给定一个由N 个不同的正整数组成的数组。任务是找到对给定数组进行排序的最小成本。交换两个元素X和Y的成本是X*Y 。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {8, 4, 5, 3, 2, 7}
Output: 57
Explanation:
Swap element at index 4 with index 5 – cost(arr[4]*arr[5]) = (2*7) = 14,
Array becomes {8, 4, 5, 3, 7, 2}
then, swap element at index 0 with 5 – cost(arr[0]*arr[5]) = (8*2) = 16,
Array becomes {2, 4, 5, 3, 7, 8}
then, swap element at index 2 with 3 – cost(arr[2]*arr[3]) = (5*3) = 15,
Array becomes {2, 4, 3, 5, 7, 8}
then, swap element at index 1 with 2 – cost(arr[1]*arr[2]) = (4*3) = 12,
Array becomes {2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8}
Array is now sorted and total cost = 14+16+15+12 = 57.
Input: arr[] = {1, 8, 9, 7, 6}
Output: 36
方法:这个想法是为了对循环进行排序,我们有两种选择,要么仅使用循环的局部最小值,要么同时使用数组的局部和整体最小值。选择一种成本较低的交换元素。以下是步骤:
- 计算局部最小值(比如local_minimum ),它是当前循环中的最小元素,以及整体最小值(比如 total_minimum),它是整个数组中的最小元素。
- 仅使用局部最小值计算并存储对循环进行排序的成本(例如cost1 )。
- 此外,通过使用局部最小值和整体最小值来计算和存储成本以对循环进行排序(比如cost2 )。
- 现在排序这个循环的最小成本将是成本 cost1 和 cost2 中的最小值。将此成本添加到总成本中。
下面是数组 arr[] = {1, 8, 9, 7, 6} 的说明:
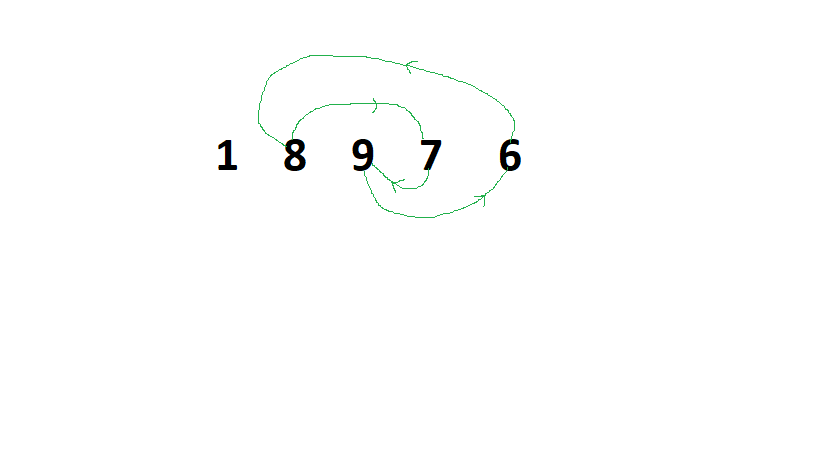
- 在上图中,循环{8, 9, 7, 6}可以使用局部最小元素6或整体最小元素1进行排序。通过仅使用局部最小元素,即交换 6 和 9、交换 6 和 7、交换 6 和 8。因此,总成本为6*9 + 6*7 + 6*8 = 144 。
- 通过使用整体最小和局部最小元素,即交换 1 和 6、交换 1 和 9、交换 1 和 7、交换 1 和 8、交换 1 和 6。因此,总成本为 1*6 +1*9 + 1*7 +1*8 +1*6 = 36。
- 上述费用中的最小值为 36。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function returns the minimum cost
// to sort the given array
int minCost(int arr[], int n)
{
// Create array of pairs in which
// 1st element is the array element
// and 2nd element is index of first
pair sorted[n];
// Initialize the total cost
int total_cost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sorted[i].first = arr[i];
sorted[i].second = i;
}
// Sort the array with respect to
// array value
sort(sorted, sorted + n);
// Initialize the overall minimum
// which is the 1st element
int overall_minimum = sorted[0].first;
// To keep track of visited elements
// create a visited array & initialize
// all elements as not visited
bool vis[n] = { false };
// Iterate over every element
// of the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// If the element is visited or
// in the sorted position, and
// check for next element
if (vis[i] && sorted[i].second == i)
continue;
// Create a vector which stores
// all elements of a cycle
vector v;
int j = i;
// It covers all the elements
// of a cycle
while (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
v.push_back(sorted[j].first);
j = sorted[j].second;
}
// If cycle is found then the
// swapping is required
if (v.size() > 0) {
// Initialize local minimum with
// 1st element of the vector as
// it contains the smallest
// element in the beginning
int local_minimum = v[0], result1 = 0,
result2 = 0;
// Stores the cost with using only
// local minimum value.
for (int k = 1; k < v.size(); k++)
result1 += (local_minimum * v[k]);
// Stores the cost of using both
// local minimum and overall minimum
for (int k = 0; k < v.size(); k++)
result2 += (overall_minimum * v[k]);
// Update the result2
result2 += (overall_minimum
* local_minimum);
// Store the minimum of the
// two result to total cost
total_cost += min(result1, result2);
}
}
// Return the minimum cost
return total_cost;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given array arr[]
int arr[] = { 1, 8, 9, 7, 6 };
int n = (sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int));
// Function Call
cout << minCost(arr, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function returns the minimum cost
// to sort the given array
static int minCost(int arr[], int n)
{
// Create array of pairs in which
// 1st element is the array element
// and 2nd element is index of first
int[][] sorted = new int[n][2];
// Initialize the total cost
int total_cost = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sorted[i][0] = arr[i];
sorted[i][1] = i;
}
// Sort the array with respect to
// array value
Arrays.sort(sorted, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
// Initialize the overall minimum
// which is the 1st element
int overall_minimum = sorted[0][0];
// To keep track of visited elements
// create a visited array & initialize
// all elements as not visited
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
// Iterate over every element
// of the array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// If the element is visited or
// in the sorted position, and
// check for next element
if (vis[i] && sorted[i][1] == i)
continue;
// Create a vector which stores
// all elements of a cycle
ArrayList v = new ArrayList<>();
int j = i;
// It covers all the elements
// of a cycle
while (!vis[j])
{
vis[j] = true;
v.add(sorted[j][0]);
j = sorted[j][1];
}
// If cycle is found then the
// swapping is required
if (v.size() > 0)
{
// Initialize local minimum with
// 1st element of the vector as
// it contains the smallest
// element in the beginning
int local_minimum = v.get(0), result1 = 0,
result2 = 0;
// Stores the cost with using only
// local minimum value.
for(int k = 1; k < v.size(); k++)
result1 += (local_minimum * v.get(k));
// Stores the cost of using both
// local minimum and overall minimum
for(int k = 0; k < v.size(); k++)
result2 += (overall_minimum * v.get(k));
// Update the result2
result2 += (overall_minimum *
local_minimum);
// Store the minimum of the
// two result to total cost
total_cost += Math.min(result1, result2);
}
}
// Return the minimum cost
return total_cost;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Given array arr[]
int arr[] = { 1, 8, 9, 7, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
// Function call
System.out.print(minCost(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function returns the minimum cost
# to sort the given array
def minCost(arr, n):
# Create array of pairs in which
# 1st element is the array element
# and 2nd element is index of first
sortedarr = []
# Initialize the total cost
total_cost = 0
for i in range(n):
sortedarr.append([arr[i], i])
# Sort the array with respect to
# array value
sortedarr.sort()
# Initialize the overall minimum
# which is the 1st element
overall_minimum = sortedarr[0][0]
# To keep track of visited elements
# create a visited array & initialize
# all elements as not visited
vis = [False] * n
# Iterate over every element
# of the array
for i in range(n):
# If the element is visited or
# in the sorted position, and
# check for next element
if vis[i] and sortedarr[i][1] == i:
continue
# Create a vector which stores
# all elements of a cycle
v = []
j = i
size = 0
# It covers all the elements
# of a cycle
while vis[j] == False:
vis[j] = True
v.append(sortedarr[j][0])
j = sortedarr[j][1]
size += 1
# If cycle is found then the
# swapping is required
if size != 0:
# Initialize local minimum with
# 1st element of the vector as
# it contains the smallest
# element in the beginning
local_minimum = v[0]
result1 = 0
result2 = 0
# Stores the cost with using only
# local minimum value.
for k in range(1, size):
result1 += local_minimum * v[k]
# Stores the cost of using both
# local minimum and overall minimum
for k in range(size):
result2 += overall_minimum * v[k]
# Update the result2
result2 += (overall_minimum *
local_minimum)
# Store the minimum of the
# two result to total cost
total_cost += min(result1, result2)
# Return the minimum cost
return total_cost
# Driver code
# Given array arr[]
A = [ 1, 8, 9, 7, 6 ]
# Function call
ans = minCost(A, len(A))
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by kumarkashyap36
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live