1.最长的工作优先(LJF):
它是CPU调度算法,其中首先执行突发行最大的进程。一旦进程进入就绪队列,该进程仅在执行完成后退出,因此它是一个非抢占式进程。如果进程的突发时间相同,则选择总时间最短的作业。此CPU调度算法导致系统的吞吐量较低。
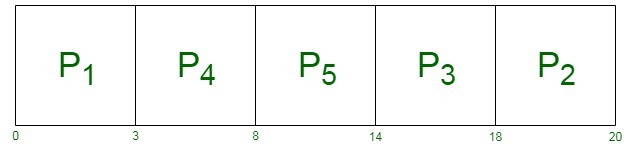
| Process | AT | BT |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 6 |
2.最长剩余工作优先(LRJF):
它是最长作业优先CPU调度算法的抢先版本。每秒选择过程“突发时间”,然后选择最长的作业。如果进程的突发时间相同,则选择总体到达时间短的作业。
由于同时检查了进程的剩余突发时间,因此它遭受了饥饿的困扰。它也被称为“最长剩余时间优先”算法。
| Process | AT | BT |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 6 |

LJF和LRJF CPU调度算法之间的区别:
| LJF | LRJF |
|---|---|
| Non preemptive | Preemptive |
| It suffers from starvation | It also suffers from starvation |
| Waiting Time is high | Waiting Time is not so high, and processes get chances for execution after some interval. |
| Switching context is less, since a process that once enters running state is executed completely. | Switching context is more, since the process are continually checked for execution. |
| The processes are executed based on their CPU time and arrival time alone, without increasing CPU overload. | The processes are repeatedly checking for an idle CPU, thereby increasing the overload. |
| No process can complete its execution until longest job persists. | The processes can complete execution before the longest process. |