给定两个长度为N 的二进制字符串A和B ,任务是通过对两个二进制字符串进行任意重新排序来找到可能的不同 XOR 的数量。由于数字可以足够大,求模数10 9 + 7
例子:
Input: A = “00”, B = “01”
Output: 2
Explanation:
There are two possible results by rearranging the digits of the string B.
They are: “10” and “01”
Input: A = “010”, B = “100”
Output: 4
Explanation:
There are four possible results possible by rearranging the digits of both the strings.
They are: “000”, “110”, “011”, “101”
方法:
- 既然我们知道
0 XOR 0 = 0
0 XOR 1 = 1
1 XOR 0 = 1
1 XOR 1 = 0
因此,要在结果字符串的任何索引处获得 XOR 值作为“1”,输入字符串必须在该索引处具有奇数个 1 。
- 现在,我们将尝试以某种方式重新排列二进制字符串,即最大数量的索引具有奇数个 1。这可以通过以下示例进行可视化:
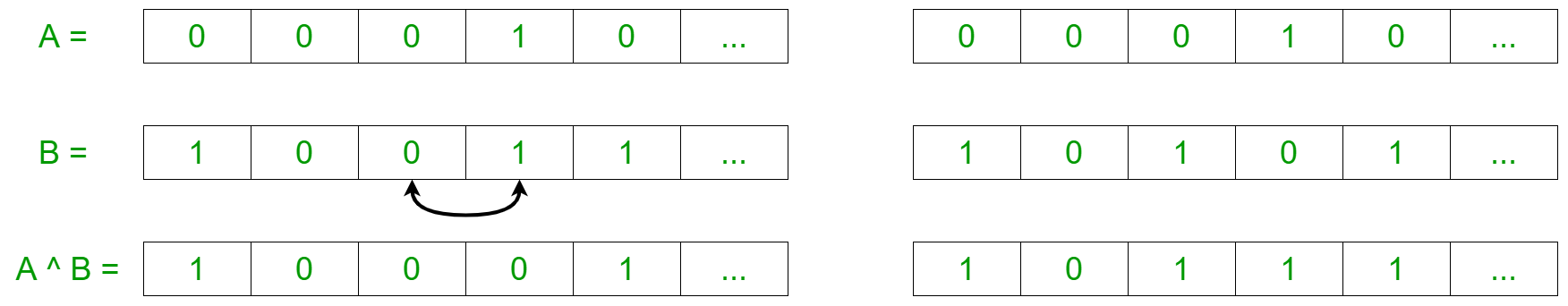
- 因此,从上面的观察来看,想法是通过对字符串重新排序来找到可能的最小和最大数量的 1 。
- 查找最大“1”:当形成最大 {0, 1} 和 {1, 0} 对时,结果中将出现最大“1”。所以,
Maximum number of {0, 1} pairs = minimum(count of ‘0’ in A, count of ‘1’ in B)
Maximum number of {1, 0} pairs = minimum(count of ‘1’ in A, count of ‘0’ in B)
Therefore, Maximum number of ‘1’s in the XOR = Maximum number of {0, 1} pairs + Maximum number of {1, 0} pairs
- 找到最小的“1”:这种情况可以看作是结果中“0”的最大数量的逆过程。类似地,当形成最大 {0, 0} 和 {1, 1} 对时,结果中的最大“0”将出现。所以,
Maximum number of {0, 0} pairs = minimum(count of ‘0’ in A, count of ‘0’ in B)
Maximum number of {1, 1} pairs = minimum(count of ‘1’ in A, count of ‘1’ in B)
Maximum number of ‘0’s in the XOR = Maximum number of {0, 0} pairs + Maximum number of {1, 1} pairs
Therefore, Minimum number of ‘1’s in the XOR = N – Maximum number of ‘0’s in the XOR
- 所有 1 的组合都可以在这两个数字(最小值和最大值)之间形成,相差 2。
- 最后,可以通过从最小 1 数和最大 1 数以 2 为步长的组合数计算得出结果的可能方法总数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++14
// C++ program to find the number of
// distinct XORs formed by rearranging
// two binary strings
#include
using namespace std;
// function to compute modulo power
long long power(long long a, long long b, long long mod)
{
long long aa = 1;
while(b)
{
if(b&1)
{
aa = aa * a;
aa %= mod;
}
a = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
return aa;
}
// Function to calculate nCr % p
// over a range
long long nCrRangeSum(long long n, long long r1,
long long r2, long long p)
{
// Initialize the numerator
// and denominator
long long num = 1, den = 1;
// Initialize the sum
long long sum = 0;
// nC0 is 1
if (r1 == 0)
sum += 1;
// Traversing till the range
for (int i = 0; i < r2; i++)
{
// Computing the numerator
num = (num * (n - i)) % p;
// Computing the denominator
den = (den * (i + 1)) % p;
// If 'i' lies between the given range
// and is at an even long long interval from
// the starting range because
// the combinations at a step of 2
// is required
if(i - r1 >= -1 and (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0)
{
// Computing nCr and adding the value
// sum
sum += (num * power(den, p - 2, p)) % p;
sum %= p;
}
}
return sum;
}
// Function to find the number of
// distinct XORs formed by
// rearranging two binary strings
int compute(string A, string B, int N)
{
// Initializing the count variable
// to 0
int c0A = 0, c1A = 0, c0B = 0, c1B = 0;
// Iterating through A
for (char c:A) {
// Increment the c1A variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1A += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0A += 1;
}
// Iterating through B
for (char c:B){
// Increment the c1B variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1B += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0B += 1;
}
// Finding the minimum number of '1's in the XOR
// and the maximum number of '1's in the XOR
int max1xor = min(c0A, c1B) + min(c1A, c0B);
int min1xor = N - min(c0B, c0A) - min(c1A, c1B);
// Compute the number of combinations between
// the minimum number of 1's and the maximum
// number of 1's and perform % with 10^9 + 7
int ans = nCrRangeSum(N, min1xor, max1xor, 1000000000 + 7);
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
long long N = 3;
string A = "010";
string B = "100";
cout << compute(A, B,N);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 Java
// JAVA program to find the number of
// distinct Bitwise XORs formed by rearranging
// two binary strings
class GFG
{
// function to compute modular exponentiation
// i.e. to find (a^b) % mod
static long mod_power(long a, long b,
long mod)
{
long result = 1l;
while(b > 0)
{
if((b&1) == 0) // b is even
{
result = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
else // b is odd
{
result = result * a;
result %= mod;
}
}
return result;
}
// method to evaluate nCr modulo p
// over an interval
static long nCr_RangeSum(long n, long r1,
long r2, long p)
{
// initializing numerator
// and denominator
long num = 1, den = 1;
// initialize the sum
long sum = 0l;
// nC0 is 1
if(r1 == 0)
sum += 1l;
// Iterating through the range
for(int i = 0; i < r2; i++)
{
// computing the numerator
num = (num * (n - i)) % p;
// computing the denominator
den = (den * (i + 1)) % p;
// If 'i' lies between the given range
// and is at an even interval from
// the starting range because
// the combinations at a step of 2
// is required
if(i - r1 >= -1 && (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0)
{
// Computing nCr and adding the value
// to the sum
sum += (num * mod_power(den, p - 2, p)) % p;
sum %= p;
}
}
return sum;
}
// method to find the number of
// distinct XORs formed by
// rearrangement of two binary strings
static long compute(String A, String B, int N)
{
// Initializing the counter variables
// to 0
int c0A = 0, c1A = 0, c0B = 0, c1B = 0;
// Iterating through A's characters
for (char c : A.toCharArray())
{
// Increment the c1A variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1A += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0A += 1;
}
// Iterating through B's characters
for (char c : B.toCharArray())
{
// Increment the c1B variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1B += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0B += 1;
}
// Finding the minimum number of '1's in the XOR
// and the maximum number of '1's in the XOR
int max1xor = Math.min(c0A, c1B) + Math.min(c1A, c0B);
int min1xor = N - Math.min(c0B, c0A) - Math.min(c1A, c1B);
// Compute the number of combinations between
// the minimum number of 1's and the maximum
// number of 1's and perform modulo with 10^9 + 7
long ans = nCr_RangeSum(N, min1xor, max1xor, 1000000000 + 7);
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3; // length of each string
String A = "010";
String B = "100";
System.out.print(compute(A, B, N));
}
}
// This Code is contributed by Soumitri Chattopadhyay.Python3
# Python3 program to find the number of
# distinct XORs formed by rearranging
# two binary strings
# Function to calculate nCr % p
# over a range
def nCrRangeSum(n, r1, r2, p):
# Initialize the numerator
# and denominator
num = den = 1
# Initialize the sum
sum = 0
# nC0 is 1
if r1 == 0:
sum += 1
# Traversing till the range
for i in range(r2):
# Computing the numerator
num = (num * (n - i)) % p
# Computing the denominator
den = (den * (i + 1)) % p
# If 'i' lies between the given range
# and is at an even interval from
# the starting range because
# the combinations at a step of 2
# is required
if(i - r1 >= -1 and (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0):
# Computing nCr and adding the value
# sum
sum += (num * pow(den, p - 2, p)) % p
sum %= p
return sum
# Function to find the number of
# distinct XORs formed by
# rearranging two binary strings
def compute(A, B):
# Initializing the count variable
# to 0
c0A = c1A = c0B = c1B = 0
# Iterating through A
for c in A:
# Increment the c1A variable
# if the current element is 1
if c == '1':
c1A += 1
# Increment the c0A variable
# if the current element is 0
elif c == '0':
c0A += 1
# Iterating through B
for c in B:
# Increment the c1B variable
# if the current element is 1
if c == '1':
c1B += 1
# Increment the c0A variable
# if the current element is 0
elif c == '0':
c0B += 1
# Finding the minimum number of '1's in the XOR
# and the maximum number of '1's in the XOR
max1xor = min(c0A, c1B) + min(c1A, c0B)
min1xor = N - min(c0B, c0A) - min(c1A, c1B)
# Compute the number of combinations between
# the minimum number of 1's and the maximum
# number of 1's and perform % with 10^9 + 7
ans = nCrRangeSum(N, min1xor, max1xor, 10**9 + 7)
# Return the answer
return ans
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 3
A = "010"
B = "100"
print(compute(A, B))C#
// C# program to find the number of
// distinct Bitwise XORs formed by
// rearranging two binary strings
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to compute modular exponentiation
// i.e. to find (a^b) % mod
static long mod_power(long a, long b,
long mod)
{
long result = 1;
while (b > 0)
{
if ((b & 1) == 0) // b is even
{
result = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
else // b is odd
{
result = result * a;
result %= mod;
}
}
return result;
}
// Function to evaluate nCr modulo p
// over an interval
static long nCr_RangeSum(long n, long r1,
long r2, long p)
{
// Initializing numerator
// and denominator
long num = 1, den = 1;
// Initialize the sum
long sum = 0;
// nC0 is 1
if (r1 == 0)
sum += 1;
// Iterating through the range
for(int i = 0; i < r2; i++)
{
// Computing the numerator
num = (num * (n - i)) % p;
// Computing the denominator
den = (den * (i + 1)) % p;
// If 'i' lies between the given range
// and is at an even interval from
// the starting range because
// the combinations at a step of 2
// is required
if (i - r1 >= -1 && (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0)
{
// Computing nCr and adding the value
// to the sum
sum += (num * mod_power(
den, p - 2, p)) % p;
sum %= p;
}
}
return sum;
}
// Function to find the number of distinct
// XORs formed by rearrangement of two
// binary strings
static long compute(string A, string B, int N)
{
// Initializing the counter variables
// to 0
int c0A = 0, c1A = 0, c0B = 0, c1B = 0;
// Iterating through A's characters
foreach(char c in A)
{
// Increment the c1A variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1A += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0A += 1;
}
// Iterating through B's characters
foreach(char c in B)
{
// Increment the c1B variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1B += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0B += 1;
}
// Finding the minimum number of
// '1's in the XOR and the maximum
// number of '1's in the XOR
int max1xor = Math.Min(c0A, c1B) +
Math.Min(c1A, c0B);
int min1xor = N - Math.Min(c0B, c0A) -
Math.Min(c1A, c1B);
// Compute the number of combinations
// between the minimum number of 1's
// and the maximum number of 1's and
// perform modulo with 10^9 + 7
long ans = nCr_RangeSum(N, min1xor,
max1xor, 1000000000 + 7);
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
// Length of each string
int N = 3;
string A = "010";
string B = "100";
Console.WriteLine(compute(A, B, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat4
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live