给定一棵树,它具有由N-1 条边连接的N 个节点和一个断开的节点,任务是在将给定的树与给定的断开组件连接后找到给定树的每个节点的直径。
例子:
Input:
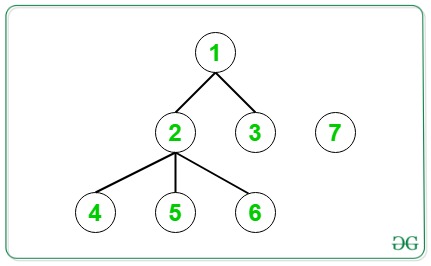
Output: 3 3 4 4 4 4
Explanation:
Initially diameter of tree = 3.
If an edge is added between node 1 and node 7, then the diameter of the tree is equal to 3(7 -> 1 -> 2 -> 5).
If an edge is added between node 2 and node 7, then the diameter of the tree is equal to 3(3 -> 1 -> 2 -> 5).
If an edge is added between node 3 and node 7, then the diameter of the tree is equal to 4(7 -> 3 -> 1 -> 2 -> 5).
If an edge is added between node 4 and node 7, then the diameter of the new tree is equal to 4(7-> 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3).
If an edge is added between node 5 and node 7, then the diameter of the new tree will be 4(7-> 5 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3).
If an edge is added between node 6 and node 7, then the diameter of the new tree will be 4((7-> 6 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3)).
Input:
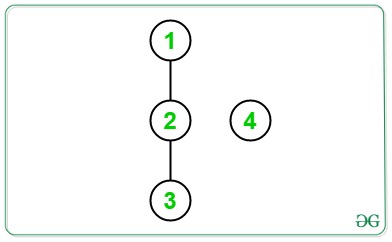
Output: 3 2 3
Explanation:
Initial diameter of the tree = 2
If an edge is added between node 1 and node 4, then the diameter of the tree is equal to 3(4 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3).
If an edge is added between node 2 and node 4, then the diameter of the tree is equal to 2(4 -> 2 -> 3).
If an edge is added between node 3 and node 4, then the diameter of the tree is equal to 3(4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1).
处理方法:为解决该问题,需要进行以下观察:
- The diameter increases by 1 when the disconnected node is connected to an edge which forms the end of the diameter.
- For all other nodes, the diameter remains unchanged on connecting the disconnected node.
根据以上观察,按照下面给出的步骤解决问题:
- 执行给定树的 DFS 遍历。
- 在遍历时,跟踪所经过的最远距离和最远节点。
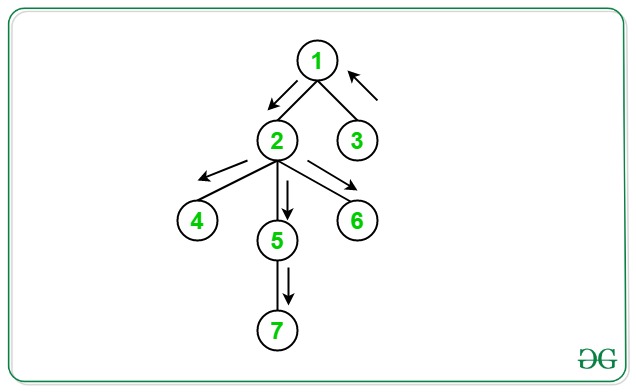
- 现在,从上一步得到的最远节点开始执行DFS ,并跟踪距离该节点最远的节点。
- 现在,执行DFS并分别在距离上述步骤获得的两个节点最远的Map中添加节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Keeps track of the farthest
// end of the diameter
int X = 1;
// Keeps track of the length of
// the diameter
int diameter = 0;
// Stores the nodes which are at
// ends of the diameter
map mp;
// Perform DFS on the given tree
void dfs(int current_node, int prev_node,
int len, bool add_to_map,
vector >& adj)
{
// Update diameter and X
if (len > diameter) {
diameter = len;
X = current_node;
}
// If current node is an end of diameter
if (add_to_map && len == diameter) {
mp[current_node] = 1;
}
// Traverse its neighbors
for (auto& it : adj[current_node]) {
if (it != prev_node)
dfs(it, current_node, len + 1,
add_to_map, adj);
}
}
// Function to call DFS for the
// required purposes
void dfsUtility(vector >& adj)
{
// DFS from a random node and find
// the node farthest from it
dfs(1, -1, 0, 0, adj);
int farthest_node = X;
// DFS from X to calculate diameter
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, 0, adj);
// DFS from farthest_node to find
// the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, 1, adj);
// DFS from X (other end of diameter) and
// check the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(X, -1, 0, 1, adj);
}
void printDiameters(vector >& adj)
{
dfsUtility(adj);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
// If node i is the end of
// a diameter
if (mp[i] == 1)
// Increase diameter by 1
cout << diameter + 1 << ", ";
// Otherwise
else
// Remains unchanged
cout << diameter << ", ";
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3 7
/|\
/ | \
4 5 6 */
vector > adj(7);
// creating undirected edges
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(1);
adj[1].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(1);
adj[2].push_back(4);
adj[4].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(5);
adj[5].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(6);
adj[6].push_back(2);
printDiameters(adj);
return 0;
} Java
// Java Program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Keeps track of the farthest
// end of the diameter
static int X = 1;
// Keeps track of the length of
// the diameter
static int diameter = 0;
// Stores the nodes which are at
// ends of the diameter
static HashMap mp = new HashMap<>();
// Perform DFS on the given tree
static void dfs(int current_node, int prev_node,
int len, boolean add_to_map,
Vector [] adj)
{
// Update diameter and X
if (len > diameter)
{
diameter = len;
X = current_node;
}
// If current node is an end of diameter
if (add_to_map && len == diameter)
{
mp.put(current_node, true);
}
// Traverse its neighbors
for (int it : adj[current_node])
{
if (it != prev_node)
dfs(it, current_node, len + 1,
add_to_map, adj);
}
}
// Function to call DFS for the
// required purposes
static void dfsUtility(Vector [] adj)
{
// DFS from a random node and find
// the node farthest from it
dfs(1, -1, 0, false, adj);
int farthest_node = X;
// DFS from X to calculate diameter
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, false, adj);
// DFS from farthest_node to find
// the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, true, adj);
// DFS from X (other end of diameter) and
// check the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(X, -1, 0, true, adj);
}
static void printDiameters(Vector [] adj)
{
dfsUtility(adj);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
// If node i is the end of
// a diameter
if (mp.containsKey(i) &&
mp.get(i) == true)
// Increase diameter by 1
System.out.print(diameter + 1 + ", ");
// Otherwise
else
// Remains unchanged
System.out.print(diameter + ", ");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3 7
/|\
/ | \
4 5 6 */
Vector []adj = new Vector[7];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector();
// creating undirected edges
adj[1].add(2);
adj[2].add(1);
adj[1].add(3);
adj[3].add(1);
adj[2].add(4);
adj[4].add(2);
adj[2].add(5);
adj[5].add(2);
adj[2].add(6);
adj[6].add(2);
printDiameters(adj);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 Python3
# Python3 program to implement
# the above approach
from collections import defaultdict
# Keeps track of the farthest
# end of the diameter
X = 1
# Keeps track of the length of
# the diameter
diameter = 0
# Stores the nodes which are at
# ends of the diameter
mp = defaultdict(lambda :0)
# Perform DFS on the given tree
def dfs(current_node, prev_node,
len, add_to_map, adj):
global diameter, X
# Update diameter and X
if len > diameter:
diameter = len
X = current_node
# If current node is an end of diameter
if add_to_map and len == diameter:
mp[current_node] = 1
# Traverse its neighbors
for it in adj[current_node]:
if it != prev_node:
dfs(it, current_node, len + 1,
add_to_map, adj)
# Function to call DFS for the
# required purposes
def dfsUtility(adj):
# DFS from a random node and find
# the node farthest from it
dfs(1, -1, 0, 0, adj)
farthest_node = X
# DFS from X to calculate diameter
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, 0, adj)
# DFS from farthest_node to find
# the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, 1, adj)
# DFS from X (other end of diameter) and
# check the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(X, -1, 0, 1, adj)
def printDiameters(adj):
global diameter
dfsUtility(adj)
for i in range(1, 6 + 1):
# If node i is the end of
# a diameter
if mp[i] == 1:
# Increase diameter by 1
print(diameter + 1, end = ", ")
# Otherwise
else:
# Remains unchanged
print(diameter, end = ", ")
# Driver code
# constructed tree is
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / | \
# 4 5 6
# |
# 7
adj = []
for i in range(7):
adj.append([])
# Creating undirected edges
adj[1].append(2)
adj[2].append(1)
adj[1].append(3)
adj[3].append(1)
adj[2].append(4)
adj[4].append(2)
adj[2].append(5)
adj[5].append(2)
adj[2].append(6)
adj[6].append(2)
printDiameters(adj)
# This code is contributed by Stuti PathakC#
// C# Program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Keeps track of the farthest
// end of the diameter
static int X = 1;
// Keeps track of the
// length of the diameter
static int diameter = 0;
// Stores the nodes which are at
// ends of the diameter
static Dictionary mp
= new Dictionary();
// Perform DFS on the given tree
static void dfs(int current_node, int prev_node,
int len, bool add_to_map,
List[] adj)
{
// Update diameter and X
if (len > diameter)
{
diameter = len;
X = current_node;
}
// If current node is an end of diameter
if (add_to_map && len == diameter)
{
mp.Add(current_node, true);
}
// Traverse its neighbors
foreach(int it in adj[current_node])
{
if (it != prev_node)
dfs(it, current_node, len + 1,
add_to_map, adj);
}
}
// Function to call DFS for
// the required purposes
static void dfsUtility(List[] adj)
{
// DFS from a random node and find
// the node farthest from it
dfs(1, -1, 0, false, adj);
int farthest_node = X;
// DFS from X to calculate diameter
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, false, adj);
// DFS from farthest_node to find
// the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(farthest_node, -1, 0, true, adj);
// DFS from X (other end of diameter) and
// check the farthest node(s) from it
dfs(X, -1, 0, true, adj);
}
static void printDiameters(List[] adj)
{
dfsUtility(adj);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
// If node i is the end
// of a diameter
if (mp.ContainsKey(i) && mp[i] == true)
// Increase diameter by 1
Console.Write(diameter + 1 + ", ");
// Otherwise
else
// Remains unchanged
Console.Write(diameter + ", ");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3 7
/|\
/ | \
4 5 6 */
List[] adj = new List[ 7 ];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
// creating undirected edges
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[1].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(4);
adj[4].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(5);
adj[5].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(6);
adj[6].Add(2);
printDiameters(adj);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4,
时间复杂度: O(V + E) ,其中 V 是顶点数,E 是图中的边数。
辅助空间: O(V)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live