给定一个整数N和一个位置数组arr[]表示已经放置的非攻击车的位置,任务是按字典顺序找到可以放置在 N*N 棋盘上的非攻击车的位置。
车的移动:任何车都可以水平或垂直移动任意数量的空方格。
例子:
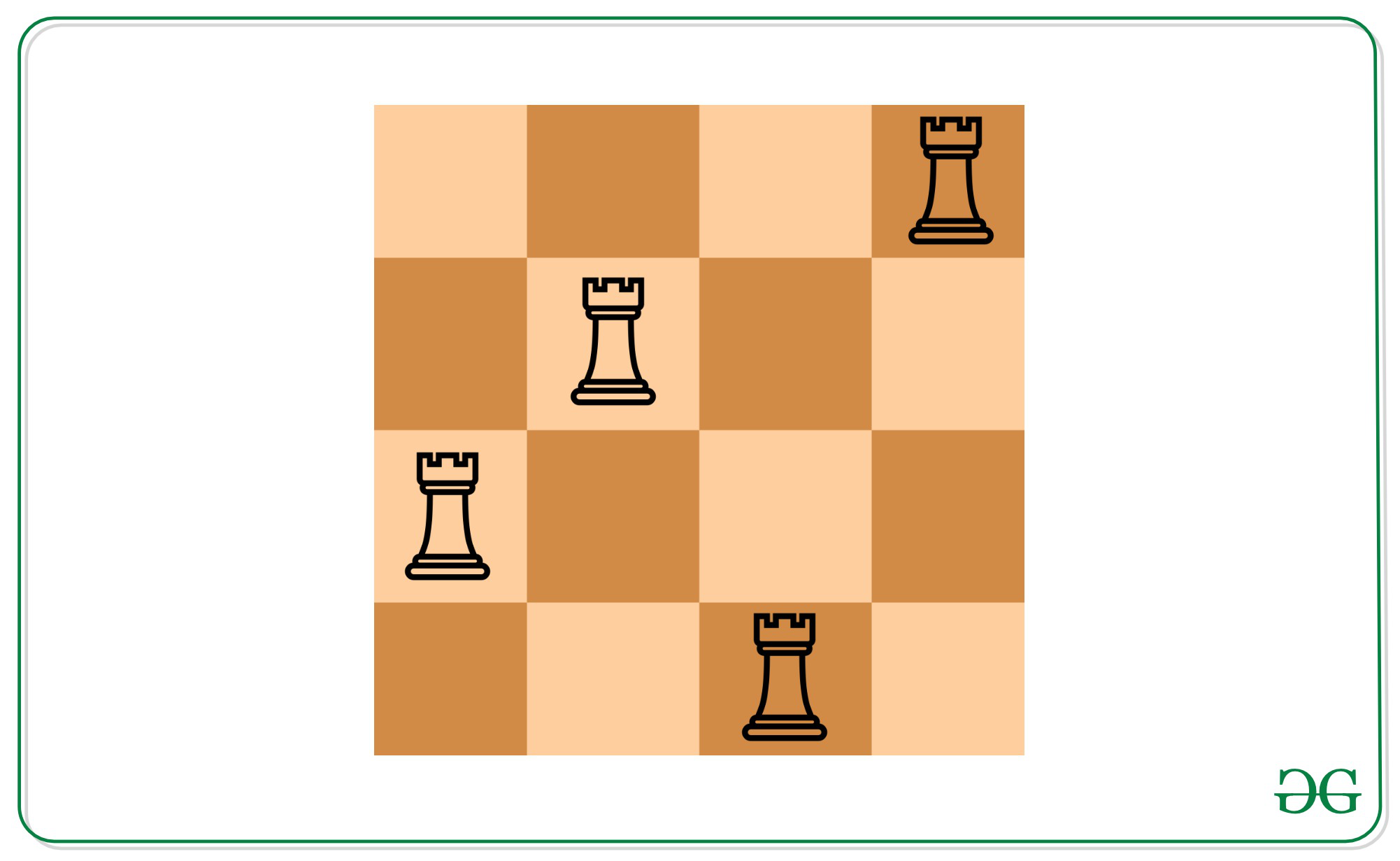
Inupt: N = 4, arr[] = {(1, 4), (2, 2)}
Output: 2
3 1
4 3
Explanation:
There can be two more rooks can be placed on the 4*4 Chessboard
Input: N = 5, arr[] = {}
Output: 5
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
朴素的方法:初始化一个大小为 N*N 的二维矩阵mat[][]在每个单元格处为 0,并将 Rooks 的初始位置标记为 1 的车。然后遍历矩阵 mat[][],检查第i 行和第j 列包含任何车,保持车的数量。如果任何行包含而列都不包含任何放置的车,则在那里放置一个车并将此单元格添加到您的结果字符串中。
最后,打印放置的车数和放置车的位置
时间复杂度: O(N 3 )
空间复杂度: O(N 2 )
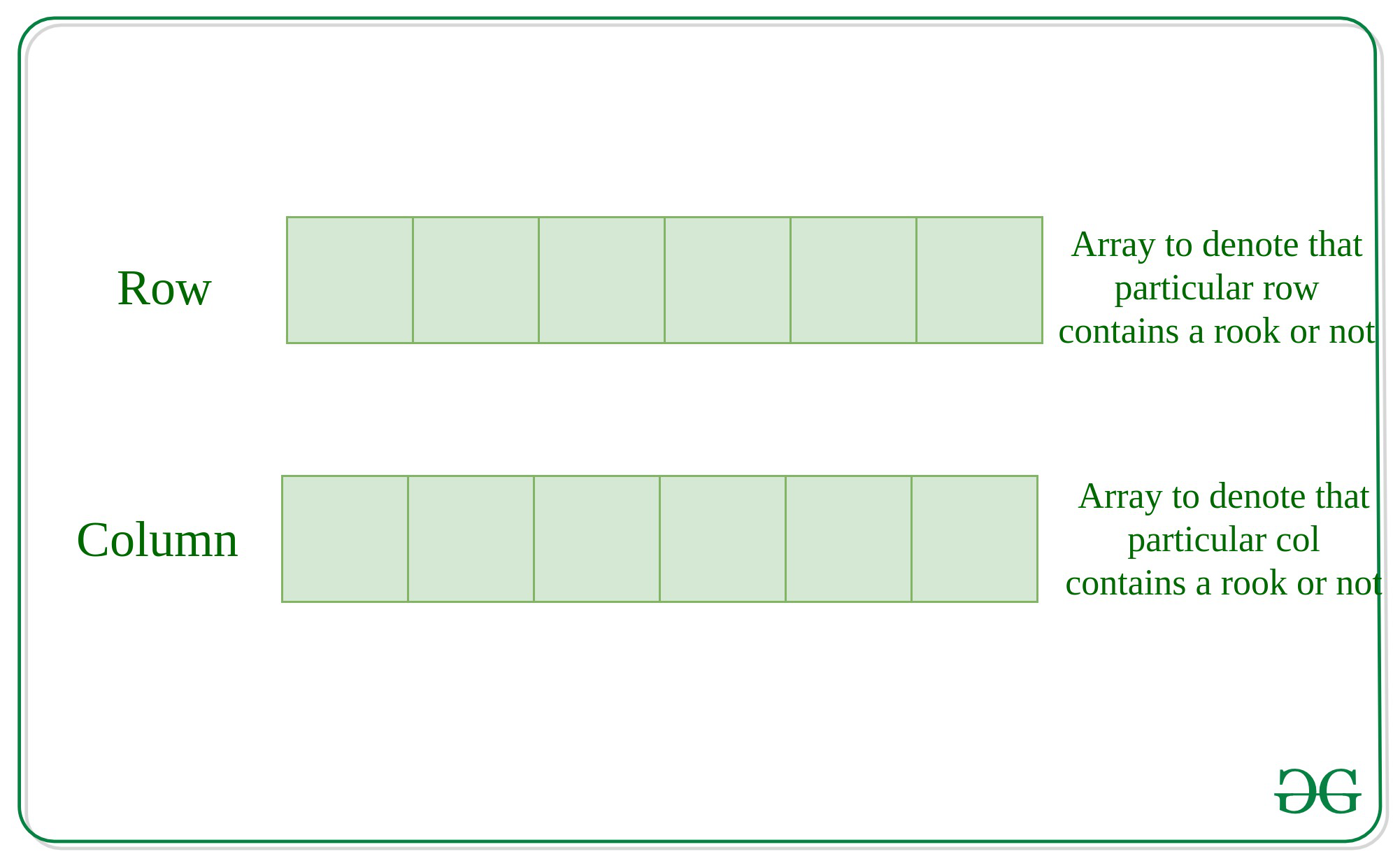
高效的方法:这个想法是创建两个大小为N 的数组,以存储第i 行或第i 列是否包含任何车,现在可以高效地搜索该行和相应列是否已经包含车.
时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
空间复杂度: O(N)

最有效的方法:问题中的关键观察是可以放置的最大车是NK 。也就是说,如果两个车在同一行或同一列上,它们就会相互攻击。由于给定的车中没有两个相互攻击,因此输入中给出的所有行都是唯一的。同样,输入中给出的所有列都是唯一的。因此,我们只剩下 NK 个未使用的行和 NK 个未使用的列来放置新车。
换句话说,如果我们尝试按照鸽巢原则放置超过 NK 只鸽子,如果有 N+1 只鸽子和 N 个位置要填充,那么至少有一个地方包含超过 1 只鸽子。
并找到按字典顺序排列的最小答案。这个答案可以通过将最小的未使用行与最小的未使用列、第二小的未使用行与第二小的未使用列等配对来实现。
时间复杂度: O(N)
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find
// count of placing non-attacking
// rooks on the N x N chessboard
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the count of
// placing non-attacking rooks
// on the N x N chessboard
void findCountRooks(int row[], int col[],
int n, int k)
{
// Count of the Non-attacking rooks
int res = n - k;
cout << res << "\n";
int ri = 0, ci = 0;
while (res-- > 0)
{
// Printing lexographically
// smallest configuration
while (ri < k && row[ri] == 1)
{
ri++;
}
while (ci < k && col[ci] == 1)
{
ci++;
}
cout << (ri + 1) << " "
<< (ci + 1) << "\n";
ri++;
ci++;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 4;
int k = 2;
int row[] = { 1, 2 };
int col[] = { 4, 2 };
// Function call
findCountRooks(row, col, n, k);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by jana_sayantan Java
// Java implementation to find
// count of placing non-attacking
// rooks on the N x N chessboard
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P2Placerooks {
// Function to find the count of
// placing non-attacking rooks
// on the N x N chessboard
static void findCountRooks(
int row[], int col[], int n, int k)
{
// Count of the Non-attacking rooks
int res = n - k;
System.out.println(res + " ");
int ri = 0, ci = 0;
while (res-- > 0) {
// Printing lexographically
// smallest configuration
while (ri < k && row[ri] == 1) {
ri++;
}
while (ci < k && col[ci] == 1) {
ci++;
}
System.out.println((ri + 1)
+ " " + (ci + 1)
+ " ");
ri++;
ci++;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
int k = 2;
int row[] = { 1, 2 };
int col[] = { 4, 2 };
// Function Call
findCountRooks(row, col, n, k);
}
}Python3
# Python3 implementation to find
# count of placing non-attacking
# rooks on the N x N chessboard
# Function to find the count of
# placing non-attacking rooks
# on the N x N chessboard
def findCountRooks(row, col, n, k):
# Count of the Non-attacking rooks
res = n - k
print(res)
ri = 0
ci = 0
while (res > 0):
# Printing lexographically
# smallest configuration
while (ri < k and row[ri] == 1):
ri += 1
while (ci < k and col[ci] == 1):
ci += 1
print((ri + 1), "", (ci + 1))
ri += 1
ci += 1
res -= 1
# Driver Code
n = 4
k = 2
row = [ 1, 2 ]
col = [ 4, 2 ]
# Function call
findCountRooks(row, col, n, k)
# This code is contributed by sanjoy_62C#
// C# implementation to find
// count of placing non-attacking
// rooks on the N x N chessboard
using System;
class P2Placerooks{
// Function to find the count of
// placing non-attacking rooks
// on the N x N chessboard
static void findCountRooks(int []row,
int []col,
int n, int k)
{
// Count of the Non-attacking rooks
int res = n - k;
Console.WriteLine(res + " ");
int ri = 0, ci = 0;
while (res-- > 0)
{
// Printing lexographically
// smallest configuration
while (ri < k && row[ri] == 1)
{
ri++;
}
while (ci < k && col[ci] == 1)
{
ci++;
}
Console.WriteLine((ri + 1) + " " +
(ci + 1) + " ");
ri++;
ci++;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
int k = 2;
int []row = { 1, 2 };
int []col = { 4, 2 };
// Function call
findCountRooks(row, col, n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji2
2 1
3 2
性能分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(N)
- 辅助空间: O(1)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live