一个变量的特定的,无限微小的变化的特定变化率。函数的平均变化率可以用割线确定,瞬时变化率可以用切线确定。正如您将学到的,这些比率也可以使用一种称为演算的特殊类型的数学来确定。
变化率是多少?
变化率是一个变量相对于另一个变量的变化的变化。常见的变化率是速度,它衡量行驶距离相对于经过时间的变化。奥运金牌获得者Usain Bolt在100米冲刺中以44.72公里/小时的最高速度成为世界上跑得最快的人。平均而言,他的速度为37.58公里/小时,速度稍慢(不过非常令人印象深刻)。博尔特的最高速度就是瞬时变化率的一个例子,而他的平均速度就是平均变化率。
平均变化率
通过连接曲线上的两个点可以找到正割线。两点之间的割线斜率表示该间隔的平均变化率。
公式:
Average Rate of Change = Slope(m) = △y/△x = ![]() =
= ![]()
如何使用割线找到两点之间的平均变化率:
第1步:绘制一条连接这两个点的割线。
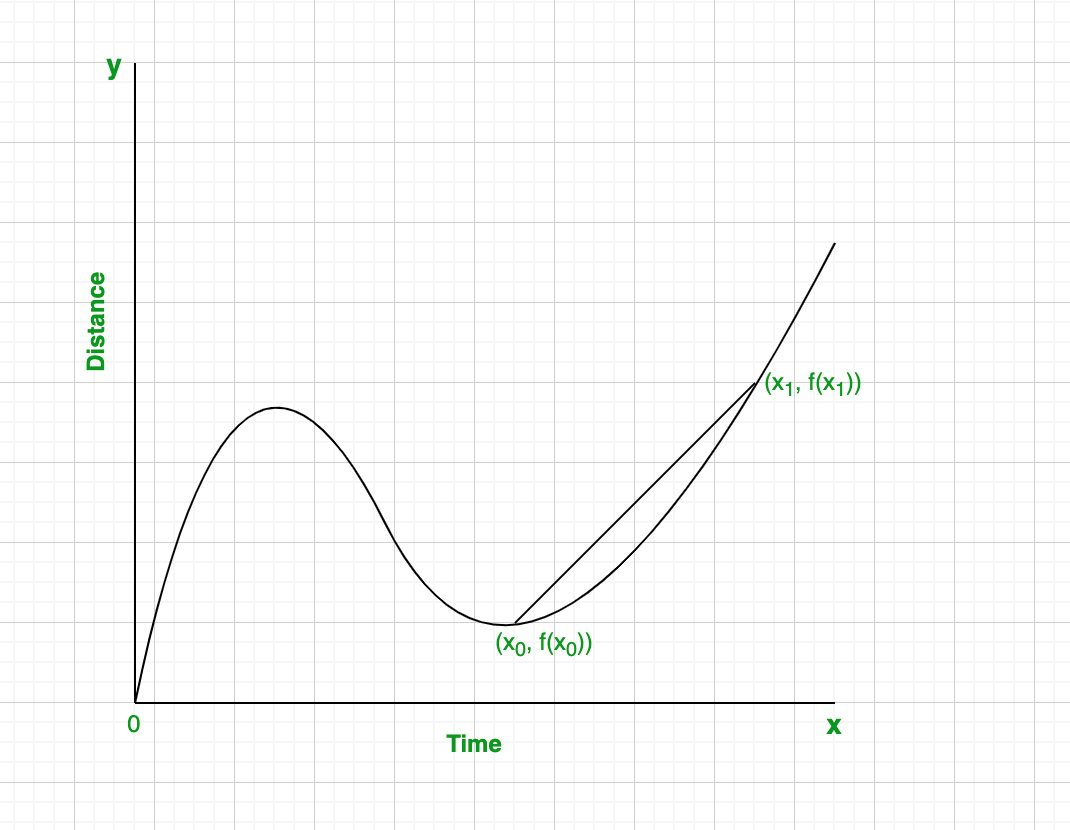
步骤2:使用两点的坐标来计算斜率。
Equation of slope:
Slope =![]()
The avarage change of the function over the given time interval[x0, x1]
Slope = ![]()
The slope of the secant line represents the average
rate of change of the graph in that interval.
一旦计算出割线的斜率,就可以使用该斜率写一个方程式来表示它。
For Example:
Equation of slope:
y – y0 = m(x – x0)
m = slope of secant line = 4/7
x0 = 2
y0 = 9![]()
Hence, the equation of the secant line between x = 2 and x = 9 is
y – 9 = ![]()
衍生产品(瞬时变化率)
在一个点的切线通过绘制一条直线,在该点接触的曲线,而不跨过曲线找到。换句话说,该线在局部应仅接触一个点。一点处切线的斜率表示该点的瞬时变化率或导数。
公式:
Instantaneous Rate of Change = ![]()
如何使用切线在一点上找到导数:
步骤1:在该点画一条切线。

步骤2:使用该线上任意两点的坐标来计算斜率。
Equation of slope:
Slope = ![]()
The avarage change of the function over the given time interval x0
Slope = ![]()
The slope of the tangent line at a point represents
the instantaneous rate of change, or derivative, at that point.
一旦计算出切线的斜率,就可以编写一个方程式来表示它。
For Example: Equation of slope:
y – y0 = m(x – x0)
m = slope of tangent line = ![]()
x0 = 16
y0 = 6![]()
Hence, the equation of the tangent line at x = 16 is
y – 16 = \frac{5}{6}(x – 6)
导数符号
在18世纪初期,伟大的数学家艾萨克·牛顿( Isaac Newton)与戈特弗里德·威廉·莱布尼兹(Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz)之间就谁是第一个发明微积分的问题发生了争议。这种说法被称为Prioritätsstreit ,或德语中的“优先权争议”。分歧对数学世界产生了持久的影响,给我们留下了两个标准的导数符号。拉格朗日符号是另一种常见的派生符号,由法国数学家和哲学家约瑟夫·路易斯·拉格朗日( Joseph-Louis Lagrange)建立。
如果我们采用函数y = f(x),那么
1. Leibniz表示法:
“First derivative of y with respect to x”
⇒![]()
“Second derivative of y with respect to x”
⇒![]()
“First derivative of y with respect to x
at x = 2”
⇒![]()
2.牛顿符号:
The number of dots above the function
variable represents how many times the
function has been differentiated.
“First derivative of y”
⇒![]()
“Second derivative of y”
⇒![]()
“First derivative of y at x = 2”
⇒![]()
3.拉格朗日符号:
The number of apostrophes after the function
variable represents how many times the
function has been differentiated.
“First derivative of y”
⇒y’
“First derivative of y at x = 2”
⇒y'(2)
“Second derivative of y”
⇒y”
4.欧拉符号
“First derivative”
⇒ Dxf
“Second derivative”
⇒ Dx2f
Here, D represents the differential operator
样本问题
问题1.找到区间x = 4,x = 6的平均变化率。
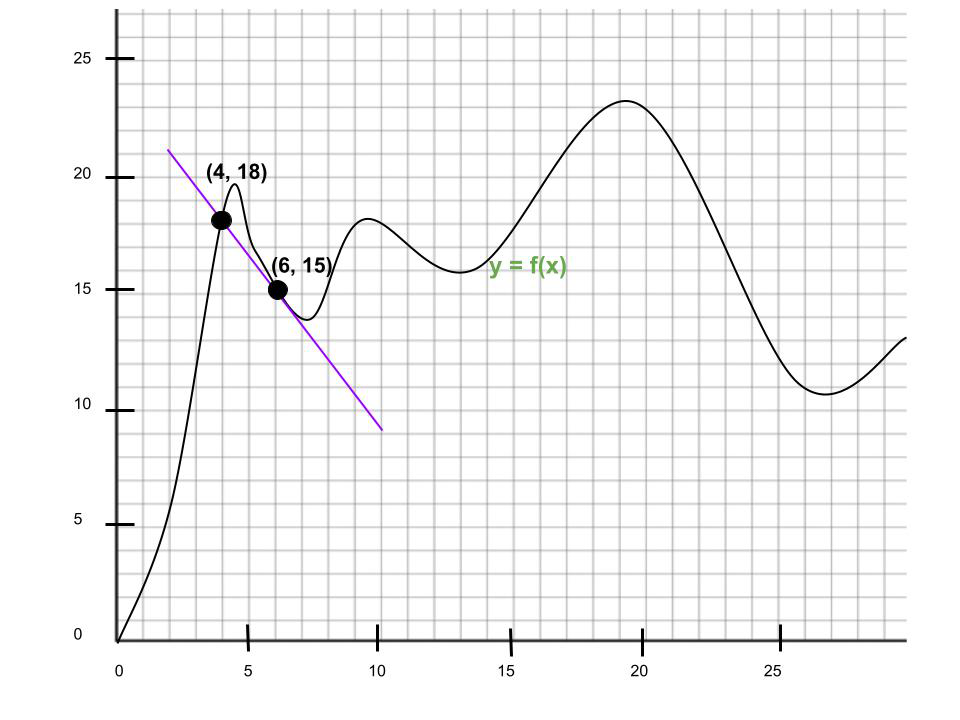
解决方案:
Point 1: (4, 18)
Point 2: (6, 15)
Slope = ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
Hence, the average rate of change = ![]()
问题2.写出x = 16处的切线方程。

解决方案:
Point of intersection: (16, 18)
Slope = ![]()
= ![]()
Equation of tangent line:
![]()
问题3.在x = 20时图的导数是什么?用Leibniz表示法表达您的答案。
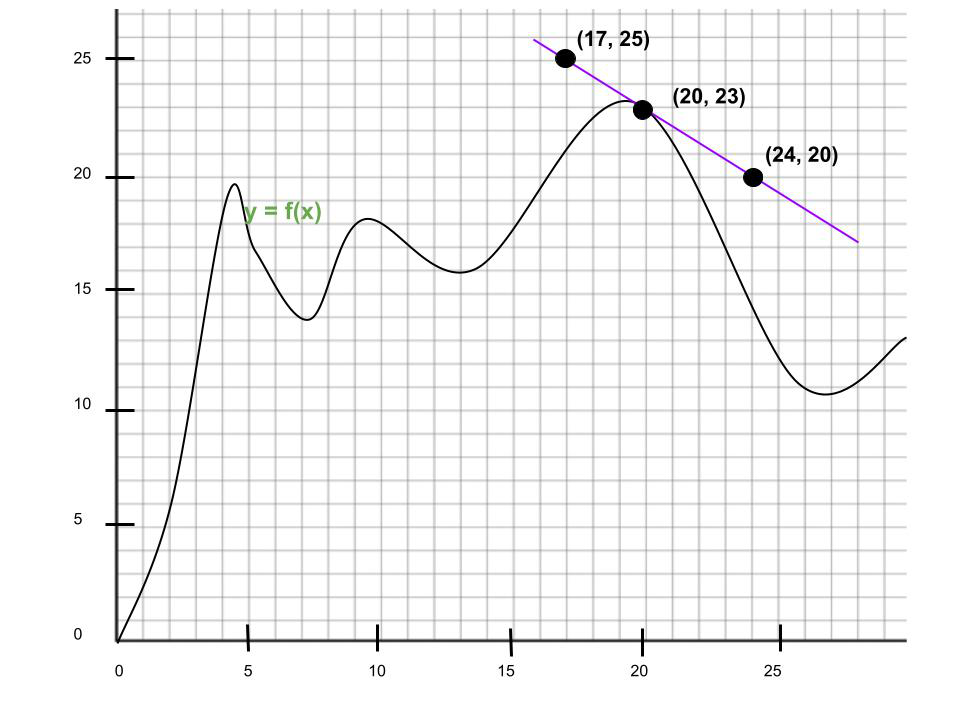
解决方案:
Given point of intersection: (20, 23)
Slope of tangent line = ![]()
= ![]()
So, the Leibniz notation: ![]()
问题4.在x = 4处找到图的导数。用牛顿符号表示答案。

解决方案:
Given point of intersection: (4, 18)
Slope of tangent line = ![]() =
= ![]()
So, the Newton’s notation![]()
问题5:求出区间x = 4,x = 25的平均变化率。这与x = 4时的导数相比如何?
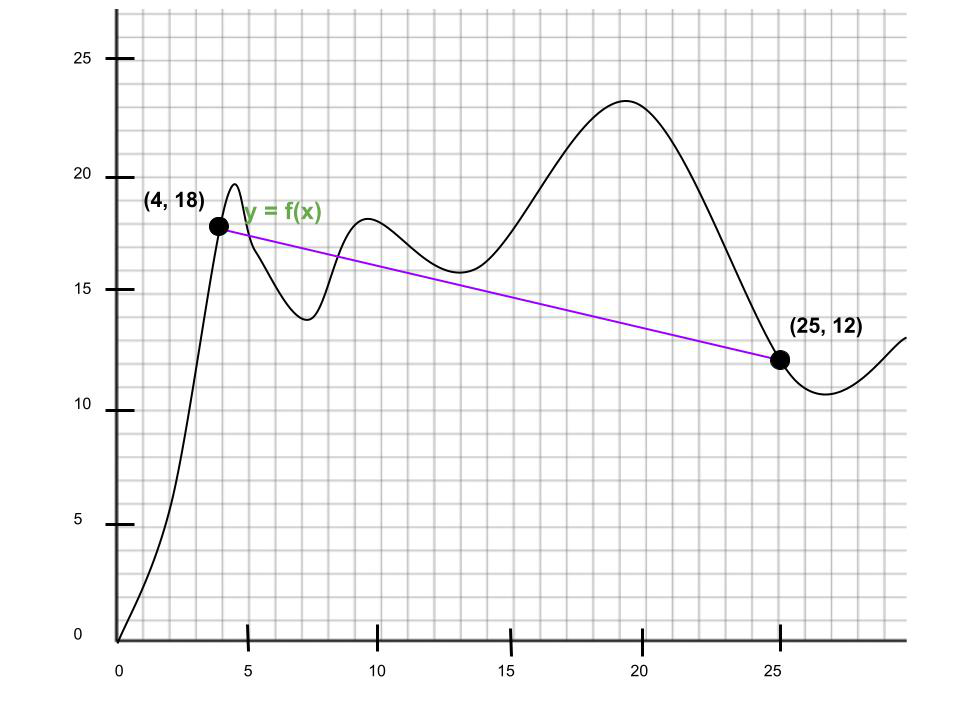
解决方案:
Slope of secant line = ![]()
= ![]()
The average rate of change over x = 4, x = 25 is -6/21,
which is less than the derivative of y at x = 4, which we found to
be 7/3.
问题6:求出给定函数f(x)= 2x 2 + 18在x = 9时的瞬时变化率?
解决方案:
Given: f(x) = 2x2 + 18
f'(x) = 4x + 0
f'(x) = 4x
Now we have to find the instantaneous rate of change at x = 9
f(9) = 4x
f(9) = 4(9)
f(9) = 36
问题7.求出给定函数f(x)= 4x 2 + 12x + 8的瞬时变化率,其中x = 4?
解决方案:
Given: f(x) = 4x2 + 12x + 8
f'(x) = 8x + 12
Now we have to find the instantaneous rate of change at x = 4
f(4) = 8x + 12
f(4) = 8(4) + 12
f(4) = 44