数字的平方是通过将数字乘以自身获得的值。平方根和平方根的行为相反,即;它们的定义相互反义。因此,平方根与自身相乘时将提供其原始值。例如,3的平方是9,而9的平方根是3。
用更广义的方式,我们可以说,如果“ P”是给我们的数字,则P 2表示P的平方。而P的平方根表示为√P。可以说平方根是平方的逆运算。
方格
All square numbers can be expressed by a product of a number with itself.
4、9、25、36、49、64、81、100…等等。这些数字有什么特别之处吗?所有这些数字都是平方数。要看到这一点,让我们检查一下这些数字中的这种模式
2*2 = 22 = 4
3*3 = 32 = 9
4*4 = 42 = 16
5*5 = 52 = 25
正方形的数学符号:正方形用数字2表示,即数字x 2上的指数
25 = 52
16 = 42
9 = 32
这些符号表示“ 2平方”,“ 3平方”和“ 4平方”。此表示法也称为数字的“上标”或“幂”。在这里,我们有一个2的幂,被称为数字的平方。
因此,通常,如果自然数p可以表示为q 2 ,其中q也是自然数,则p是平方数。
问题:55是平方数吗?
回答:
Let’s look at the square of 7, 72 = 49 and square of 8, 82 = 64
55 lies between both of these squares, but there is no natural number between 7 and 8.
So, there is no natural number whose square is 55.
当涉及加法时,减法是加法的反运算,反之亦然。但是在平方的情况下,平方根是平方运算的逆。
例如:
- 2 2 = 4,所以4的平方根是2。
- 3 2 = 9,所以9的平方根是3。
也可以看出(-3) 2和(3) 2都等于9。因此,9具有两个平方根。
因此,我们得出结论,任何正平方数都有两个平方根。但是为了简单起见,我们现在仅假设正平方根。
平方数的性质
属性1:在单位位置,没有平方数以2、3、7或8结尾
让我们看一下下表,它包含前20个自然数及其平方。
如果您研究此表,您将意识到所有平方数均以1、4、9、6、0和5结尾。在单位位置,所有这些平方都没有以2、3、7或8结尾。
But it’s not necessary that the numbers ending with 1,4,9,6,0 and 5 will be square numbers. For example: 46, it is not a square number.
属性2:偶数的平方始终为偶数,奇数的平方始终为奇数。
为了支持这一说法,让我们举个例子,
122 = 12 × 12 = 144. (both are even numbers)
112 = 11 × 11 = 121 (both are odd numbers)
302 = 30 × 30 = 900 (both are even numbers)
特性3:完美正方形结尾处的零个数始终是偶数。换句话说,以零的奇数结尾的数字绝不是完美的平方。
2500是一个完美的平方,因为零的数目是2(偶数),而25000不是一个完美的平方,因为零的数目是3(奇数)。
平方根
正如我们在上面已经看到的,数字的平方根是该值与自身相乘时将得出其原始数。
平方根被表示与称为自由基或基数,随后其被称为被开方即√x数符号√。
例如:
√4 = 2
√9 = 3
√16 = 4
√25 = 5
平方根的性质
属性1:如果一个数字的单位数字是2、3、7或8,则它在N(自然数的集合)中没有根。
132, 433, 688 does not have perfect square roots as unit digits are 2,3, and 8 respectively. This property is evident also from Property 1 of Square Numbers.
属性2:如果数字以零的奇数结尾,则它没有平方根。如果平方数后跟偶数个零,则它具有平方根,其中零数最终是该数中零数的一半。
2000 does not have a perfect square root as the number of zeroes is 3(odd). 900 have a perfect square root as the number of zeroes is 2(even). So square root of 900 will contain only 1 zero. (half of two zeroes).√900 = 30.
特性3:偶数平方根的平方根是偶数,而奇数平方根的平方根是奇数。
Example: √144 = 12 (both are even numbers) and √225 = 15 (both are odd numbers).
平方根和平方中有趣的图案
加三角数
三角形数字是其点图案可以排列成三角形的数字。例如:
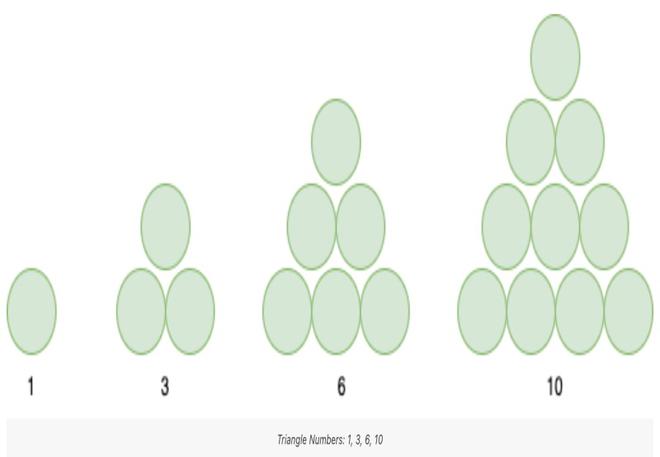
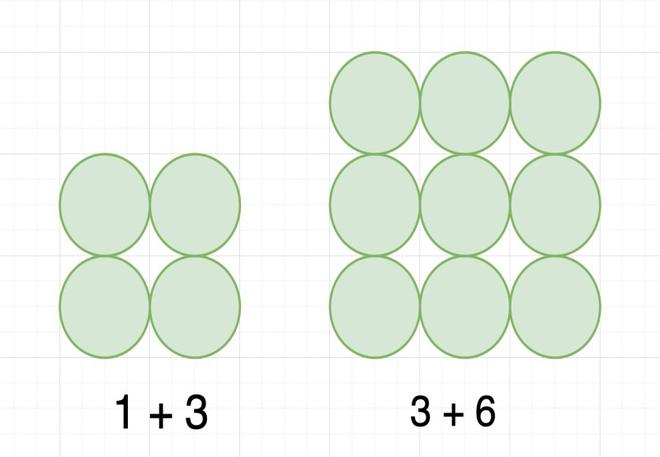
如果我们组合两个连续的三角形数字,我们可以得到一个正方形的数字。
1、11、111、1111的平方…
这些数字的平方会产生漂亮的图案。
12 = 1
112 = 1 2 1
1112 = 1 2 3 2 1
11112 = 1 2 3 4 3 2 1
111112 = 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1
单位数为5的数字平方
假设一个数字的单位数字为5,即;
a52 = (10a + 5)2
= 10a(10a + 5) + 5(10a + 5)
= 100a + 50a + 50a + 25
= 100a (a + 1) + 25
例子:
252 = 625 = (2 × 3) hundreds + 25
352 = 1225 = (3 × 4) hundreds + 25
752 = 5625 = (7 × 8) hundreds + 25
1252 = 15625 = (12 × 13) hundreds + 25
平方和平方根上的样本问题
寻找广场
问题1:求23的平方。
回答:
232 = (20 + 3)2
= 20(20 + 3) + 3(20 +3)
= 202 + 20 × 3 + 3 × 20 + 32
= 400 + 60 + 60 + 9
= 529
问题2:找到39的平方。
回答:
392 = (30 + 9)2
= 30 (30 + 9) + 9 (30 + 9)
= 302 + 30 × 9 + 9 × 30 + 92
= 900 + 270 + 270 + 81
= 1521
寻找平方根
我们可以通过对数进行素分解来找到平方根。让我们看一些例子:
| Prime Factorization of a Number | Prime Factorization of its square |
| 6 = 2 × 3 | 36 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 |
| 12 = 2 × 2 × 3 | 144 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 |
| 15 = 5 × 3 | 225 = 5 × 5 × 3 × 3 |
我们可以看到,在平方的素数分解中,每个素数都比该数本身的素数分解发生两次。
通过配对素因子,我们可以得出平方根。
问题1:找到144的平方根。
回答:
144 = (2 × 2) × (2 × 2) × (3 × 3)
= 22 × 22 × 32
= (2 × 2 × 3)2
= 122
Therefore, √144 = 12
Sometimes a number is not a perfect square.
问题2:2352是完美的正方形吗?如果不是,请找到2352的最小倍数,这是一个理想的正方形。找到新数字的平方根。
回答:
2352 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 7 × 7
= 24 × 3 × 72
As the prime factor 3 has no pair, 2352 is not a perfect square.
If 3 gets a pair then the number will become perfect square.
2352 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 7 × 7
= 24 × 32 × 72
2352 = 22 × 3 × 7 = 84
查找十进制数的平方根
有几种找到十进制数平方根的方法,最著名和最简单的手动找到平方根的方法称为素因数分解法。对于大数,我们采用长除法,因为前一种方法在大数情况下变得乏味。
让我们用一个例子来学习如何找到十进制数的平方根:
示例:19.36的平方根
Step 1: Make pairs of an integral part and decimal part of the number. Add a zero to the extreme right of the decimal part if required.
![]()
Step 2: Find the perfect square of an integral part, find the number closest to the integral part (Either small or equal). In this case, the square of 4 is 16 which is closest to 19:
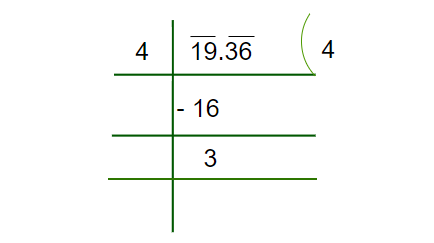
Step 3: Put the decimal Part next to the Remainder obtained. Double the divisor of an Integral Part and place it in the next divisor, now we have to find the unit place value of this number.
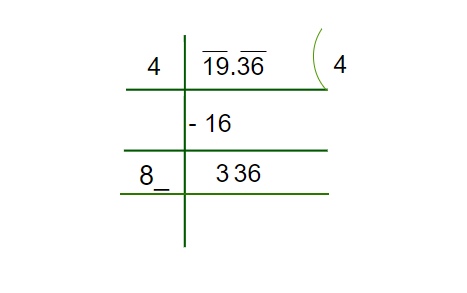
Step 4: Now we have to find the unit place’s number which should be multiplied in order to get 336, here we can see, if we multiply 84 with 4, we will get 336.
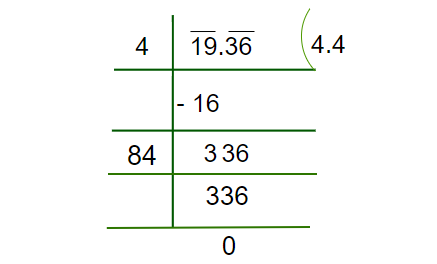
Hence, we obtained 4.4 as the square root of 19.36