给定一个大小为 n 的正整数数组 arr[]。我们需要对给定的数组执行以下 3 个查询 –
1) 给定 L 和 R,我们必须找到位于 [L,R] 范围内的所有元素的平方和
2) 给定 L、R 和 X,我们必须将 [L,R] 范围内的所有元素设置为 X
3) 给定 L、R 和 X,我们必须将位于 [L,R] 范围内的所有元素的值增加 X
输入格式:第一行包含测试用例数T
下一行包含两个正整数 – N(数组大小)和 Q(要询问的查询数)。
下一行包含 N 个整数数组
接下来的 Q 行中的每一行都包含要询问的 Q 查询。每行以一个数字开头,表示查询类型,后跟必需的输入参数。所有 3 个查询的输入格式将如下所示 –
0 LRX : 将范围 [L, R] 中的所有数字设置为“X”
1 LRX : 将“X”添加到范围 [L, R] 中的所有数字
2 LR : 返回范围 {L, R] 中数字的平方和
输出格式:对于每个测试用例,在第一行输出“Case
Input:
1
3 3
1 2 3
0 1 2 2
1 1 3 3
2 1 3
Output : Case 1:
86
Explanation : With 1st query (type 0), array elements from range [1,2] will set as 2. Updated array will become [2,2,3]
With 2nd query (type 1), array elements from range [1,3] will be incremented by 3. Updated array will become [5,5,6]
With 3rd query (type 2), Sum of Squares for range [1,3] will be 5^2+5^2+6^2 =86
Input:
1
4 5
1 2 3 4
2 1 4
0 3 4 1
2 1 4
1 3 4 1
2 1 4
Output : Case 1:
30
7
13 优化方案
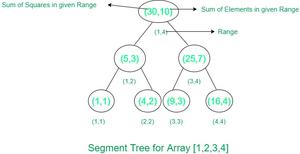
示例段树
借助带有延迟传播的 Segment 树,我们可以在 O(logn) 时间内执行所有给定的查询。
要了解 Segment Tree 的工作原理,请点击此链接 – https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/segment-tree-set-1-sum-of-given-range/
为此,我们将创建一个带有两个变量的段树——第一个将存储一个范围内的平方和,另一个将存储给定范围内的元素总和。 (我们稍后会讨论为什么这里需要两个变量)。为了更新给定范围内的值,我们将使用惰性传播技术。
有关延迟传播的更多信息,请使用链接 – https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/lazy-propagation-in-segment-tree/
在这里,如果我们必须将给定范围内的所有数字设置为 X,那么我们可以使用此公式来更新一个特定节点(位于给定范围内)的值——
更新平方和 = (R-L+1)*X*X
更新总和 = (R-L+1)*X
(因为在该特定节点下存在需要设置为 X 的 R-L+1 元素)
如果我们需要用值 X 增加给定范围 [L,R] 中的所有值,我们可以使用这个公式来更新一个特定节点(位于给定范围内)的值——
更新的平方和 = [L,R] 范围内的平方和 + (R-L+1)*X*X + 2*X*([L,R] 范围内的总和)
更新的总和 = 范围内的总和 [L,R] + (R-L+1)*X
(因为在该特定节点下存在 R-L+1 个元素,需要按 X 递增。每个节点的值可以表示为:(Previous_val + X)。要计算根节点的新平方和,我们可以使用这个表达——
(Previous_val1+ x)^2 + (Previous_val2 + x)^2 + …..(对于所有子节点)
上面的表达式将简化为 [L,R] 范围内的平方和 + (R-L+1)*X*X + 2*X*([L,R] 范围内的总和)
在这里你可以看到我们需要计算元素的总和,因此我们将它与平方和一起存储在我们的线段树中以加快我们的计算。
如何使用惰性树进行更新
在这里你可以看到我们需要3棵懒惰的树——
1.用于维护设置更新
2. 用于维护 X 更新的增量
3.为了维护操作顺序,以防单个节点有多个查询
现在创建 3 棵懒惰的树,不会节省空间。但是我们可以通过创建 1 个带有两个变量的惰性树(更改,类型)来解决这个问题——一个用于维护更新值 (X),另一个用于类型(我们需要进行增量或设置的更新)。
现在要处理单个节点上的多个查询的顺序,有两种可能性——
1)先自增再设置查询——这种情况下我们其实不需要自增,直接设置X即可。因为设置一个节点的值为X,自增前后都会保持不变。
2)先设置然后递增查询——这里我们有效地将每个节点的值更新为:X(设置查询)+ X(递增查询)。所以我们可以保持我们的查询类型为集合和更改值(即将设置的节点值)为(X_set + X_increment)
例如 – arr[]=[1,2,3,4] 首先用 2 设置 [3,4] 然后用 1 增加 [3,4]
设置查询后的数组 = [1,2,2,2]
递增查询后的数组 = [1,2,3,3]
我们可以通过将所有给定范围节点的值设置为:
(X_set + X_increment) = 2 + 1 = 3
更新数组 = [1,2,3,3]
C++
// We will use 1 based indexing
// type 0 = Set
// type 1 = increment
#include
using namespace std;
class segmenttree{
public:
int sum_of_squares;
int sum_of_element;
};
class lazytree{
public:
int change;
int type;
};
// Query On segment Tree
int query(segmenttree*tree,lazytree*lazy,int start,int end,int low,int high,int treeindex){
if(lazy[treeindex].change!=0){
int change=lazy[treeindex].change;
int type=lazy[treeindex].type;
if(lazy[treeindex].type==0){
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares=(end-start+1)*change*change;
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element=(end-start+1)*change;
if(start!=end){
lazy[2*treeindex].change=change;
lazy[2*treeindex].type=type;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change=change;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].type=type;
}
}
else{
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares+=((end-start+1)*change*change)+(2*change*tree[treeindex].sum_of_element);
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element+=(end-start+1)*change;
if(start!=end){
if(lazy[2*treeindex].change==0 || lazy[2*treeindex].type==1){
lazy[2*treeindex].change+=change;
lazy[2*treeindex].type=type;
}else{
lazy[2*treeindex].change+=change;
}
if(lazy[2*treeindex+1].change==0 || lazy[2*treeindex+1].type==1){
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change+=change;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].type=type;
}else{
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change+=change;
}
}
}
lazy[treeindex].change=0;
}
if(start>high || end=low && high>=end){
return tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares;
}
int mid=(start+end)/2;
int ans=query(tree,lazy,start,mid,low,high,2*treeindex);
int ans1=query(tree,lazy,mid+1,end,low,high,2*treeindex+1);
return ans+ans1;
}
// Update on Segment Tree
void update(int*arr,segmenttree*tree,lazytree*lazy,int start,int end,int low,int high,int change,int type,int treeindex){
if(lazy[treeindex].change!=0){
int change=lazy[treeindex].change;
int type=lazy[treeindex].type;
if(lazy[treeindex].type==0){
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares=(end-start+1)*change*change;
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element=(end-start+1)*change;
if(start!=end){
lazy[2*treeindex].change=change;
lazy[2*treeindex].type=type;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change=change;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].type=type;
}
}
else{
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares+=((end-start+1)*change*change)+(2*change*tree[treeindex].sum_of_element);
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element+=(end-start+1)*change;
if(start!=end){
if(lazy[2*treeindex].change==0 || lazy[2*treeindex].type==1){
lazy[2*treeindex].change+=change;
lazy[2*treeindex].type=type;
}else{
lazy[2*treeindex].change+=change;
}
if(lazy[2*treeindex+1].change==0 || lazy[2*treeindex+1].type==1){
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change+=change;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].type=type;
}else{
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change+=change;
}
}
}
lazy[treeindex].change=0;
}
if(start>high || end=low && high>=end){
if(type==0){
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares=(end-start+1)*change*change;
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element=(end-start+1)*change;
if(start!=end){
lazy[2*treeindex].change=change;
lazy[2*treeindex].type=type;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change=change;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].type=type;
}
}else{
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares+=((end-start+1)*change*change)+(2*change*tree[treeindex].sum_of_element);
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element+=(end-start+1)*change;
if(start!=end){
if(lazy[2*treeindex].change==0 || lazy[2*treeindex].type==1){
lazy[2*treeindex].change+=change;
lazy[2*treeindex].type=type;
}else{
lazy[2*treeindex].change+=change;
}
if(lazy[2*treeindex+1].change==0 || lazy[2*treeindex+1].type==1){
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change+=change;
lazy[2*treeindex+1].type=type;
}else{
lazy[2*treeindex+1].change+=change;
}
}
}
return;
}
int mid=(start+end)/2;
update(arr,tree,lazy,start,mid,low,high,change,type,2*treeindex);
update(arr,tree,lazy,mid+1,end,low,high,change,type,2*treeindex+1);
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares=tree[2*treeindex].sum_of_squares+tree[2*treeindex+1].sum_of_squares;
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element=tree[2*treeindex].sum_of_element+tree[2*treeindex+1].sum_of_element;
}
// creation of segment tree
void create(int*arr,segmenttree*tree,int start,int end,int treeindex){
if(start==end){
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares=start*start;
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element=start;
return;
}
int mid=(start+end)/2;
create(arr,tree,start,mid,treeindex*2);
create(arr,tree,mid+1,end,2*treeindex+1);
tree[treeindex].sum_of_squares=tree[treeindex*2].sum_of_squares+tree[2*treeindex+1].sum_of_squares;
tree[treeindex].sum_of_element=tree[treeindex*2].sum_of_element+tree[2*treeindex+1].sum_of_element;
}
int main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
int case1=1;
while(t--){
cout<<"Case "<>n>>q;
int*arr=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>arr[i];
}
segmenttree*tree=new segmenttree[2*n];
lazytree*lazy=new lazytree[2*n];
create(arr,tree,1,n,1);
while(q--){
int type;
cin>>type;
if(type==2){
int start,end;
cin>>start>>end;
cout<>start>>end>>change;
update(arr,tree,lazy,1,n,start,end,change,type,1);
}
}
}
} 时间复杂度:
树构造的时间复杂度为 O(n)。总共有2n-1个节点,每个节点的值在树构造中只计算一次。
查询的时间复杂度为 O(Logn)。
update 的时间复杂度也是 O(Logn)。
空间复杂度: O(2*N)。
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live