给定一棵二叉树,任务是打印二叉树每一层的中间节点。考虑M是任何级别的节点数,如果M是奇数,则打印第(M/2)个节点。否则,打印第(M/2)个节点和第((M/2) + 1)个节点。
例子:
Input: Below is the given Tree:
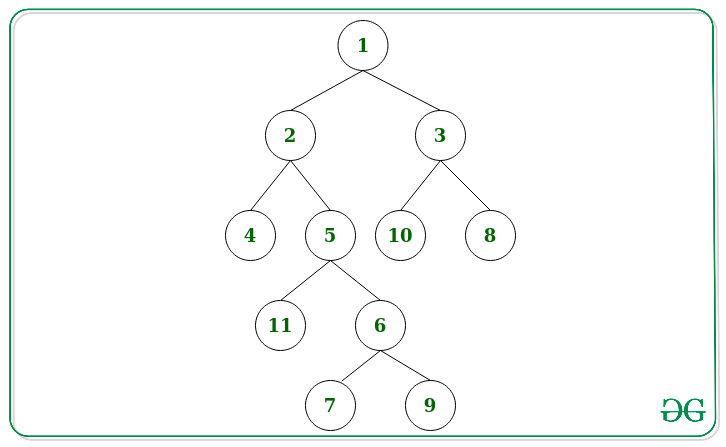
Output:
1
2 3
5 10
11 6
7 9
Explanation:
The mid nodes of each level is:
Level 0 – 1
Level 1 – 2 and 3
Level 2 – 5 and 10
Level 3 – 11 and 6
Level 4 – 7 and 9
Input: Below is the given Tree:

Output:
1
2 3
5
8 9
11
12 13
15 14
Explanation:
The mid nodes of each level is:
Level 0 – 1
Level 1 – 2 and 3
Level 2 – 5
Level 3 – 8 and 9
Level 4 – 11
Level 5 – 12 and 13
Level 6 – 15 and 14
方法:想法是对给定的树执行 DFS 遍历,并将每个级别的所有节点存储在向量图中。现在遍历 Map 并相应地打印中间节点。以下是步骤:
- 初始化一个向量M的映射,将每一层对应的所有节点存储在一个向量中。
- 对从级别 0开始的给定树执行 DFS 遍历,并递归调用左右子树,级别递增1 。
- 将上述DFS Traversal中每一层对应的所有节点存储为M[level].push_back(root->data) 。
- 现在,遍历 Map M并对每个级别执行以下操作:
- 找到与地图M 中每个级别相关联的向量(例如A )的大小(例如S )。
- 如果S是奇数则简单地打印A的[(S – 1)/ 2]的值作为中间(S / 2)个节点。
- 否则打印A[(S – 1)/2]和A[(S – 1)/2 + 1] 的值作为中间(S/2) th和((S/2) + 1) th 节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure Node of Binary Tree
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
// Function to create a new node
struct node* newnode(int d)
{
struct node* temp
= (struct node*)malloc(
sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = d;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
// Return the created node
return temp;
}
// Function that performs the DFS
// traversal on Tree to store all the
// nodes at each level in map M
void dfs(node* root, int l,
map >& M)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Push the current level node
M[l].push_back(root->data);
// Left Recursion
dfs(root->left, l + 1, M);
// Right Recursion
dfs(root->right, l + 1, M);
}
// Function that print all the middle
// nodes for each level in Binary Tree
void printMidNodes(node* root)
{
// Stores all node in each level
map > M;
// Perform DFS traversal
dfs(root, 0, M);
// Traverse the map M
for (auto& it : M) {
// Get the size of vector
int size = it.second.size();
// For odd number of elements
if (size & 1) {
// Print (M/2)th Element
cout << it.second[(size - 1) / 2]
<< endl;
}
// Otherwise
else {
// Print (M/2)th and
// (M/2 + 1)th Element
cout << it.second[(size - 1) / 2]
<< ' '
<< it.second[(size - 1) / 2 + 1]
<< endl;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/*
Binary tree shown below is:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 10 8
/ \
11 6
/ \
7 9
*/
// Given Tree
struct node* root = newnode(1);
root->left = newnode(2);
root->right = newnode(3);
root->left->left = newnode(4);
root->left->right = newnode(5);
root->left->right->left = newnode(11);
root->left->right->right = newnode(6);
root->left->right->right->left = newnode(7);
root->left->right->right->right = newnode(9);
root->right->left = newnode(10);
root->right->right = newnode(8);
// Function Call
printMidNodes(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static Map > M;
// Structure Node of
// Binary Tree
static class node
{
int data;
node left;
node right;
public node() {}
public node(int data,
node left,
node right)
{
super();
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
};
// Function to create a new node
static node newnode(int d)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = d;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
// Return the created node
return temp;
}
// Function that performs the DFS
// traversal on Tree to store all the
// nodes at each level in map M
static void dfs(node root, int l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return;
// Push the current level node
if(!M.containsKey(l))
{
Vector temp = new Vector();
temp.add(root.data);
M.put(l, temp);
}
else
M.get(l).add(root.data);
// Left Recursion
dfs(root.left, l + 1);
// Right Recursion
dfs(root.right, l + 1);
}
// Function that print all the middle
// nodes for each level in Binary Tree
static void printMidNodes(node root)
{
// Stores all node in each level
M = new HashMap >();
// Perform DFS traversal
dfs(root, 0);
// Traverse the map M
for (Map.Entry> it : M.entrySet())
{
// Get the size of vector
int size = it.getValue().size();
// For odd number of elements
if (size % 2 == 1)
{
// Print (M/2)th Element
System.out.print(it.getValue().get((size - 1) / 2) + "\n");
}
// Otherwise
else
{
// Print (M/2)th and
// (M/2 + 1)th Element
System.out.print(it.getValue().get((size - 1) / 2) + " " +
it.getValue().get(((size - 1) / 2) + 1) + "\n");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
Binary tree shown below is:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 10 8
/ \
11 6
/ \
7 9
*/
// Given Tree
node root = newnode(1);
root.left = newnode(2);
root.right = newnode(3);
root.left.left = newnode(4);
root.left.right = newnode(5);
root.left.right.left = newnode(11);
root.left.right.right = newnode(6);
root.left.right.right.left = newnode(7);
root.left.right.right.right = newnode(9);
root.right.left = newnode(10);
root.right.right = newnode(8);
// Function Call
printMidNodes(root);
}
}
//This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Structure Node of Binary Tree
class node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to create a new node
def newnode(d):
temp = node(d)
# Return the created node
return temp
# Function that performs the DFS
# traversal on Tree to store all the
# nodes at each level in map M
def dfs(root, l, M):
# Base Case
if (root == None):
return
# Push the current level node
if l not in M:
M[l] = []
M[l].append(root.data)
# Left Recursion
dfs(root.left, l + 1, M)
# Right Recursion
dfs(root.right, l + 1, M)
# Function that print all the middle
# nodes for each level in Binary Tree
def printMidNodes(root):
# Stores all node in each level
M = dict()
# Perform DFS traversal
dfs(root, 0, M)
# Traverse the map M
for it in M.values():
# Get the size of vector
size = len(it)
# For odd number of elements
if (size & 1):
# Print (M/2)th Element
print(it[(size - 1) // 2])
# Otherwise
else:
# Print (M/2)th and
# (M/2 + 1)th Element
print(str(it[(size - 1) // 2]) + ' ' +
str(it[(size - 1) // 2 + 1]))
# Driver Code
if __name__=="__main__":
'''
Binary tree shown below is:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 10 8
/ \
11 6
/ \
7 9
'''
# Given Tree
root = newnode(1)
root.left = newnode(2)
root.right = newnode(3)
root.left.left = newnode(4)
root.left.right = newnode(5)
root.left.right.left = newnode(11)
root.left.right.right = newnode(6)
root.left.right.right.left = newnode(7)
root.left.right.right.right = newnode(9)
root.right.left = newnode(10)
root.right.right = newnode(8)
# Function Call
printMidNodes(root)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program for
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static Dictionary M;
// Structure Node of
// Binary Tree
class node
{
public int data;
public node left;
public node right;
public node(int data,
node left,
node right)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
};
// Function to create a new node
static node newnode(int d)
{
node temp = new node(d, null, null);
// Return the created node
return temp;
}
// Function that performs the DFS
// traversal on Tree to store all the
// nodes at each level in map M
static void dfs(node root, int l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return;
// Push the current level node
if(!M.ContainsKey(l))
{
ArrayList temp = new ArrayList();
temp.Add(root.data);
M[l] = temp;
}
else
M[l].Add(root.data);
// Left Recursion
dfs(root.left, l + 1);
// Right Recursion
dfs(root.right, l + 1);
}
// Function that print all the middle
// nodes for each level in Binary Tree
static void printMidNodes(node root)
{
// Stores all node in each level
M = new Dictionary();
// Perform DFS traversal
dfs(root, 0);
// Traverse the map M
foreach (KeyValuePair it in M)
{
// Get the size of vector
int size = it.Value.Count;
// For odd number of elements
if (size % 2 == 1)
{
// Print (M/2)th Element
Console.Write(it.Value[(size - 1) / 2] + "\n");
}
// Otherwise
else
{
// Print (M/2)th and
// (M/2 + 1)th Element
Console.Write(it.Value[(size - 1) / 2] + " " +
it.Value[((size - 1) / 2) + 1] + "\n");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
/*
Binary tree shown below is:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 10 8
/ \
11 6
/ \
7 9
*/
// Given Tree
node root = newnode(1);
root.left = newnode(2);
root.right = newnode(3);
root.left.left = newnode(4);
root.left.right = newnode(5);
root.left.right.left = newnode(11);
root.left.right.right = newnode(6);
root.left.right.right.left = newnode(7);
root.left.right.right.right = newnode(9);
root.right.left = newnode(10);
root.right.right = newnode(8);
// Function Call
printMidNodes(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76 输出:
1
2 3
5 10
11 6
7 9时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live