N叉树的直径
N 叉树的直径是树的任意两个节点之间存在的最长路径。这两个节点必须是两个叶子节点。以下示例具有最长的路径[直径] 阴影。
示例 1:
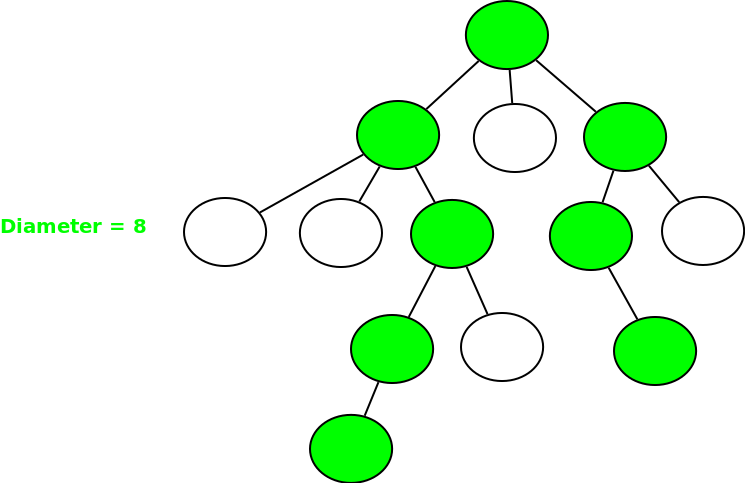
示例 2:
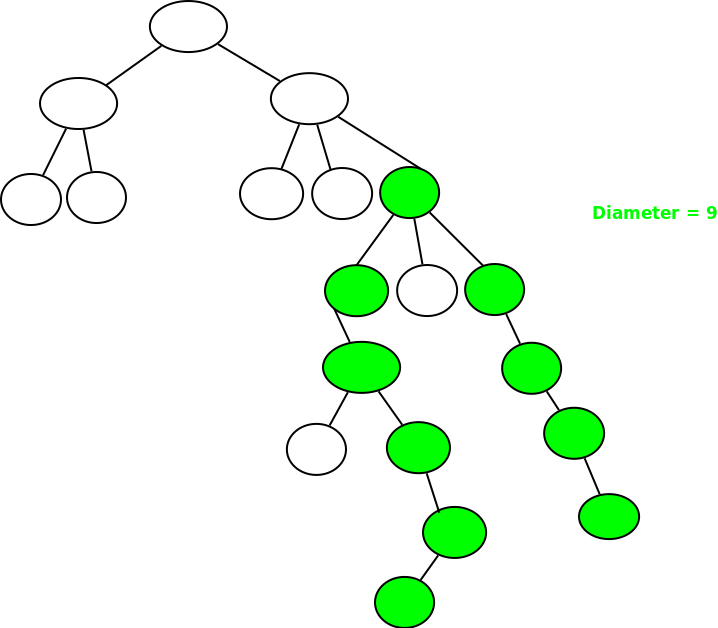
先决条件:二叉树的直径。路径可以从其中一个节点开始,向上到达这些节点的 LCA 之一,然后再次向下到达某个其他子树的最深节点,或者可以作为当前节点的子节点之一的直径存在。
解决方案将存在于以下任何一项中:
I] 当前节点的其中一个子节点的直径
II] 最高两个子树的高度之和 + 1
C++
// C++ program to find the height of an N-ary
// tree
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
struct Node
{
char key;
vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node *newNode(int key)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
return temp;
}
// Utility function that will return the depth
// of the tree
int depthOfTree(struct Node *ptr)
{
// Base case
if (!ptr)
return 0;
int maxdepth = 0;
// Check for all children and find
// the maximum depth
for (vector::iterator it = ptr->child.begin();
it != ptr->child.end(); it++)
maxdepth = max(maxdepth , depthOfTree(*it));
return maxdepth + 1;
}
// Function to calculate the diameter
// of the tree
int diameter(struct Node *ptr)
{
// Base case
if (!ptr)
return 0;
// Find top two highest children
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0;
for (vector::iterator it = ptr->child.begin();
it != ptr->child.end(); it++)
{
int h = depthOfTree(*it);
if (h > max1)
max2 = max1, max1 = h;
else if (h > max2)
max2 = h;
}
// Iterate over each child for diameter
int maxChildDia = 0;
for (vector::iterator it = ptr->child.begin();
it != ptr->child.end(); it++)
maxChildDia = max(maxChildDia, diameter(*it));
return max(maxChildDia, max1 + max2 + 1);
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ | /|\
* K J G C H I
* /\ \
* N M L
*/
Node *root = newNode('A');
(root->child).push_back(newNode('B'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('F'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('D'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('E'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('K'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('J'));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('G'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('C'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('H'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('I'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('N'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('M'));
(root->child[3]->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('L'));
cout << diameter(root) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find the height of an N-ary
// tree
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
static class Node
{
char key;
Vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = (char) key;
temp.child = new Vector();
return temp;
}
// Utility function that will return the depth
// of the tree
static int depthOfTree(Node ptr)
{
// Base case
if (ptr == null)
return 0;
int maxdepth = 0;
// Check for all children and find
// the maximum depth
for (Node it : ptr.child)
maxdepth = Math.max(maxdepth,
depthOfTree(it));
return maxdepth + 1;
}
// Function to calculate the diameter
// of the tree
static int diameter(Node ptr)
{
// Base case
if (ptr == null)
return 0;
// Find top two highest children
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0;
for (Node it : ptr.child)
{
int h = depthOfTree(it);
if (h > max1)
{
max2 = max1;
max1 = h;
}
else if (h > max2)
max2 = h;
}
// Iterate over each child for diameter
int maxChildDia = 0;
for (Node it : ptr.child)
maxChildDia = Math.max(maxChildDia,
diameter(it));
return Math.max(maxChildDia, max1 + max2 + 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ | /|\
* K J G C H I
* /\ \
* N M L
*/
Node root = newNode('A');
(root.child).add(newNode('B'));
(root.child).add(newNode('F'));
(root.child).add(newNode('D'));
(root.child).add(newNode('E'));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode('K'));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode('J'));
(root.child.get(2).child).add(newNode('G'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('C'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('H'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('I'));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(0).child).add(newNode('N'));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(0).child).add(newNode('M'));
(root.child.get(3).child.get(2).child).add(newNode('L'));
System.out.print(diameter(root) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Python3
# Python program to find the height of an N-ary
# tree
# Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.key = x
self.child = []
# Utility function that will return the depth
# of the tree
def depthOfTree(ptr):
# Base case
if (not ptr):
return 0
maxdepth = 0
# Check for all children and find
# the maximum depth
for it in ptr.child:
maxdepth = max(maxdepth , depthOfTree(it))
return maxdepth + 1
# Function to calculate the diameter
# of the tree
def diameter(ptr):
# Base case
if (not ptr):
return 0
# Find top two highest children
max1, max2 = 0, 0
for it in ptr.child:
h = depthOfTree(it)
if (h > max1):
max2, max1 = max1, h
elif (h > max2):
max2 = h
# Iterate over each child for diameter
maxChildDia = 0
for it in ptr.child:
maxChildDia = max(maxChildDia, diameter(it))
return max(maxChildDia, max1 + max2 + 1)
# Driver program
if __name__ == '__main__':
# /* Let us create below tree
# * A
# * / / \ \
# * B F D E
# * / \ | /|\
# * K J G C H I
# * /\ \
# * N M L
# */
root = Node('A')
(root.child).append(Node('B'))
(root.child).append(Node('F'))
(root.child).append(Node('D'))
(root.child).append(Node('E'))
(root.child[0].child).append(Node('K'))
(root.child[0].child).append(Node('J'))
(root.child[2].child).append(Node('G'))
(root.child[3].child).append(Node('C'))
(root.child[3].child).append(Node('H'))
(root.child[3].child).append(Node('I'))
(root.child[0].child[0].child).append(Node('N'))
(root.child[0].child[0].child).append(Node('M'))
(root.child[3].child[2].child).append(Node('L'))
print(diameter(root))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program to find the height of
// an N-ary tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
class Node
{
public char key;
public List child;
};
// Utility function to create
// a new tree node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = (char) key;
temp.child = new List();
return temp;
}
// Utility function that will return
// the depth of the tree
static int depthOfTree(Node ptr)
{
// Base case
if (ptr == null)
return 0;
int maxdepth = 0;
// Check for all children and find
// the maximum depth
foreach (Node it in ptr.child)
maxdepth = Math.Max(maxdepth,
depthOfTree(it));
return maxdepth + 1;
}
// Function to calculate the diameter
// of the tree
static int diameter(Node ptr)
{
// Base case
if (ptr == null)
return 0;
// Find top two highest children
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0;
foreach (Node it in ptr.child)
{
int h = depthOfTree(it);
if (h > max1)
{
max2 = max1;
max1 = h;
}
else if (h > max2)
max2 = h;
}
// Iterate over each child for diameter
int maxChildDia = 0;
foreach (Node it in ptr.child)
maxChildDia = Math.Max(maxChildDia,
diameter(it));
return Math.Max(maxChildDia,
max1 + max2 + 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ | /|\
* K J G C H I
* /\ \
* N M L
*/
Node root = newNode('A');
(root.child).Add(newNode('B'));
(root.child).Add(newNode('F'));
(root.child).Add(newNode('D'));
(root.child).Add(newNode('E'));
(root.child[0].child).Add(newNode('K'));
(root.child[0].child).Add(newNode('J'));
(root.child[2].child).Add(newNode('G'));
(root.child[3].child).Add(newNode('C'));
(root.child[3].child).Add(newNode('H'));
(root.child[3].child).Add(newNode('I'));
(root.child[0].child[0].child).Add(newNode('N'));
(root.child[0].child[0].child).Add(newNode('M'));
(root.child[3].child[2].child).Add(newNode('L'));
Console.Write(diameter(root) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript
C++
// C++ program to find the height of an N-ary
// tree
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
struct Node
{
char key;
vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node *newNode(int key)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
return temp;
}
int diameter(struct Node *ptr,int &diameter_of_tree)
{
// Base case
if (!ptr)
return 0;
// Find top two highest children
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0;
for (vector::iterator it = ptr->child.begin();it != ptr->child.end(); it++)
{
int h = diameter(*it,diameter_of_tree);
if (h > max1)
max2 = max1, max1 = h;
else if (h > max2)
max2 = h;
}
// Find whether our node can be part of diameter
diameter_of_tree = max(max1 + max2 + 1,diameter_of_tree);
return max(max1,max2) + 1;
}
int main()
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ / /|\
* K J G C H I
* /\ |
* N M L
*/
Node *root = newNode('A');
(root->child).push_back(newNode('B'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('F'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('D'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('E'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('K'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('J'));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('G'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('C'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('H'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('I'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('N'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('M'));
(root->child[3]->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('L'));
// for storing diameter
int diameter_of_tree = 0;
diameter(root,diameter_of_tree);
cout << diameter_of_tree << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is improved by bhuvan Java
// Java program to find the height of an N-ary
// tree
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
static class Node {
char key;
Vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = (char)key;
temp.child = new Vector();
return temp;
}
// for storing diameter_of_tree
public static int diameter_of_tree = 0;
// Function to calculate the diameter
// of the tree
static int diameter(Node ptr)
{
// Base case
if (ptr == null)
return 0;
// Find top two highest children
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0;
for (Node it : ptr.child) {
int h = diameter(it);
if (h > max1) {
max2 = max1;
max1 = h;
}
else if (h > max2)
max2 = h;
}
diameter_of_tree
= Math.max(max1 + max2 + 1, diameter_of_tree);
return (Math.max(max1, max2) + 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ / /|\
* K J G C H I
* /\ |
* N M L
*/
Node root = newNode('A');
(root.child).add(newNode('B'));
(root.child).add(newNode('F'));
(root.child).add(newNode('D'));
(root.child).add(newNode('E'));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode('K'));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode('J'));
(root.child.get(2).child).add(newNode('G'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('C'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('H'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('I'));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(0).child)
.add(newNode('N'));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(0).child)
.add(newNode('M'));
(root.child.get(3).child.get(2).child)
.add(newNode('L'));
diameter(root);
System.out.print(diameter_of_tree + "\n");
}
}
// This code is improved by Bhuvan C++
// C++ implementation to find
// diameter of a tree using
// DFS in ONE TRAVERSAL
#include
using namespace std;
#define maxN 10005
// The array to store the
// height of the nodes
int height[maxN];
// Adjacency List to store
// the tree
vector tree[maxN];
// variable to store diameter
// of the tree
int diameter = 0;
// Function to add edge between
// node u to node v
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// add edge from u to v
tree[u].push_back(v);
// add edge from v to u
tree[v].push_back(u);
}
void dfs(int cur, int par)
{
// Variables to store the height of children
// of cur node with maximum heights
int max1 = 0;
int max2 = 0;
// going in the adjacency list of the current node
for (auto u : tree[cur]) {
// if that node equals parent discard it
if (u == par)
continue;
// calling dfs for child node
dfs(u, cur);
// calculating height of nodes
height[cur] = max(height[cur], height[u]);
// getting the height of children
// of cur node with maximum height
if (height[u] >= max1) {
max2 = max1;
max1 = height[u];
}
else if (height[u] > max2) {
max2 = height[u];
}
}
height[cur] += 1;
// Diameter of a tree can be calculated as
// diameter passing through the node
// diameter doesn't includes the cur node
diameter = max(diameter, height[cur]);
diameter = max(diameter, max1 + max2 + 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// n is the number of nodes in tree
int n = 7;
// Adding edges to the tree
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 7);
// Calling the dfs function to
// calculate the diameter of tree
dfs(1, 0);
cout << "Diameter of tree is : " << diameter - 1
<< "\n";
return 0;
} Java
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int maxN = 10005;
// The array to store the
// height of the nodes
static int[] height = new int[maxN];
// Adjacency List to store
// the tree
static ArrayList> tree = new ArrayList>();
// variable to store diameter
// of the tree
static int diameter = 0;
// Function to add edge between
// node u to node v
static void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// add edge from u to v
tree.get(u).add(v);
// add edge from v to u
tree.get(v).add(u);
}
static void dfs(int cur, int par)
{
// Variables to store the height of children
// of cur node with maximum heights
int max1 = 0;
int max2 = 0;
// going in the adjacency list of the current node
for (int u : tree.get(cur)) {
// if that node equals parent discard it
if (u == par)
continue;
// calling dfs for child node
dfs(u, cur);
// calculating height of nodes
height[cur] = Math.max(height[cur], height[u]);
// getting the height of children
// of cur node with maximum height
if (height[u] >= max1) {
max2 = max1;
max1 = height[u];
}
else if (height[u] > max2) {
max2 = height[u];
}
}
height[cur] += 1;
// Diameter of a tree can be calculated as
// diameter passing through the node
// diameter doesn't includes the cur node
diameter = Math.max(diameter, height[cur]);
diameter = Math.max(diameter, max1 + max2 + 1);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < maxN; i++)
{
tree.add(new ArrayList());
}
// n is the number of nodes in tree
int n = 7;
// Adding edges to the tree
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 7);
// Calling the dfs function to
// calculate the diameter of tree
dfs(1, 0);
System.out.println("Diameter of tree is : " +(diameter - 1));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ab2127. Python3
# C++ implementation to find
# diameter of a tree using
# DFS in ONE TRAVERSAL
maxN = 10005
# The array to store the
# height of the nodes
height = [0 for i in range(maxN)]
# Adjacency List to store
# the tree
tree = [[] for i in range(maxN)]
# variable to store diameter
# of the tree
diameter = 0
# Function to add edge between
# node u to node v
def addEdge(u, v):
# add edge from u to v
tree[u].append(v)
# add edge from v to u
tree[v].append(u)
def dfs(cur, par):
global diameter
# Variables to store the height of children
# of cur node with maximum heights
max1 = 0
max2 = 0
# going in the adjacency list of the current node
for u in tree[cur]:
# if that node equals parent discard it
if(u == par):
continue
# calling dfs for child node
dfs(u, cur)
# calculating height of nodes
height[cur] = max(height[cur], height[u])
# getting the height of children
# of cur node with maximum height
if(height[u] >= max1):
max2 = max1
max1 = height[u]
elif(height[u] > max2):
max2 = height[u]
height[cur] += 1
# Diameter of a tree can be calculated as
# diameter passing through the node
# diameter doesn't includes the cur node
diameter = max(diameter, height[cur])
diameter = max(diameter, max1 + max2 + 1)
# Driver Code
# n is the number of nodes in tree
n = 7
# Adding edges to the tree
addEdge(1, 2)
addEdge(1, 3)
addEdge(1, 4)
addEdge(2, 5)
addEdge(4, 6)
addEdge(4, 7)
# Calling the dfs function to
# calculate the diameter of tree
dfs(1, 0)
print("Diameter of tree is :", diameter - 1)
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155Javascript
输出
7对上述解决方案的优化:
我们可以在不计算树的深度的情况下找到直径,在上述解决方案中进行微小的更改,类似于找到二叉树的直径。
C++
// C++ program to find the height of an N-ary
// tree
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
struct Node
{
char key;
vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node *newNode(int key)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
return temp;
}
int diameter(struct Node *ptr,int &diameter_of_tree)
{
// Base case
if (!ptr)
return 0;
// Find top two highest children
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0;
for (vector::iterator it = ptr->child.begin();it != ptr->child.end(); it++)
{
int h = diameter(*it,diameter_of_tree);
if (h > max1)
max2 = max1, max1 = h;
else if (h > max2)
max2 = h;
}
// Find whether our node can be part of diameter
diameter_of_tree = max(max1 + max2 + 1,diameter_of_tree);
return max(max1,max2) + 1;
}
int main()
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ / /|\
* K J G C H I
* /\ |
* N M L
*/
Node *root = newNode('A');
(root->child).push_back(newNode('B'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('F'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('D'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('E'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('K'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('J'));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('G'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('C'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('H'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('I'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('N'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('M'));
(root->child[3]->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('L'));
// for storing diameter
int diameter_of_tree = 0;
diameter(root,diameter_of_tree);
cout << diameter_of_tree << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is improved by bhuvan
Java
// Java program to find the height of an N-ary
// tree
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
static class Node {
char key;
Vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = (char)key;
temp.child = new Vector();
return temp;
}
// for storing diameter_of_tree
public static int diameter_of_tree = 0;
// Function to calculate the diameter
// of the tree
static int diameter(Node ptr)
{
// Base case
if (ptr == null)
return 0;
// Find top two highest children
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0;
for (Node it : ptr.child) {
int h = diameter(it);
if (h > max1) {
max2 = max1;
max1 = h;
}
else if (h > max2)
max2 = h;
}
diameter_of_tree
= Math.max(max1 + max2 + 1, diameter_of_tree);
return (Math.max(max1, max2) + 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ / /|\
* K J G C H I
* /\ |
* N M L
*/
Node root = newNode('A');
(root.child).add(newNode('B'));
(root.child).add(newNode('F'));
(root.child).add(newNode('D'));
(root.child).add(newNode('E'));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode('K'));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode('J'));
(root.child.get(2).child).add(newNode('G'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('C'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('H'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode('I'));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(0).child)
.add(newNode('N'));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(0).child)
.add(newNode('M'));
(root.child.get(3).child.get(2).child)
.add(newNode('L'));
diameter(root);
System.out.print(diameter_of_tree + "\n");
}
}
// This code is improved by Bhuvan
输出
7不同的优化解决方案:无向树中的最长路径
在一次遍历中使用DFS获取直径的另一种方法:
树的直径可以计算为每个节点
- 当前节点不是直径的一部分(即直径位于当前节点的其中一个子节点上)。
- 当前节点是直径的一部分(即直径通过当前节点)。
节点:邻接表已用于存储树。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find
// diameter of a tree using
// DFS in ONE TRAVERSAL
#include
using namespace std;
#define maxN 10005
// The array to store the
// height of the nodes
int height[maxN];
// Adjacency List to store
// the tree
vector tree[maxN];
// variable to store diameter
// of the tree
int diameter = 0;
// Function to add edge between
// node u to node v
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// add edge from u to v
tree[u].push_back(v);
// add edge from v to u
tree[v].push_back(u);
}
void dfs(int cur, int par)
{
// Variables to store the height of children
// of cur node with maximum heights
int max1 = 0;
int max2 = 0;
// going in the adjacency list of the current node
for (auto u : tree[cur]) {
// if that node equals parent discard it
if (u == par)
continue;
// calling dfs for child node
dfs(u, cur);
// calculating height of nodes
height[cur] = max(height[cur], height[u]);
// getting the height of children
// of cur node with maximum height
if (height[u] >= max1) {
max2 = max1;
max1 = height[u];
}
else if (height[u] > max2) {
max2 = height[u];
}
}
height[cur] += 1;
// Diameter of a tree can be calculated as
// diameter passing through the node
// diameter doesn't includes the cur node
diameter = max(diameter, height[cur]);
diameter = max(diameter, max1 + max2 + 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// n is the number of nodes in tree
int n = 7;
// Adding edges to the tree
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 7);
// Calling the dfs function to
// calculate the diameter of tree
dfs(1, 0);
cout << "Diameter of tree is : " << diameter - 1
<< "\n";
return 0;
}
Java
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int maxN = 10005;
// The array to store the
// height of the nodes
static int[] height = new int[maxN];
// Adjacency List to store
// the tree
static ArrayList> tree = new ArrayList>();
// variable to store diameter
// of the tree
static int diameter = 0;
// Function to add edge between
// node u to node v
static void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// add edge from u to v
tree.get(u).add(v);
// add edge from v to u
tree.get(v).add(u);
}
static void dfs(int cur, int par)
{
// Variables to store the height of children
// of cur node with maximum heights
int max1 = 0;
int max2 = 0;
// going in the adjacency list of the current node
for (int u : tree.get(cur)) {
// if that node equals parent discard it
if (u == par)
continue;
// calling dfs for child node
dfs(u, cur);
// calculating height of nodes
height[cur] = Math.max(height[cur], height[u]);
// getting the height of children
// of cur node with maximum height
if (height[u] >= max1) {
max2 = max1;
max1 = height[u];
}
else if (height[u] > max2) {
max2 = height[u];
}
}
height[cur] += 1;
// Diameter of a tree can be calculated as
// diameter passing through the node
// diameter doesn't includes the cur node
diameter = Math.max(diameter, height[cur]);
diameter = Math.max(diameter, max1 + max2 + 1);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < maxN; i++)
{
tree.add(new ArrayList());
}
// n is the number of nodes in tree
int n = 7;
// Adding edges to the tree
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 7);
// Calling the dfs function to
// calculate the diameter of tree
dfs(1, 0);
System.out.println("Diameter of tree is : " +(diameter - 1));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ab2127.
Python3
# C++ implementation to find
# diameter of a tree using
# DFS in ONE TRAVERSAL
maxN = 10005
# The array to store the
# height of the nodes
height = [0 for i in range(maxN)]
# Adjacency List to store
# the tree
tree = [[] for i in range(maxN)]
# variable to store diameter
# of the tree
diameter = 0
# Function to add edge between
# node u to node v
def addEdge(u, v):
# add edge from u to v
tree[u].append(v)
# add edge from v to u
tree[v].append(u)
def dfs(cur, par):
global diameter
# Variables to store the height of children
# of cur node with maximum heights
max1 = 0
max2 = 0
# going in the adjacency list of the current node
for u in tree[cur]:
# if that node equals parent discard it
if(u == par):
continue
# calling dfs for child node
dfs(u, cur)
# calculating height of nodes
height[cur] = max(height[cur], height[u])
# getting the height of children
# of cur node with maximum height
if(height[u] >= max1):
max2 = max1
max1 = height[u]
elif(height[u] > max2):
max2 = height[u]
height[cur] += 1
# Diameter of a tree can be calculated as
# diameter passing through the node
# diameter doesn't includes the cur node
diameter = max(diameter, height[cur])
diameter = max(diameter, max1 + max2 + 1)
# Driver Code
# n is the number of nodes in tree
n = 7
# Adding edges to the tree
addEdge(1, 2)
addEdge(1, 3)
addEdge(1, 4)
addEdge(2, 5)
addEdge(4, 6)
addEdge(4, 7)
# Calling the dfs function to
# calculate the diameter of tree
dfs(1, 0)
print("Diameter of tree is :", diameter - 1)
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
Javascript
输出
Diameter of tree is : 4